Abstract
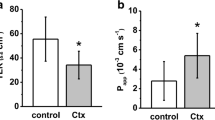
The effect of cholera toxin on small intestinalcapillary function, utilizing the Evans blue dye method,was analyzed. The modulatory influence of plasma-derivedor recombinant human antisecretory factor on this variable was also investigated. MaleSprague-Dawley rats were briefly anesthetized withether, and a jejunal loop was constructed that waschallenged for 90 min with phosphate-buffered saline or cholera toxin. Five minutes prior to death, therats received an intravenous injection of Evans blue.The tissue content of dye in the loop was quantitatedspectrophotometrically or demonstrated histochemically. Cholera toxin increased the recovery of Evansblue; extravasation of the dye was prominent in the topof the villi, while the crypts were spared. It issuggested that the toxin caused increased transcapillary permeation of albumin in a heterogenous fashionin the gut wall. This effect of the toxin was preventedby pretreatment with the antisecretory factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Craig JP: Cholera toxins. InMicrobial Toxins IIA, Bacterial Protein Toxins. S Kadis, TC Montie, SJ Ajl (eds.). New York, Academic Press, 1971, pp 189-254
Finkelstein RA: Laboratory production and isolation of ente-rotoxins and isolation of a candidate live vaccine for diarrheal disease. InCholera and Re lated Diarrhe as, 43rd Nobel Symposium. Ö Ouchterlony, J Holmgren (eds). Basel, S. Karger, 1980, pp 64-79
Sasmal D, Guhathakurta B, Ghosh AN, Pal CR, Datta A: Studies on adhesion, haemagglutination and other biological properties of Vibrio choleraeO139. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 10:199-206, 1995
Keusch GT, Atthasampunna P, Finkelstein RA: A vascular permeability defect in experimental cholera. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 124:822-825, 1967
Dalldorff FG, Keusch GT, Livingston HL: Transcellular permeability of capillaries in experimental cholera. Am J Pathol 57:153-160, 1969
Yardley JH, Brown GD: Horse radish peroxidase tracer studies in the intestine in experimental cholera. Lab Invest 28:482- 493, 1973
Carpenter CCJ, Greenough III WB, Sack RB: The relationship of superior mesenteric artery blood flow to gut electrolyte loss in experimental cholera. J Infect Dis 119:182-193, 1969
Cedgård S, Hallbäck D-A, Jodal M, Lundgren O, Redfors S: The effects of cholera toxin on intramural blood flow distribution and capillary hydraulic conductivity in the cat small intestine. Acta Physiol Scand 102:148-158, 1978
Johnston ME, Kennedy TG: Estrogen and uterine sensitization for the decidual cell reaction in the rat: Role of prostaglandin E2 and adenosine 3’:5’-cylic monophosphate. Biol Reprod 31:959-966, 1984
Lange S, Jennische E, Lönnroth I: Antisecretory factor enhances in vivointernalization of cholera toxin and of horseradish peroxidase into rat enterocytes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immun Scand 102:465-473, 1994
Cassuto J, Jodal M, Tuttle R, Lundgren O: On the role of intramural nerves in the pathogenesis of cholera toxin-induced intestinal secretion. Scand J Gastroenterol 16:377-384, 1981
Folkow B, Neil E: Circulation. London, Oxford University Press, 1971, 593 pp
Larsen J-J: A study on inhibition of cholera toxin-induced intestinal hypersecretion by neuroleptics. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 50:294-299, 1982
Lönnroth I, Jwnnische E: Reversal of entrerotoxic diarrhea by anaesthetic and membrane-stabilizing agents. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 51:330-335, 1982
Rawson RA: The binding of T-1824 and structurally related diazodyes by the plasma proteins. Am J Physiol 138:708-717, 1943
LeVeen HH, Fishman WH: Combination of Evans Blue with plasma protein: Its significance in capillary perme ability studies, blood dye, disappearance curves, and its use as a protein tag. Am J Physiol 151:26-33, 1947
Saria A, Lundberg JM: Evans blue fluorescence: quantitative and morphological evaluation of vascular permeability in animal tissues. J Neurosci Methods 8:41-49, 1983
Gamse R, Holzer P, Lembeck F: Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurone s and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol 68:207-213, 1980
Steinwall O, Klatzo I: Selective vulnerability of the blood- brain barrier in chemically induced lesions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 25:542-559, 1966
Lönnroth I, Lange S, Skadhauge E: The antisecretory factors: Inducible proteins which modulate secretion in the small intestine. Comp Biochem Physiol A 90:611-617, 1988
Lönnroth I, Lange S: Purification and characterization of the antisecretory factor: a protein in the central nervous system and in the gut which inhibits intestinal hypersecretion induced by cholera toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta 883:138-144, 1986
Johansson E, Lönnroth I, Lange S, Jonson I, Jennische E, Lönnroth C: Molecular cloning and expression of a pituitary gland protein modulating intestinal fluid secretion. J Biol Chem 270:20615-20620, 1995
Lange S: A rat model for an in vivo assay of enterotoxic diarrhea. FEMS Microbiol Lett 15:239-242, 1982
Nellgård P, Cassuto J: Inflammation as a major cause of fluid losses in small-bowel obstruction. Scand J Gastroenterol 28:1035-1041, 1993
Lange S, Delbro DS, Jennische E: Evans Blue permeation of intestinal mucosa in the rat. Scand J Gastroenterol 29:38-46, 1994
Milliken GA, Johnson DE: Simultaneous inference procedures and multiple comparisons. InAnalysis of Messy Data. London, Lifetime Learning Publications, 1984, pp 29-45
Wilde WS, Hill JH, Wilson E, Scielke GP: Exchange of free and albumin-bound Evans blue in interstitium of hamster kidney. Am J Physiol 220:1991-1999, 1971
Granger DN, Cook BH, Taylor AE: Structural locus of transmucosal albumin efflux in canine ileum. Gastroenterology 71:1023-1027, 1976
Gustafsson B, Persson CGA: Allergen-induced mucosal exudation of plasma into rat ileum and its inhibition by budesonide. Scand J Gastroenterol 27:587-593, 1992
Persson CGA, Gustafsson B, Erjefält JS, Sundler F: Mucosal exsudation of plasma is a noninjurious intestinal defense mechanism. Allergy 48:581-586, 1993
Brunsson I: Enteric nerve s mediate the fluid secretory re-sponse due to Salmonella typhimuriumR5 infection in the rat small intestine. Acta Physiol Scand 131:609-617, 1987
Uhing MR, Kimura RE: The effect of surgical bowel manipulation and anesthesia on intestinal glucose absorption in rats. J Clin Invest 95:2790-2798, 1995
Ohishi I, Odagiri Y: Histopathological effect of botulinum C2 toxin on mouse intestines. Infect Immun 43:54-58, 1984
Triadafilopoulos G, Pothoulakis C, Weiss R, Giampaolo C, LaMont TJ: Comparative study of Clostridium difficiletoxin A and cholera toxin in rabbit ileum. Gastroenterology 97:1186- 1192, 1989
Magnusson K-E, Kihlström E, Sundqvist T: Effect of cholera toxin on rat intestinal permeability assessed with fluorescent dextran 3000. FEMS Microbiol Lett 29:15-18, 1985
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lange, S., Delbro, D.S., Jennische, E. et al. Recombinant or Plasma-Derived Antisecretory Factor Inhibits Cholera Toxin-Induced Increase in Evans Blue Permeation of Rat Intestinal Capillaries. Dig Dis Sci 43, 2061–2070 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018863315666
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018863315666