Abstract
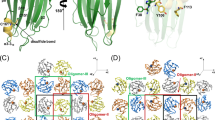
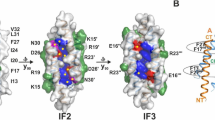
Staphylococcal LukF, LukS, HγII, and α–hemolysin are self–assembling, channel–forming proteins related in sequence and function. In the α–hemolysin heptamer, the channel–forming β–strands and the amino latch make long excursions from the protomer core. Here we report the crystal structure of the water soluble form of LukF. In the LukF structure the channel–forming region folds into an amphipathic, three–strand β–sheet and the amino latch forms a β–strand extending a central β–sheet. The LukF structure illustrates how a channel–forming toxin masks protein–protein and protein–membrane interfaces prior to cell binding and assembly, and together with the α–hemolysin heptamer structure, they define the end points on the pathway of toxin assembly.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tomita, T. & Kamio, Y. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 61, 565–572 (1997).
Gouaux, E. J. Struct. Biol. 121, 110–122 (1998).
Prévost, G. et al. J. Med. Microbiol. 42, 237– 245 (1995).
Prévost, G. et al. Infect. Immun. 63, 4121– 4129 (1995).
Staali, L., Monteil, H. & Colin, D.A. J. Memb. Biol. 162, 209– 216 (1998).
Finck–Barbançon, V., Duportail, G., Meunier, O. & Colin, D.A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1182, 275–282 (1993).
Sugawara, N., Tomita, T. & Kamio, Y. FEBS Lett. 410, 333– 337 (1997).
Cooney, J., Kienle, Z., Foster, T.J. & O'Toole, P.W. Infect. Immun. 61, 768–771 ( 1993).
Gouaux, E., Hobaugh, M.R. & Song, L. Prot. Sci. 6, 2631– 2635 (1997).
Song, L. et al. Science 274, 1859–1866 (1996).
Bhakdi, S. et al. Arch. Microbiol. 165, 73– 79 (1996).
Walker, B., Krishnasastry, M., Zorn, L. & Bayley, H. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 21782–21786 (1992).
Valeva, A., Palmer, M. & Bhakdi, S. Biochemistry 36, 13298– 13304 (1997).
Hendrickson, W.A., Horton, J.R. & LeMaster, D.M. EMBO J. 9, 1665– 1672 (1990).
Hendrickson, W.A. Science 254, 51–58 ( 1991).
Valeva, A. et al. EMBO J. 15, 1857–1864 (1996).
Walker, B. & Bayley, H. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 23065–23071 (1995).
Kleywegt, G.J. & Jones, T.A. Meth. Enz. 277, 525–545 (1997).
Meunier, O., et al. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1326, 275– 286 (1997).
Menzies, B.E. & Kernodle, D.S. Infect. Immun. 62 , 1843–1847 (1994).
Krishnasastry, M., Walker, B., Braha, O. & Bayley, H. FEBS Lett. 356, 66–71 (1994).
Walker, B., Braha, O., Cheley, S. & Bayley, H. Chem. & Biol. 2, 99–105 ( 1995).
Jursch, R. et al. Infect. Immun. 62, 2249– 2256 (1994).
Cheley, S. et al. Protein Engineer. 10, 1433– 1443 (1997).
Nariya, H., et al. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 57, 2198– 2199 (1993).
Leahy, D.J., Erickson, H.P., Aukhil, I., Joshi, P. & Hendrickson, W.A. Proteins 19, 48–54 (1994).
Szebenyi, D.M.E., Arvai, A., Ealick, S., LaIuppa, J.M. & Nielsen, C. J. Synchrotron Rad. 4, 128– 135 (1997).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Meth. Enz. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Terwilliger, T.C. & Berendzen, J. Acta Crystallogr. D53, 571–579 ( 1997).
Terwilliger, T.C. & Eisenberg, D. Acta Crystallogr. A39, 813–817 ( 1983).
The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D50, 760– 763 (1994).
Read, R.J. Meth. Enz. 277, 110–128 (1997).
Brünger, A.T. X–PLOR. Version 3.1. A system for X–ray crystallography and NMR (Yale University Press, New Haven, Connecticut; 1992 ).
Navaza, J. AMoRe: Acta Crystallgr. A50, 157–163 (1994).
Sim, G.A. Acta Crystallogr. 13, 511–512 (1960).
Rice, L.M. & Brünger, A.T. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 19, 277–290 ( 1994).
Hauser, H., Pascher, I. & Sundell, S. J. Mol. Biol. 137, 249– 264 (1980).
Biosym/MSI Insight Program Manual. (San Diego, California; 1995).
Jones, T.A. & Kjeldgaard, M. Meth. Enz. 277, 173–208 (1997).
Rahman, A., Nariya, H., Izaki, K., Kato, I. & Kamio, Y. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 184, 640– 646 (1992).
Kraulis, P.J. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merritt, E.A. & Murphy, M.E.P. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 869–873 (1994).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 11, 281–296 (1991).
Acknowledgements
The assistance of G.–Q. Chen, Y. Sun and N. Armstrong in synchrotron data collection and the help from S. Galdiero in data collection and processing are greatly appreciated. Superb support of the X–ray laboratory at Columbia by J. Lidestri is acknowledged as is general assistance from members of the Hendrickson group. Suggestions from L. Shapiro and D. Leahy on the growth of B834 E. coli and advice from T. Terwilliger on using Solve are also acknowledged. The MAD data collection component of this research was conducted at the Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS), which is supported by the National Science Foundation under award DMR–9311772, using the Macromolecular Diffraction at CHESS (MacCHESS) facility, which is supported by an award from the NIH. The diffraction data from the LukF–DiC3PC crystals was measured at 14–BM–D (BioCARS) at the Advanced Photon Source and we thank the beamline staff for their assistance. This work was also supported by the NIH (E.G.) and a Grant–In–Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science Sport and Culture of Japan to YK. E.G. is a NSF Young Investigator and the recipient of an Alfred P. Sloan Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olson, R., Nariya, H., Yokota, K. et al. Crystal structure of Staphylococcal LukF delineates conformational changes accompanying formation of a transmembrane channel. Nat Struct Mol Biol 6, 134–140 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/5821
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/5821
This article is cited by
-
Story of Pore-Forming Proteins from Deadly Disease-Causing Agents to Modern Applications with Evolutionary Significance
Molecular Biotechnology (2023)
-
Sequence Diversity in the Pore-Forming Motifs of the Membrane-Damaging Protein Toxins
The Journal of Membrane Biology (2020)
-
Staphylococcus aureus Toxins: From Their Pathogenic Roles to Anti-virulence Therapy Using Natural Products
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering (2019)
-
Cryo-EM structure of lysenin pore elucidates membrane insertion by an aerolysin family protein
Nature Communications (2016)
-
Pore-forming toxins: ancient, but never really out of fashion
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2016)