Abstract
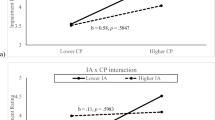
Previous studies have found that early neuromotor deficits may be a precursor of later psychopathology. The present study examined the relationship between neuromotor dysfunction and behavioral deviance in children characterized by a variety of risk factors (parental schizophrenia, parental psychiatric disorder other than schizophrenia, and parental maltreatment). The sample consisted of 108 children (average age 9.75 years) who were assessed twice, approximately 1 year apart. It was found that maltreated children had poorer neuromotor functioning and more behavior problems than children who were not maltreated, regardless of parental psychiatric status. The results also indicated that the relationship between neuromotor functioning and problem behaviors varied as a function of parental psychiatric status. These findings suggest that, although the effects of maltreatment are generalized and pervasive, there are distinctive relationships between neuromotor functioning and behavioral deviance depending on the nature of the risk factors a child has been exposed to.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Achenbach, T. M., & Edelbrock, C. S. (1981). Behavioral problems and competencies reported by parents of normal and disturbed children aged four through sixteen. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 46, 1–82.
Achenbach, T. M. (1982). Child Behavior Checklist. Burlington: University of Vermont.
American Psychiatric Association. (1980). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (3rd ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Bergman, A., & Walker, E. (1995). The relationship between cognitive functions and behavioral deviance in children at risk for psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 36, 265–278.
Bruininks, R. H. (1978). Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency examiner's manual. Circle Pines, Minnesota: American Guidance Service.
Brumback, R. A. (1993). Is depression a neurologic disease? Behavioral Neurology, 11, 79–104.
Cohen, J., & Cohen, P. (1975). Applied multiple regression/correlation analysis for the behavioral sciences. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
El-Guebaly, N., Offord, D. R., Sullivan, K. T., & Lynch, G. W. (1978). Psychosocial adjustment of the offspring of psychiatric inpatients: The effect of alcoholic, depressive and schizophrenic parentage. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal, 23, 281–289
Fish, B., Marcus, J., Hans, S. L., Auerbach, J. G., & Perdue, S. (1992). Infants at risk for schizophrenia: Sequela of genetic neurointegrative defect. Archives of General Psychiatry, 49, 221–235.
Gillberg, I. C., & Gillberg, C. (1989). Children with preschool minor neurological disorders IV: Behavior and school achievement at age 13. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 31, 3–13.
Hans, S., & Marcus, J. (1991). Neurobehavioral development of infants at risk for schizophrenia. In E. F. Walker (Ed.), Schizophrenia: A life-course developmental perspective (pp. 35–53). New York: Academic Press.
Hollander, E., DeCaria, C. M., Aronwitz, B., Klein, D. F., Liebowitz, M. R., & Shaffer, D. (1991). A pilot follow-up study of childhood soft signs and the development of adult psychopathology. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 3, 186–189.
Marlow, N., Roberts, L., & Cooke, R. (1993). Outcomes at 8 years for children with birth weights of 1250g or less. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 68, 286–290.
McGlashan, T. (1984). Testing four diagnostic systems for schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry, 41, 141–144.
McNeil, T. J., Harty, B., Blennow, G., & Cantor-Graae, E. (1993). Neuromotor deviation in offspring of psychotic mothers: A selective developmental deficiency in two groups of children at heightened psychiatric risk? Journal of Psychiatric Research, 27, 39–54.
Meehl, P. (1989). Schizotaxia revisited. Archives of General Psychiatry, 46, 935–944.
Neumann, C. S., & Walker, E. F. (1996). Childhood neuromotor soft signs, behavior problems and adult psychopathology. In T. H. Ollendick, & R. J. Prinz (Eds.), Advances in clinical child psychology (pp. 173–203).
Prechtl, H. F. R., & Stemmer, C. H. (1962). The choreiform syndrome in children. Developmental Medicine and Child. Neurology, 4, 119–127.
Shaffer, D., O'Connor, P. A., Shaffer, S. Q., & Prupis, S. (1983). Neurological “soft signs”: Their origins and significance for behavior. In M. Rutter (Ed.), Developmental neuropsychology (pp. 144–163). New York: Guilford Press.
Sloane, M. P., & Meier, J. H. (1983). Typology for parents of abused children. Child Abuse and Neglect, 11, 41–57.
Soorani-Lansing, R. J., Hadders-Algra, M., Olinga, A. A., Huisjes, H. J., & Touwen, B. C. L. (1993). Is minor neurological dysfunction at 12 years related to behavior and cognition? Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 35, 321–330.
Spitzer, R. L., & Endicott, J. (1978). Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia (SADS). New York: New York State Psychiatric Institute.
Szatmari, P., & Taylor, D. C. (1984). Overflow movements and behavior problems: Scoring and using a modification of Fogs' test. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 26, 297–310.
Taylor, D. C., Powell, R. P., Cherland, E. E., & Vaughan, C. M. (1988). Overflow movements and cognitive motor and behavioral disturbance: a normative study of girls. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 30, 759–768.
Walker, E., & Lewine, R. J. (1990). Prediction of adult-onset schizophrenia from childhood home-movies of the patients. American Journal of Psychiatry, 147, 1052–1056.
Walker, E., Savoie, T., & Davis, D. (1994). Neuromotor precursors of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 20, 441–451.
Walker, E., Downey, G., & Bergman, A. (1989). The effects of parental psychopathology and maltreatment on child behavior: A test of the diathesis-stress model. Child Development, 60, 15–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergman, A.J., Wolfson, M.A. & Walker, E.F. Neuromotor Functioning and Behavior Problems in Children at Risk for Psychopathology. J Abnorm Child Psychol 25, 229–237 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025700116710
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025700116710