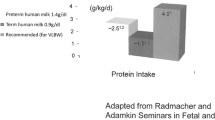
Abstract
In the breastfed infant, prolongation of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia into the third and later weeks of life in the healthy newborn is a normal and regularly occurring extension of physiologic jaundice. This is known as breastmilk jaundice. A factor in human milk increases the enterohepatic circulation of bilirubin. Insufficient caloric intake resulting from maternal and/or infant breastfeeding difficulties may also increase serum unconjugated bilirubin concentrations. This is the infantile equivalent of adult starvation jaundice. It is known as breastfeeding jaundice or “breast-nonfeeding jaundice.” This increase in severity of physiologic jaundice of the newborn also results from increased enterohepatic circulation of bilirubin, but not because of a factor in human milk. In extreme cases, it may place the infant at risk for development of bilirubin encephalopathy. Optimal breastfeeding practices, which result in minimal initial weight loss and early onset of weight gain, are associated with both reduced breastfeeding jaundice and minimization of the intensity of breastmilk jaundice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias IM, Gartner LM, Seifter S, Furman M Prolonged neonatal unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia associated with breast feeding and a steroid, pregnane-3(alpha),20(beta)-diol, in maternal milk that inhibits glucuronide formation in vitro J Clin Invest 1964 43 2037–47
Newman AJ, Gross S Hyperbilirubinemia in breast-fed infants Pediatrics 1963 32 995–1001
Winfield CR, MacFaul R Clinical study of prolonged jaundice in breast- and bottle-fed babies Arch Dis Child 1978 53 506–7
Alonso EM, Whitington PF, Whitington SH, et al Enterohepatic circulation of nonconjugated bilirubin in rats fed with human milk J Pediatr 1991 118 425–30
Gartner LM, Lee KS, Vaisman S, et al Development of bilirubin transport and metabolism in the newborn rhesus monkey J Pediatr 1977 90 513–31
Neifert MR Clinical aspects of lactation Clin Perinatol 1999 26 281–306
Gartner LM, Arias IM Studies of prolonged neonatal jaundice in the breast-fed infant J Pediatr 1966 68 54–66
Arias IM, Gartner LM Production of unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia in full-term, new-born infants following administration of pregnane-3(alpha),20(beta)-diol Nature 1964 203 1292–3
Cole AP, Hargreaves T Conjugation inhibitors and early neonatal hyperbilirubinemia Arch Dis Child 1972 47 415–8
Luzeau R, Odievre M, Levillain P, et al Lipoprotein lipase activity in human milk; inhibition in vitro of the glucuronoconjugation of bilirubin Clin Chim Acta 1975 59 133–8
Demirkol M, Bohles H Breast milk taurine and its possible influence on the development of breast milk induced jaundice of the neonate — a hypothesis In: Hixtable R, Michalk DV, editors. Taurine in Health and Disease New York: Plenum 1994 pp. 405–10
Gourley GR, Arend RA β-Glucuronidase and hyperbilirubinemia in breast-fed and formula-fed babies Lancet 1986 I 644–6
Ince Z, Coban A, Peker I, et al Breast milk beta-glucuronidase and prolonged jaundice in the neonate Acta Pediatr 1995 84 237–9
Gartner LM, Lee KS, Moscioni AD Effect of milk feeding on intestinal bilirubin absorption in the rat J Pediatr 1983 103 464–71
Maruo Y, Hishizawa K, Sato H, et al Prolonged unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia associated with breast milk and mutations of the bilirubin uridine diphosphate-glucuronyosyltransferase gene Pediatrics 2000 106 E59
American Academy of Pediatrics, Provisional Committee for Quality Improvement and Subcommittee on Hyperbilirubinemia Practice parameter: management of hyperbilirubinemia in the healthy term newborn Pediatrics 1994 94 558–65
Maisels MJ, Newman TB Kernicterus in otherwise healthy, breastfed term newborns Pediatrics 1995 96 730–3
Narayanan I, Parakash K, Gujral VV The value of human milk in the prevention of infection in the high-risk low-birth-weight infant J Pediatr 1981 99 496–8
Schanler RJ The use of human milk for premature infants Pediatr Clin North Am 2001 48 207–19
Lucas A, Baker BA Breast milk jaundice in premature infants Arch Dis Child 1986 61 1063–7
Gartner LM, Snyder RN, Chabon RA, et al Kernicterus: high incidence in prematures with low serum bilirubin concentrations Pediatrics 1970 45 906–17
Schneider AP II Breast milk jaundice in the newborn. A real entity JAMA, J Am Med Assoc 1986 255 3270–4
Gartner LM On the question of the relationship between breastfeeding and jaundice in the first 5 days of life Semin Perinatol 1994 18 502–9
American Academy of Pediatrics, Work Group on Breastfeeding Breastfeeding and the use of human milk Pediatrics 1997 100 1035–9
Shrago L Glucose water supplementation of the breastfed infant during the first three days of life J Hum Lactation 1987 3 82–6
Goldberg NM, Adams E Supplementary water for breast-fed babies in a hot and dry climate — not really a necessity Arch Dis Child 1983 58 73–4
Righard L, Alade MO Sucking technique and its effect on success of breastfeeding Birth 1992 19 185–9
Gärtner U, Goeser T, Wolkoff AW Effect of fasting on the uptake of bilirubin and sulfobromophthalein by the isolated perfused rat liver Gastroenterology 1997 113 1707–13
Gartner LM, Lee KS, Vaisman S, et al Development of bilirubin transport and metabolism in the newborn rhesus monkey J Pediatr 1977 90 513–31
Weisman LE, Merenstein GB, Digirol M, et al The effect of early meconium evacuation on early-onset hyperbilirubinemia Am J Dis Child 1983 137 666–8
Brodersen R, Herman LS Intestinal absorption of unconjugated bilirubin: a possible contributing factor in neonatal jaundice Lancet 1963 I 1242
Stevenson DK, Bartoletti AL, Ostrander CB, et al Pulmonary excretion of carbon monoxide in human infant as an index of bilirubin production: IV Effects of breastfeeding and caloric intake in the first postnatal week. Pediatrics 1980 65 1170–2
Rubaltelli FF Unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin pigments during perinatal development: IV. The influence of breast-feeding on neonatal hyperbilirubinemia Biol Neonat 1993 64 104–9
Nielsen HE, Haase P, Blaabjerg J, et al Rick factors and sib correlation in physiological neonatal jaundice Acta Paediatr Scand 1987 76 504–11
Maisels J, Gifford K Normal serum bilirubin levels in the newborn and the effect of breast-feeding Pediatrics 1986 78 837–43
De Carvalho M, Klaus MH, Merkatz RB Frequency of breast-feeding and serum bilirubin concentration Am J Dis Child 1982 136 737–8
Yamauchi Y, Ymanouchi H The relationship between rooming-in/not rooming-in and breast-feeding variables Acta Pediatr Scand 1990 79 1017–22
Kuhr M, Paneth N Feeding practices and early neonatal jaundice J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1982 1 485–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gartner, L. Breastfeeding and Jaundice. J Perinatol 21 (Suppl 1), S25–S29 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7210629
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7210629
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of human breast milk cells: gene expression profiles during pregnancy, lactation, involution, and mastitic infection
Functional & Integrative Genomics (2016)
-
Care practices and traditional beliefs related to neonatal jaundice in northern Vietnam: a population-based, cross-sectional descriptive study
BMC Pediatrics (2014)
-
Risk factors for hyperbilirubinemia in breastfed term neonates
European Journal of Pediatrics (2012)
-
Management of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: Pediatricians' practices and educational needs
BMC Pediatrics (2006)