Abstract
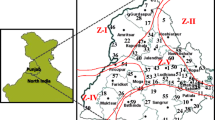
Inadequate information about the genetic structure of the polyphagous Rhizoctonia solani has made sheath blight resistance breeding a difficult task. To assess the variability in the Indian populations of sheath blight fungus, 18 isolates were collected from different rice growing regions of India and analyzed for virulence and electrophoretic profiles of 13 isozymes. The virulence spectrum of all 18 isolates was examined on susceptible IR50 and tolerant Swarnadhan varieties, based on which the isolates could be grouped as highly virulent, moderately virulent or a virulent. A total of 11 enzyme systems with 153 electrophoretic phenotypes were applied to characterize the genetic variation among the isolates. Cluster analyses based on isozyme patterns resulted in one major cluster comprising 16 virulent isolates, with two a virulent isolates loosely linked to this at 0.13 similarity. Isozyme systems of esterases (both α and β) and 6-phosphogluconic dehydrogenase could be used to fingerprint the individual isolates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ou SH. Rice Diseases. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, Slough UK, 1985; 272–286.
Sneh B, Burpee L, Ogoshi A. Identification of Rhizoctonia species. St. Paul, MN: American Phytopathological Society Press, 1991: 135.
Laroche JP, Jabaji-Hare SH, Charest PM. Differentiation of two anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani by isozyme analysis. Phytopathology 1992; 82: 1387–1393.
Liu ZL, Sinclair JB. Genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 2. Phytopathology 1992; 82: 778–787.
Liu ZL, Sinclair JB. Differentiation of intraspecific groups within anastomosis group 1 of Rhizoctonia solani using ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacers and isozyme comparison. Can J of Plant Pathology 1993; 15: 272–280.
Meisong J, Korpradiskul V. Isozyme analysis of genetic diversity among isolates of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 1-IA (AG1-IA). Mycosystema 1999; 17: 331–338.
Liu ZL, Nikrent KL, Sinclair JB. Genetic relationships among isolates of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 2 based on isozyme analyses. Can J of Plant Pathology 1990; 12: 376–382.
Carling DE, Rothrock CS, MacNish GC, Sweetingham MW, Brainard KA, Winters SW. Characterization of anastomosis group 11(AG-11) of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology 1994; 84: 1387–1393.
Cruickshank RH, Wade GC. Detection of pectic enzymes in pectin-acrylamide gels. Analytical Biochemistry 1986; 197: 177–181.
Balali GR, Neate SM, Scott ES, Whisson, DL. Heterogenity in pectic zymogram phenotypes of field isolates Rhizoctonia solani AG3. International symposium on Rhizoctonia, June 27-30, Norrwikerhout, Netherlands, 1994: 1–5.
Vilgalys R, Cubeta MA. Molecular systematics and population biology of Rhizoctonia. Ann. Rev. of Phytopathology 1994; 32: 135–155.
Vilgalys R, Gonzalez D. Ribosomal DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism in Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology 1990; 80: 151–158.
Salazar O, Schneider JHM, Julian MC, Keijer J, and Rubio V. Phylogenetic sub grouping of Rhizoctonia solani AG2 isolates based on ribosomal ITS sequences. Mycologia 1999; 91: 459–467.
Cubeta MA, Vilgalys R. Population biology of the Rhizoctonia solani complex. Phytopathology 1997; 87: 480–484.
Zuber M, Manibhushanrao K. Studies on comparative gel electrophoretic patterns of proteins and enzymes from isolates of Rhizoctonia solani causing sheath blight disease in rice. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 1982; 28: 762–771.
Reddy, CS. Virulence pattern of Rhizoctonia solani in rice. Indian Phytopathological Society — Golden Jubilee International Conference, New Delhi Nov. 10-15, 1997: 424 pp.
Bhaktavatsalam G, Satyanarayana K, Reddy APK, John VT. Evaluation for Sheath blight resistance in rice. International Rice Research Newsletter 1978; 3: 9–10.
SES (Standard Evaluation System), IRRI, Manila, Philippines, 1996: 25.
Gomez KA, Gomez A. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1984.
Lowry BB, Rosebrogh NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. of Biological Chemistry 1951; 193: 265–275.
Davis BJ. Disk electrophoresis. 2. Method and application to human serum proteins. Annals of New York Academy of Sciences 1964; 121: 404–427.
Novacky A, Hampton RE. Peroxidase isoenzymes in virus infected plants. Phytopathology 1968; 58: 301–305.
Vallejos CE. Enzyme activity staining. In: Tanksley SD, Orton TJ. eds. Isozymes in Plant Genetics and Breeding, Part A, Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1983; 469–516.
Nei M, Li WH. Mathematical models for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 1979; 76: 5269–5273.
Rohlf FJ. NTSYS-pc-.Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System. Version 2.02j. Exeter Software, Setauket, New York, 1998.
Lee FN, Rush MC. Rice Sheath blight: A major rice disease. Plant Disease 1983; 67: 829–832.
Basu A, Gupta PKS. Cultural and pathogenic variation in rice isolates of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Beitrage Zur Tropischen Landwirtschaft und Veterinatmedizin 1992; 30: 291–297.
Ogoshi A. Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intraspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Annual Review of Phytopathology 1987; 25: 125–143.
Kuninaga S, Yokosawa R. DNA base sequence homology in Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn I. Genetic relatedness within anastomosis group 1. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Japan 1982; 48: 659–667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neeraja, C., Shenoy, V., Reddy, C. et al. Isozyme polymorphism and virulence of Indian isolates of the rice sheath blight fungus. Mycopathologia 156, 101–108 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022988710654
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022988710654