Abstract
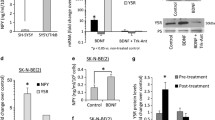
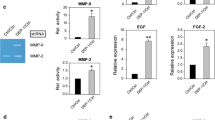
The effect of CNTF and BDNF on a proteolytic complement instrumental to invasion and on differentiation was studied in two murine neuroblastoma clones, N1 and N7. At the membrane level, gelatinase MMP-2 – mainly the activated form – was restrained by CNTF and BDNF to a residual 34% with both factors; membrane-type 1 MMP was down-regulated to 50% (10 h) and 34% (24 h) with both factors; and urokinase-type plasminogen activator was restrained mainly by BDNF to 70%. In the medium, the two gelatinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 were mainly in zymogen form: only MMP-2 was restrained in N1 cells, while only MMP-9 was restrained in N7 cells by both factors, single or in combination. These effects were paralleled by the induction of neurite outgrowth, which was more stimulated in the less differentiated clone. These dose-dependent and transient effects make CNTF and BDNF ideal candidates for constraining the potentially invasive behavior of nervous system tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parrow V, Nanberg E, Heikkila J et al. Protein kinase C remains functionally active during TPA-induced neuronal differentiation of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Physiol 1992; 152: 536–44.
Pennypacker KR, Kuhn DM, Billingsley ML. Changes in the expression of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in human SMS-KCNR neuroblastoma following retinoic acid or phorbol ester-induced differentiation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1989; 5: 251–8.
Bunone G, Borrello MG, Picetti R et al. Induction of RET protooncogene expression in neuroblastoma cells precedes neuronal differentiation and is not mediated by protein synthesis. Exp Cell Res 1995; 217: 92–9.
Chambaut-Guérin A-M, Martinez M-C, Hamimi C et al. Tumor necrosis factor in neuroblastoma SKNBE cells and their regulation by retinoic acid. J Neurochem 1995; 65: 537–44.
Menter DG, Herrmann JL, Marchetti D et al. Involvement of neurotrophins and growth factor in brain metastasis formation. Invasion Metastasis 1995; 14: 372–84.
Snider WD. Functions of the neurotrophins during nervous-system development – what the knockouts are teaching us. Cell 1994; 77: 627–38.
Lawrence G, Rylett RJ, Richardson PM et al. Differentiation effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor on human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 1995; 64: 1483–90.
Rossino P, Volpe G, Negro A, et al. Ciliary neurotrhophic factorinduced gene expression in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Neurochem Res 1995; 20: 675–80.
Barletta E, Mugnai G, Ruggieri S. Inverse relationship between invasiveness and differentiative capacity in different human neuroblastoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 1997; 70: 556–60.
Garbisa S, Biggin S, Cavallarin N et al. Tumor invasion: Molecular shears blunted by green tea. Nat Med 1999; 4(11): 1216.
Ara T, Fukuzawa M, Kusafuka T et al. Immunohistochemical expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, and TIMP-2 in neuroblastoma: Association with tumor progression and clinical outcome. J Pediat Surg 1998; 33: 1272–8.
Liotta LA, Steeg PS, Stetler-Stevenson WG. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: An imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell 1991; 64: 327–36.
Sato H, Takino T, Okada Y et al. A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumor cells. Nature 1994; 370: 61–5.
Caenazzo C, Onisto M, Sartor L et al. Augmented membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP): MMP-2 messenger RNA ratio in gastric carcinomas with poor prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 1998; 4: 2179–86.
Baramova EN, Bajou K, Remacle A et al. Involvement of PA/plasmin system in the processing of pro-MMP-9 and in the second step of pro-MMP-2 activation. FEBS Lett 1997; 405: 157–62.
Mazzieri R, Masiero L, Zanetta L et al. Control of type IV collagenase activity by components of the urokinase-plasmin system: A regulatory mechanism with cell-bound reactants. EMBO J 1997; 16: 101–4.
Negro A, Onisto M, Pellati D et al. CNTF up-regulation of TIMP-2 in neuroblastoma cells. Mol Brain Res 1997; 48: 30–6.
Sidell N, Altman A, Haussler MR et al. Effects of retinoic acid (RA) on the growth and phenotypic expression of several human neuroblastoma cell lines. Exp Cell Res 1983; 148: 21–30.
Chambaut-Guérin A-M, Hérigault S, Rouet-Benzineb P et al. Induction of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-9 (92-kDa gelatinase) by retinoic acid in human neuroblastoma SKNBE cells: Relevance to neuronal differentiation. J Neurochem 2000; 74: 508–17.
Sugiura Y, Shimada H, Seeger RC et al. Matrix metalloproteinases-2 and-9 are expressed in human neuroblastoma: Contribution of stromal cells to their production and correlation with metastasis. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 2209–16.
Barletta E, Mugnai G, Ruggieri S. Platelet activating factor inhibits the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and affects invasiveness and differentiation in a system of human neuroblastoma clones. Biol Chem 2002; 383: 189–97.
Barde YA, Edgar D, Thoenen H. Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO J 1982; 1: 549–53.
Huang EJ, Reichardt LF. Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci 2001; 24: 677–736.
Bravo J, Heath JK. Receptor recognition by gp130 cytokines. EMBO J 2000; 19: 2399–411.
Arcangeli A, Becchetti A, Mannini A et al. Integrin-mediated neurite outgrowth in neuroblastoma cells depends on the activation of potassium channels. J Cell Biol 1993; 122: 1131–43.
Negro A, Tolosano E, Skaper SD et al. Cloning and expression of human ciliary neurotrophic factor. Eur J Biochem 1991; 201: 289–94.
Kleiner DE, Stetler-Stevenson WG. Quantitative zymography: Detection of picogram quantities of gelatinases. Anal Biochem 1994; 218: 325–9.
Unemori EN, Hibbs MS, Amento EP. (1991). Constitutive expression of a 92-kD gelatinase (type V collagenase) by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts and its induction in normal human fibroblasts by inflammatory cytokines. J Clin Invest 1991; 88: 1656–62.
Heinicke E, Kumar U, Munoz DG. Quantitative dot-blot assay for proteins using enhanced chemiluminescence. J Immunol Meth 1992; 152: 227–36.
Fibbi G, Barletta E, Dini G et al. Cell invasion is affected by differential expression of the urokinase plasminogen activator/urokinase plasminogen receptor system in muscle satellite cells from normal and dystrophic patients. Lab Invest 2001; 81: 27–39.
Quattrone A, Papucci L, Santini V et al. Quantitation of bcl-2 oncogene in cultured lymphoma/leukemia cell lines and in primary leukemia B-cells by a highly sensitive RT-PCR method. Haematologica 1995; 80: 495–504.
Itoh T, Tanioka M, Matsuda H et al. Experimental metastasis is suppressed in MMP-9-deficient mice. Clin Exp Metastasis 1999; 17: 177–81.
Yamamoto M, Mohanam S, Sawaya R et al. Differential expression of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase and its correlation with gelatinase A activation in human malignant brain tumors in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 384–92.
Lardot C, Delos M, Lison D. Upregulation of urokinase in alveolar macrophages and lung tissue in response to silica particles. Am J Physiol 1998; 274: L1040–8.
Kherif S, Lafuma C, Dehaupas M et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in regenerating skeletal muscle: A study in experimentally injured and mdx muscles. Dev Biol 1999; 205: 158–70.
Planchenault T, Costa S, Fages C et al. Differential expression of laminin and fibronectin and of their related metalloproteinases in human glioma cell lines: Relation to invasion. Neurosc Lett 2001; 299: 140–4.
Annabi B, Lachambre MP, Bousquet-Gagnon N et al. Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin 3-gallate inhibits MMP-2 secretion and MT1-MMP-driven migration in glioblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002; 1542: 209–20.
De Chiara TM, Vejsada R, Poueymirou WT et al. (1995) Mice lacking the CNTF receptor, unlike mice lacking CNTF, exhibit profound motor neuron deficits at birth. Cell 1995; 83: 313–22.
De Veas RG, Schweigerer L, Medina MA. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 expression in paediatric tumour cells. Effects of tumour cell proliferation modulators on gelatinolytic activity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1995; 121: 275–8.
Fowler C, Zimmer C, Boghaert E et al. Metastasis of C1300 and TBJ murine neuroblastomas correlates with expression of matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Lett 1995; 93: 171–7.
Quaranta V. Cell migration through extracellular matrix: Membranetype metalloproteinases make the way. J. Cell Biol 2000; 149: 1167–70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sartor, L., Negro, A., Barletta, E. et al. Modulation of proteolytic potential and differentiation by CNTF and BDNF in two mouse neuroblastoma clones: Relation to invasion. Clin Exp Metastasis 19, 709–716 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021302802297
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021302802297