Abstract
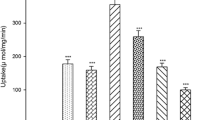
Various diesters of 9-[(l,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)-methyl]guanine (DHPG) were screened in order to identify a derivative with improved oral absorption. The solubilities and dissolution rates decreased with increasing chain length and branching of the ester group. However, the dipropionate ester showed an anomalously faster dissolution rate. The rates of hydrolysis to DHPG in the presence of intestinal homogenates were found to increase with increasing carbon number for the straight-chain alkyl esters and decreased with branching. The shorter-chain alkyl esters were relatively more stable in intestinal homogenates than in liver homogenates. Therefore they may have a better membrane permeability than DHPG due to their intact ester group. The hydrolysis rates in human blood increased with increasing carbon number for the straight-chain alkyl esters. The dipropionate ester appeared to be the most promising derivative because of its rapid dissolution rate, slower hydrolysis in the intestine, and rapid conversion to DHPG in liver and blood.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. F. Smee, J. C. Martin, J. P. H. Verheyden, and T. R. Matthews. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 23:676–682 (1983).
J. C. Martin, C. A. Dvorak, D. F. Smee, T. R. Matthews, and J. P. H. Verheyden. J. Med. Chem. 26:759–761 (1983).
Physicians' Desk Reference, 39th ed., Medical Economics, Oradell, N.J., 1985.
Pharm. J. 232:20 (1983).
P. D. Miranda, H. C. Krasny, D. A. Page, and G. B. Elion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 219:309–315 (1981).
H. J. Rogers and A. S. E. Fowle, J. Clin. Hosp. Pharm. 8:89–102 (1983).
T. Higuchi and V. Stella. Prodrugs as Novel Drug Delivery Systems, ACS Symposium Series 14, American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C., 1975.
E. B. Roche. Design of Biopharmaceutical Properties Through Prodrugs and Analogs, American Pharmaceutical Association/Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences Symposium, Washington, D.C., 1977.
A. A. Sinkula and S. H. Yalkowsky. J. Pharm. Sci. 64:181–210 (1975).
L. Colla, E. De Clerq, R. Busson, and H. Vanderhaeghe. J. Med. Chem. 26:602–604 (1983).
D. C. Baker, T. H. Haskell, and S. R. Putt. J. Med. Chem. 21:1218–1221 (1978).
D. C. Baker, T. H. Haskell, S. R. Putt, and B. J. Sloan, J. Med. Chem. 22:273–279 (1979).
J. Verheyden and J. Martin. U.S.A. Patent 4, 556,659, Dec. 3, 1985.
H. Hoeksema, G. B. Whitfield, and L. E. Rhuland. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 6:213–216 (1961).
A. D. Welch. Cancer Res. 21:1475–1490 (1961).
E. J. Benjamin, B. A. Firestone, and J. A. Schneider. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 23:168–170 (1985).
J. H. Wood, J. E. Syarto, and H. Letterman. J. Pharm. Sci. 54:1068 (1965).
E. J. Benjamin and L.-H. Lin. Drug Dev. Indust. Pharm. 11:771–790 (1985).
S. H. Yalkowsky. In E. B. Roche (ed.), Design of Biopharmaceutical Properties Through Prodrugs and Analogs, American Pharmaceutical Association/Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences Symposium, Washington, D.C., 1977, Chap. 13.
Y. Yamaoka, R. D. Roberts, and V. J. Stella. J. Pharm. Sci. 72:400–405 (1983).
H. Sasak, M. Fukumoto, M. Hashida, T. Kimura, and H. Sezaki. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 31:4083–4090 (1983).
N. F. H. Ho, J. Y. Park, W. Morozowich, and W. I. Higuchi. In E. B. Roche (ed.), Design of Biopharmaceutical Properties Through Prodrugs and Analogs, American Pharmaceutical Association/Academy of Pharmaceutical Sciences Symposium, Washington, D.C., 1977, Chap. 8.
A. Burr, H. Bundgaard, and E. Falch. Int. J. Pharm. 24:43–60 (1985).
T. Kawaguchi, Y. Suzuki, Y. Nakahara, N. Nambu, and T. Nagai. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 33:301–307 (1985).
T. Higuchi, P. Niphadkar, and T. Kawaguchi. In L. Benet, G. Levy, and B. Ferraiola (ed.), Pharmacokinet (Proc. Sidney Riegelman Meml. Symp.), Plenum, New York, 1982, pp. 67–82.
W. Dixon and E. C. Webb. Enzymes, 2nd ed., Longmans, Green, New York, 1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benjamin, E.J., Firestone, B.A., Bergstrom, R. et al. Selection of a Derivative of the Antiviral Agent 9-[(1,3-Dihydroxy-2-propoxy)-methyl]Guanine (DHPG) with Improved Oral Absorption. Pharm Res 4, 120–125 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016462801968
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016462801968