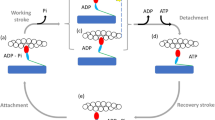
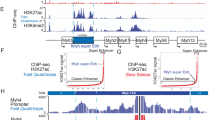
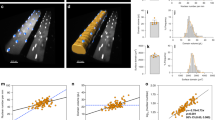
Abstract
MULTIPLE forms of myosin are known to be present in vertebrate striated muscle. On the basis of the light-chain pattern and of other structural and enzymatic features, three distinct types of myosin have been identified in fast-skeletal, slow-skeletar and cardiac muscles of mammals and birds1–5. Although skeletal muscle fibre heterogeneity has been generally recognised in these comparative studies, it has always been tacitly assumed that cardiac muscle consists of a homogeneous cell population in terms of myosin. However, the heart comprises muscle cells which differ in structure and function, such as atrial cells, ventricular cells and the specialised cells of the conducting system. We report here immunohistochemical evidence for the existence of distinct myosins in these different muscle cell types in the chicken heart.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barany, M. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 197–216 (1967).
Lowey, S. & Risby, D. Nature 234, 81–85 (1971).
Sarkar, S., Sreter, F. A. & Gergely, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 68, 946–950 (1971).
Weeds, A. G. & Pope, B. Nature 234, 84–88 (1971).
Perry, S. V. in Exploratory Concepts in Muscular Dystrophy II (ed. Milhorat, A. T.) 319–328 (Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, 1974).
Barany, M. & Close, R. I. J. Physiol., Lond. 213, 455–474 (1971).
Richards, E. G., Chung, C. S., Menzel, D. B. & Olcott, H. S. Biochemistry 6, 528–540 (1967).
Weber, K. & Osborn, M. J. biol. Chem. 244, 4406–4412 (1969).
Arndt, I. & Pepe, F. A. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 23, 159–168 (1975).
Masaki, T. J. Biochem., Tokyo 76, 441–449 (1974).
Masaki, T. & Yoshizaki, C. J. Biochem., Tokyo 76, 123–131 (1974).
The, T. H. & Feltkamp, T. E. W. Immunology 18, 865–873, 875–881 (1970).
Truex, R. C. & Smythe, M. Q. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 127, 19–33 (1965).
Sommer, J. R. & Johnson, E. A. Z. Zellforsch. mikrosk. Anat. 98, 437–468 (1969).
White, R. G. Nature 182, 1383–1384 (1958).
Padykula, H. A. & Hermann, E. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 3, 161–169 (1955).
Schiaffino, S. & Pierobon Bormioli, S. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 21, 142–145 (1973).
Guth, L. & Samaha, F. J. Expl Neurol. 25, 138–152 (1969).
Long, L., Fabian, F., Mason, D. T. & Wikman-Coffelt, J. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 76, 626–635 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SARTORE, S., PIEROBON-BORMIOLI, S. & SCHIAFFINO, S. Immunohistochemical evidence for myosin polymorphism in the chicken heart. Nature 274, 82–83 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/274082a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/274082a0
This article is cited by
-
Some aspects of cardiac heterogeneity
Basic Research in Cardiology (1994)
-
Structural and phylogenetic analysis of the chicken ventricular myosin heavy chain rod
Journal of Molecular Evolution (1991)
-
Effects of riboflavin analogues and diuretics on the spontaneously hypertensive rat heart
Basic Research in Cardiology (1990)
-
A molecular view of cardiogenesis
Experientia (1988)
-
Isomyosin expression patterns in tubular stages of chicken heart development: a 3-D immunohistochemical analysis
Anatomy and Embryology (1987)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.