Abstract
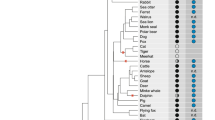
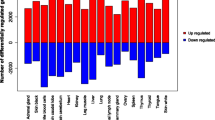
The PIS mutation is a genomic ~12-kb deletion affecting long-range gene transcription and causing XX sex reversal and hornlessness in goats by simultaneous long-range action on two genes, gPISRT1 and gFOXL2. In this study, a comparative human/mouse analysis of the orthologous region was carried out, permitting the targeting of genes in the 1-Mb environment, and identification of previously unknown mouse orthologues for Pisrt1, Bpesc1 and Chr3syt, and a human orthologue for PISRT1. PCR primers were defined and made it possible to analyse tissue-specific gene expression in mice and goats for 10 and 8 genes, respectively. The profile of expression was analysed by principal component analysis (PCA). The results indicate that FAIM (Fas apoptotic inhibitory molecule) is expressed similarly to FOXL2 (the primary determinant of ovary development located 280 kb away from the PIS mutation). However, we could demonstrate in goats that the PIS mutation has no direct effect on FAIM expression. Therefore, FAIM could contribute to normal ovarian function by inhibiting the apoptotic effect of Fas in the ovary but it relies on other regulatory elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benifla JL, Sifer C, Bringuier AF et al. (2002) Induced apoptosis and expression of related proteins in granulosa cells from women undergoing IVF: a preliminary study. Hum Reprod 17(4): 916–920.
Crisponi L, Deiana M, Loi A et al. (2001) The putative forkhead transciption factor FOXL2 is mutated in blepharophimosis/ptosis/epicanthus inversus syndrome. Nature Genet 27: 159–166.
De Baere E, Van Roy N, Spelemann F, Fukushima Y, De Paepe A, Messiaen L (1999) Closing in on the BPES gene on 3q23: Mapping of a de novo reciprocal translocation t(3;4)(q23;p15.2) breakpoint within a 45 kb cosmid and mapping of the three candidate genes RBP1, RBP2 and beta?-COP distal to the breakpoint. Genomics 57: 70–78.
De Baere E, Fukushima Y, Small K et al. (2000) Identification of BPESC1, a novel gene disrupted by a balanced chromosomal translocation, t(3;4)(q23;p15.2), in a patient with BPES. Genomics 68: 296–304.
De Baere E, Dixon MJ, Small KW et al. (2001) Spectrum of FOXL2 gene mutations in blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus inversus (BPES) families demonstrates a genotype-phenotype correlation. Hum Mol Genet 10(15): 1591–1600.
McPherson JD and International Human Genome Mapping Consortium (2001) A physical map of the human genome. Nature 409(6822): 934–941.
Pailhoux E, Vigier B, Chaffaux S et al. (2001) A 11.7-kb deletion triggers intersexuality and polledness in goats. Nature Genet 29(4): 453–458.
Pailhoux E, Vigier B, Vaiman D et al. (2002) Ontogenesis of female-to-male sex-reversal in XX polled goats. Dev Dyn 224(1): 39–50.
Pannetier M, Servel N, Cocquet J, Besnard N, Cotinot C, Pailhoux E (2003) Expresssion studies of the PIS-regulated genes suggest different mechanisms of sex determination within mammals. Cytogenet Genome Res 101: 199–205.
Petit G (1894) Nouvelle observation d'hermaphrodisme complexe des voies génitales chez un bouc. Recl Med vét Ec Alfort 71: 247–249.
Praphanphoj V, Goodman BK, Thomas GH et al. (2000) Molecular cytogenetic evaluation in a patient with a translocation (3;21) associated with blepharophimosis, ptosis, epicanthus inversus syndrome (BPES). Genomics 65(1): 67–69.
Quirck SM, Cowan RG, Huber SH (1997) Fas antigen-mediated apoptosis of ovarian surface epithelial cells. Endocrinology 138(11): 4558–4566.
Quirck SM, Porter DA, Huber SC, Cowan RG (1998) Potentiation of Fas-mediated apoptosis of murine granulosa cells by interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and cycloheximide. Endocrinology 139(12): 4860–4869.
Vaiman D (2003) Sexy transgenes: the impact of gene transfer and gene inactivation technologies on the understanding of mammalian sex determination. Transgenic Res 12: 255–269.
Vaiman D, Pailhoux E (2000) Mammalian sex reversal and intersexuality: deciphering the sex-determination cascade. Trends Genet 16(11): 488–494.
Vaiman D, Koutita O, Oustry-Vaiman A et al. (1996) Genetic mapping of the autosomal region involved in XX sex-reversal and horn development in goats. Mammalian Genome 7: 133–137.
Vaiman D, Schibler L, Oustry-Vaiman A (1999) High-resolution human/goat map of the goat polled/intersex syndrome (PIS): The human homolgue is contained in a human YAC from HSA3q23. Genomics 56: 31–39.
Waterston RH and Mouse Genome Sequencing Consortium (2002) Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of mouse genome. Nature 420(6915): 520–562.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikic, S., Vaiman, D. Conserved patterns of gene expression in mice and goats in the vicinity of the Polled Intersex Syndrome (PIS) locus. Chromosome Res 12, 465–474 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CHRO.0000034746.46789.e0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CHRO.0000034746.46789.e0