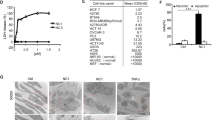
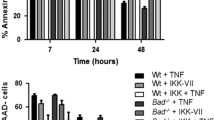
Abstract
Tumour Necrosis Factor α binding at the cell surface induces a complex series of signaling events culminating in the caspase cascade, which is central to apoptosis. However, recent work from several laboratories has questioned caspase involvement in commitment to cell death. We have therefore investigated the involvement of caspases in the crucial commitment stage of tumour necrosis factor-induced apoptosis in human T-leukaemic CEM-C7 cells and breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells, using both peptide-based and viral caspase inhibitors. Our observations converge on the conclusion that commitment to death in these systems is dependent on caspase activity, e.g. baculovirus p35 produces over 50-fold protection of colony-forming ability, the most stringent criterion of cell survival. These observations strongly support the view that the caspase family is of great biological and medical significance, since caspase dysfunction resulting in failure to commit to cell death after treatment with tumour necrosis factor or other stimuli may contribute to cancer development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: Integrating mammalian biology. Cell 2001; 104: 487–501.
Manusama ER, Nooijen PTGA, Ten Hagen TLM, et al Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in isolated perfusion systems in the treatment of cancer: The Rotterdam preclinical-clinical program. Sem Surg Oncol 1998; 14: 232–237.
Kaneda Y, Yamamoto Y, Kamada H, et al Antitumor activity of tumor necrosis factor alpha conjugated with divinyl ether and maleic anhydride copolymer on solid tumors in mice. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 290–295.
Smith CA, Farrah T, Goodwin RG The TNF receptor superfamily of cellular and viral-proteins-activation, costimulation, and death. Cell 1994; 76: 959–962.
Chinnaiyan AM, Tepper CG, Seldin MF, et al FADD/MORT1 is a common mediator of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 4961–4965.
Boldin MP, Goncharov TM, Goltsev YV, Wallach D Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1-induced and TNF receptor-induced cell-death. Cell 1996; 85: 803–815.
Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kischkel FC, et al FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death-inducing signaling complex. Cell 1996; 85: 817–827.
Alnemri ES, Livingston DJ, Nicholson DW, et al Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell 1996; 87: 171.
Thompson CB Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 1995; 267: 1456–1462.
_ Martin SJ, Green DR Protease activation during apoptosis: Death by a thousand cuts? Cell 1995; 82: 349–352.
_ Yuan J Molecular control of life and death. Curr Biol 1995; 7: 211–214.
_ Hale AJ, Smith CA, Sutherland LC, et al Apoptosis: Molecular regulation of cell death. Eur J Biochem 1996; 236: 1–26.
_ Whyte M ICE/CED-3 proteases in apoptosis. Trends in Cell Biol 1996; 6: 245–248.
_ Alnemri ES Mammalian cell death proteases: A family of highly conserved aspartate specific cysteine proteases. J Cell Biochem 1997; 64: 33–42.
_ Villa P, Kaufmann SH, Earnshaw WC Caspases and caspase inhibitors. TIBS 1997; 22: 388–393.
_ Chow SC, Weis M, Kass GEN, Holmstroem TH, Eriksson JE, Orrenius S Involvement of multiple proteases during Fasmediated apoptosis in T lymphocytes. FEBS Letts 1995; 364: 134–138.
_ Enari M, Hug H, Nagata S Involvement of an ICE-like protease in Fas-mediated apoptosis. Nature 1995; 375: 78–81.
_ Fearnhead HO, MacFarlane M, Dinsdale D, Cohen GM DNA degradation and proteolysis in thymocyte apoptosis. Toxicol Letts 1995; 82/83: 135–141.
_ Los M, Van De Craen M, Penning LC, et al Requirement of an ICE/CED-3 protease for Fas/APO-1-mediated apoptosis. Nature 1995; 375: 81–83.
_ Zhu HJ, Fearnhead HO, Cohen GM An ICE-like protease is a common mediator of apoptosis induced by diverse stimuli in human monocytic THP1 cells. FEBS Letts 1995; 374: 303–308.
_ Jacobson MD, Weil M, Raff MC Role of CED3/ICE-family proteases in staurosporine-induced programmed cell-death. J Cell Biol 1996; 33: 1041–1051.
_ Schlegel J, Peters I, Orrenius S, et al CPP32/apopain is a key interleukin 1β converting enzyme-like protease involved in Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 1841–1844.
_ Slee EA, Zhu HJ, Chow SC, MacFarlane M, Nicholson DW, Cohen GM Benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp (OMe) fluoromethylketone (Z-VAD.FMK) inhibits apoptosis by blocking the processing of CPP32. Biochem J 1996; 315: 21–24.
_ Gagliardini V, Fernandez PA, Lee RKK, et al Prevention of vertebrate neuronal death by the crm-a gene. Science 1994; 263: 826–828.
_ Beidler DR, Tewari M, Friesen PD, Poirier G, Dixit VM The baculovirus p35 protein inhibits Fas-and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 16526–16528.
_ Robertson NM, Zangrilli J, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Friesen PD, Litwack G, Alnemri ES Baculovirus P35 inhibits the glucocorticoid-mediated pathway of cell death. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 43–47.
_ Datta R, Kojima H, Banach D, et al Activation of a CrmAinsensitive, p35-sensitive pathway in ionizing radiationinduced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 1965–1969.
_ Yuan JY, Shaham S, Ledoux S, Ellis JM, Horvitz HJR The C elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1β converting enzyme. Cell 1993; 75: 641–652.
_ Ellis HM, Horvitz HR Genetic-control of programmed celldeath in the nematode C elegans. Saibo 1986; 44: 817–829.
_ Xiang JL, Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ BAX-induced cell death may not require interleukin 1beta-converting enzyme-like proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 14559–14563.
_ McCarthy NJ, Whyte MKB, Gilbert CS, Evan GI Inhibition of Ced-3/ICE-related proteases does not prevent cell death induced by oncogenes, DNA damage, or the Bcl-2 homologue Bak. J Cell Biol 1997; 136: 215–227.
_ Brunet CL, Gunby RH, Benson RSP, Hickman JA, Watson AJM, Brady G Commitment to cell death measured by loss of clonogenicity is separable from the appearance of apoptotic markers. Cell Death Differ 1998; 5: 107–115.
_ Amarante-Mendes GP, Finucane DM, Martin SJ, Cotter TG, Salvesen GS, Green DR Anti-apoptotic oncogenes prevent caspase-dependent and independent commitment to cell death. Cell Death Differ 1998; 5: 298–306.
_ Longthorne VL, Williams GT Caspase activity is required for commitment to Fas-mediated apoptosis. EMBO J 1997; 16: 3805–3812.
_ Bump NJ, Hackett M, Hugunin M, et al Inhibition of ICE family proteases by baculovirus antiapoptotic protein p35. Science 1995; 269: 1885–1888.
_ Xu GZ, Cirilli M, Huang YH, Rich RL, Myszka DG, Wu H Covalent inhibition revealed by the crystal structure of the caspase-8/p35 complex. Nature 2001; 410: 494–497.
_ Norman MR, Thompson EB Characterization of a glucocorticoid-sensitive human lymphoid cell line. Cancer Res 1997; 37: 3785–3791.
_ Williams GT, Critchlow MR, Hedge VL, O'Hare KB Molecular failure of apoptosis; inappropriate cell survival and mutagenesis? Toxicol Letts 1998; 103: 485–489.
_ Mosmann T Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival-application to proliferation and cyto-toxicity assays. J Immunol Meths 1983; 65: 55–63.
_ Li P, Allen H, Banerjee S, Franklin S, Herzog L, Johnston C Mice deficient in IL-1-beta-converting enzyme are defective in production of mature IL-1-beta and resistant to endotoxicshock. Cell 1995; 80: 401–411.
_ Kuida K, Zheng TS, Na SQ, et al Decreased apoptosis in the brain and premature lethality in CPP32-deficient mice. Nature 1996; 384: 368–372.
_ Mashima T, Naito M, Kataoka S, Kawai H, Tsuruo T Aspartate-based inhibitor of interleukin-1beta-converting enzyme prevents antitumor agent-induced apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia U937 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 1995; 209: 907–915.
_ Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Ottaviano Y, Davidson NE, Poirier GG Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase—an early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 1993; 53: 3976–3985.
_ Fernandes-Alnemri T, Litwack G, Alnemri ES Cpp32, a novel human apoptotic protein with homology to Caenorhabditis elegans cell-death protein CED-3 and mammalian interleukin-1-beta-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 30761–30764.
_ Tewari M, Quan LT, O'Rourke K, Desnoyers S, Zeng Z, Beidler DR Yama/cpp32-beta, a mammalian homolog of ced-3, is a crm-A-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell 1995; 81: 801–809.
_ Chow SC, Slee EA, MacFarlane M, Cohen GM Caspase-1 is not involved in CD95/Fas-induced apoptosis in Jurkat T-cells. Exp Cell Res 1999; 246: 491–500.
_ Tewari M, Dixit VM Fas-and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is inhibited by the poxvirus crmA gene product. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 3255–3260.
_ Miura M, Friedlander RM, Yuan J Tumor necrosis factorinduced apoptosis is mediated by a CrmA-sensitive cell death pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 8318–8322.
_ Zhou Q, Snipas S, Orth K, Muzio M, Dixit VM, Salvesen GS Target protease specificity of the viral serpin CrmA. J Biol Chem 1996; 272: 7797–7800.
_ Ruemmele FM, Dionne S, Levy E, Seidman EG TNFα-induced IEC-6 cell apoptosis requires activation of ICE caspases whereas complete inhibition of the caspase cascade leads to necrotic cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 1999; 269: 169–166.
_ Packham G, Lahti JM, Fee BE, Gawn JM, Coustansmith E, Campana D Fas activates NF-kappa B and induces apoptosis in T-cell lines by signaling pathways distinct from those induced by TNF-alpha. Cell Death Differ 1997; 4: 130–139.
_ Higuchi M, Proske RJ, Yeh ETH Inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I by TNF results in cytochrome c release. Oncogene 1998; 17: 2515–2524.
_ Martinou I, Desagher S, Eskes R, et al The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria during apoptosis of NGFdeprived sympathetic neurons is a reversible event. J Cell Biol 1999; 144: 883–889.
_ Storz P, Döppler H, Horn-Müller J, Müller G, Pfizenmaier K TNF down-regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-dependent mitogenic signal pathways as an important step in cytostasis induction and commitment to apoptosis of Kym-1 rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 955–965.
_ Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan C, et al Reduced apoptosis and cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9. Cell 1998; 94: 325–327.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hedge, V.L., Williams, G.T. Commitment to apoptosis induced by tumour necrosis factor-α is dependent on caspase activity. Apoptosis 7, 123–132 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014306314138
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014306314138