Abstract
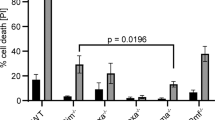
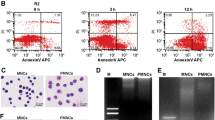
HL-60 cell differentiation into neutrophil like cells is associated with their induction of apoptosis. We investigated the cellular events that occur pre and post mitochondrial permeability transition to determine the role of the mitochondria in the induction of differentiation induced apoptosis. Pro-apoptotic Bax was translocated to and cleaved at the mitochondrial membrane in addition to t-Bid activation. These processes contributed to mitochondrial membrane disruption and the release of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO. The release of cytochrome c was caspase independent, as the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD.fmk, which inhibited apoptosis, did not block the release of cytochrome c. In contrast, the release of Smac/DIABLO was partially inhibited by caspase inhibition indicating differential release pathways for these mitochondrial pro-apoptotic factors. In addition to caspase inhibition we assessed the effects of the Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic family on differentiation induced apoptosis. BH4-Bcl-xl-TAT recombinant protein did not delay apoptosis, but did block the release of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO. Bcl-2 over-expression also inhibited differentiation induced apoptosis but was associated with the inhibition of the differentiation process.
Differentiation mediated mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO, may not trigger the induction of apoptosis, as BH4-Bclxl-TAT blocks the release of pro-apoptotic factors from the mitochondria, but does not prevent apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin SJ, Bradley JG, Cotter TG. GL-60 cells induced to differentiate towards neutrophils subsequently die via apoptosis. Clin Exp Immunol 1990; 79: 448–453.
Doyle BT, O’Neill AJ, Newsholme P, Fitzpatrick JM, Watson RWG. The loss of IAP expression during HL-60 cell differentiation is caspase-independent. J Leukoc Biol 2002; 71: 247–254.
Van Loo G, Saelens X, Van Gurp M, MacFaralne M, Martin SJ, Vandenabeele P. The role of mitochondrial factors in apoptosis: A Russia roulette with more than one bullet. Cell Death Differ 2002; 9: 1031–1042.
Liu X, Kim LN, Jemmerson R, Wang X. Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: Requirement for dATP-cytochrome c. Cell 1996; 86: 147–157.
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamami N, et al. Mitochondrial release of caspase-2 and-9 during the apoptotic process. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 1331–1341.
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 2000; 102: 33–42.
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, et al. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell 2000; 102: 43–53.
Cain K, Bratto SB, Langlais C, et al. Apaf-1 oligomerizes into biological active ~ 700 kDa and inactive ~ 1.4–Mda apoptosome complexes. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 6067–6070.
Goyal L. Cell death inhibition: Keeping caspases in check. Cell 2001; 104; 805–808.
Verhagen AM, Vaux DL. Cell death regulation by the mammalian IAP antagonist DIABLO/Smac. Apoptosis 2002; 7: 163–166.
Armstrong JS, Steinauer KK, Hornung B, et al. Role of glutathione depletion and reactive oxygen species generation in apoptotic signalling in a human B lymphoma cell line. Cell Death Differ 2002; 9: 252–263.
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S. VDAC regulation by the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 1174–1181.
Korsmeyer SJ, Wei MC, Saito S, Oh KJ, Schlesinger PH. Pro-apoptotic cascade activities BID, which oligomerizes BAK or BAX into pores that result in the release of cytochrome c. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 1166–1173.
Madesh M, Antonsson B, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES. Rapid kenitics of tBid-induced cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO release and mitochondrial depolarisation. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 5651–5659.
Zhao Y, Li S, Childs EE, Kuharsky DK, Yin X-M. Activation of pro-death Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondria apoptosis pathway in tumour necrosis factor-α-induced liver injury. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 27432–27440.
Mancini M, Nicholson DW, Roy S, et al. The caspase 3 precursor has a cytosolic and mitochondrial distribution: Implications for apoptotic signalling. J Cell Biol 1998; 140: 1485–1495.
Li S, Zhao Y, He X, et al. Relief of extrinsic pathway inhibition by Bid-dependent mitochondrial release of Smac in Fas-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 26912–26920.
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, et al. Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: Release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 1997; 275: 1129–1132.
Shimizu S, Konishi A, Kodama T, Tsujimoto Y. BH4 domain of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members closes voltage-dependent anion channels and inhibits apoptotic mitochondrial changes and cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3100–3105.
Watson RW, Rotstein OD, Parodo J, Bitar R, Hackman D, Marshall JC. Granulocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells results in spontaneous apoptosis mediated by increased caspase expression. FEBS Lett 1997; 412: 603–609.
Carter BZ, Milella M, Alteri DC, Andreeff M. Cytokine-regulated expression of survivin in myeloid leukaemia. Blood 2001; 97: 2784–2790.
Santos-Beneit AM, Mollinedo F. Expression of genes involved in initiation, regulation and execution of apoptosis in human neutrophils and during neutrophil differentiation of HL-60 cells. J Leukoc Biol 2000; 67: 712–724.
Adams JM, Cory S. Life or death decisions by the Bcl-2 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci 2001; 26: 61–66.
Huang DCS, Strasser A. BH3–only proteins-essential initiators of apoptotic cell death. Cell 2000; 103: 839–842.
Hsu YT, Wolter K, Youle RJ. Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of Bax and Bcl-X(L) during apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 3668–3672.
Wood DE, Newcomb EW. Cleavage of Bax enhances its cell death function. Exp Cell Res 2000; 256: 375–382.
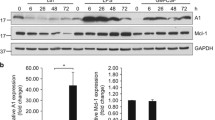
Werner AB, De Vries E, Tait SWG, Bontjer I, Borst J. Bcl-2 family member Bf1–1/A1 sequesters truncated Bid to inhibit its collaboration with pro-apoptotic Bak or Bax. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 22781–22788.
Martinou J-C, Green DR. Breaking the mitochondrial barrier. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 63–66.
Kim HJ, Mun JY, Chun YJ, Choi KH, Kim MY. Bax-dependent apoptosis induced by ceramide in HL-60 cells. FEBS Lett 2001; 505: 264–268.
Ruffolo SC, Breckenridge DG, Nguyen M, et al. BID-dependent and BID-independent pathways for Bax insertion into mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 1101–1108.
Luo X, Budihhardji I, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X. Bid a Bcl-2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 1998; 94: 481–490.
Von Ahsen O, Renken C, Perkins G, Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Newmeyer DD. Preservation of mitochondrial structure and function after Bid-or Bax-mediated cytochrome c release. J Cell Biol 2000; 150: 1027–1036.
Hu S, Yang X. Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 and 2 are ubiquitin ligases for the apoptosis inducer Smac/DIABLO. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 10055–10060.
Wood DE, Newcomb EW. Caspase-dependent activation of calpain during drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 8309–8315.
Kluck RM, Esposti MD, Perkins G, et al. The pro-apoptotic proteins, Bid and Bax, cause a limit permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane that is enhanced by cytosol. J Cell Biol 1999; 147: 809–822.
Deng Y, Lin Y, Wu X. TRAIL-induced apoptosis requires Bax-dependent mitochondrial release of Smac/DIABLO. Genes & Dev 2002; 16: 33–45.
Sun XM, Bratton SB, Butterworth M, MacFarlane M, Cohen GM. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl inhibit CD-95–mediated apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial release of Smac/DIABLO and subsequent inactivation of XIAP. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 11345–11351.
Shimizu S, Konishi A, Kodama T, Tsujimoto Y. BH4 domain of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members closes voltage-dependent anion channels and inhibits apoptotic mitochondrial changes and cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 3100–3105.
Benito A, Grillot D, Nunez G, Fernandez-Luna JL. Regulation and function of Bcl-2 during differentiation-induced cell death in HL-60 promyelocytic cells. Am J Pathol 1995; 146: 481–490.
Moulding DA, Akgul C, Derouet M, White MR, Edwards SW. Bcl-2 family expression in human neutrophils during delayed and accelerated apoptosis. J Leukoc Biol 2001; 70: 783–792.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doyle, B.T., O’Neill, A.J., Fitzpatrick, J.M. et al. Differentiation-induced HL-60 cell apoptosis: A mechanism independent of mitochondrial disruption?. Apoptosis 9, 345–352 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPT.0000025811.60286.ec
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPT.0000025811.60286.ec