Abstract
Purpose. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of cyclodextrins (β-CD, HP-β-CD and (SBE)7m-β-CD), and co-administration of a water-soluble polymer (HPMC) and cyclodextrins, on the oral bioavailability of glibenclamide in dogs.
Methods. Effects of cyclodextrins on the aqueous solubility of glibenclamide, with and without hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC), were determined by a phase-solubility method. Solid inclusion complexes were prepared by freeze-drying. Glibenclamide was administered orally and intravenously to beagle dogs.
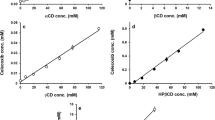
Results. Aqueous solubility of glibenclamide increased as a function of cyclodextrin concentration, showing an AL-type diagram for β-CD and an Ap-type diagrams for both of the β-CD derivatives studied. HPMC enhanced the solubilising effect of cyclodextrins, but did not affect the type of phase-solubility diagram. Orally administered glibenclamide and its physical mixture with HP-β-CD showed poor absolute bioavailability, while orally administered glibenclamide/cyclodextrin-complexes significantly enhanced the absolute bioavailability of glibenclamide. Orally administered glibenclamide/β-CD/HPMC and glibenclamide/(SBE)7m-β-CD/HPMC complexes showed similar absolute bioavailability compared to formulations not containing HPMC, even though 80% (in the case of (SBE)7m-β-CD) or 40% (in the case of β-CD) less cyclodextrin was used.
Conclusions. The oral bioavailability of glibenclamide was significantly increased by cyclodextrin complexation. HPMC increased the solubilising effect of cyclodextrins and, therefore, the amount of cyclodextrin needed in the solid dosage form was significantly reduced by their co-administration. In conclusion, the pharmaceutical usefulness of cyclodextrins in oral administration may be substantially improved by co-administration of a water-soluble polymer.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
In J. E. F. Reynolds (eds.), Martindale The Extra Pharmacopoeia 29 th edition, The Pharmaceutical Press, London, 1989, pp. 389.
L. Groop, E. Wåhlin-Boll, K.-J. Tötterman, A. Melander, E.-M. Tolppanen, and F. Fyhrqvist. Pharmacokinetics and metabolic effects of glibenclamide and glipizide in type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 28:697–704 (1985).
J. B. Chalk, M. Patterson, M. T. Smith, and M. J. Eadie. Correlations between in vitro dissolution, in vivo bioavailability and hypoglycaemic effect of oral glibenclamide. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 31:177–182 (1986).
O. Shaheen, S. Othman, I. Jalal, A. Awidi, and W. Al-Turk. Comparison of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a conventional and a new rapidly dissolving glibenclamide preparation. Int. J. Pharm. 38:123–131 (1987).
M. T. Esclusa-Diaz, J. J. Torres-Labandeira, M. Kata, and J. L. Vila-Jato. Inclusion complexation of glibenclamide with 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in solution and in solid state. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1:291–296 (1994).
N. M. Sanghavi, H. Venkatesh, and V. Tandel. Solubilization of glibenclamide with β-cyclodextrin & its derivates. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 20:1275–1283 (1994).
A. Mitrevej, N. Sinchaipanid, V. Junyaprasert, and L. Warintornuwat. Effect of grinding of β-cyclodextrin and glibenclamide on tablet properties. Part I. in vitro. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 22:1237–1241 (1996).
A. Gerlóczy, M. Vikmon, J. Szemán L. Jicsinszky, D. Acerbi, P. Ventura, M. Pasini, and J. Szejtli. Absorption Studies on Glibenclamide/Sodium/ β-Cyclodextrin complex in Rabbits. In P. Couvreur, D. Duchêne, I. Kalles (eds.), Minutes of the Formulation of Poorly-available Drugs for Oral Administration, Editions de Santé, Paris, 1996, pp. 257–260.
V. J. Stella and R. A. Rajewski. Cyclodextrins: Their future in drug formulation and delivery. Pharm. Res. 14:556–567 (1997).
R. A. Rajewski and V. J. Stella. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 2. In vivo drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 85:1142–1169 (1996).
T. Loftsson, H. Fridriksdóttir, A. M. Sigurdadóttir, and H. Ueda. The effect of water-soluble polymers on drug-cyclodextrin complexation. Int. J. Pharm. 110:169–177 (1994).
T. Loftsson, H. Fridriksdóttir, and T. K. Gudmundsdóttir. The effect of water-soluble polymers on aqueous solubility of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 127:293–296 (1996).
H. Fridriksdóttir, T. Loftsson, and E. Stefánsson. Formulation and testing of methazolamide cyclodextrin eye drop solutions. J. Contr. Rel. 44:95–99 (1997).
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier. Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed., Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 1982.
T. Higughi and K. A. Connors. Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instr. 4:117–212 (1965).
D. O. Thompson. Cyclodextrins-Enabling Excipients: Their Present and Future Use in Pharmaceuticals. In S. Bruck (ed.), Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 14:1–104 (1997).
M. D. Johnson, B. L. Hoesterey, and B. D. Anderson. Solubilization of a tripeptide HIV protease inhibitor using a combination of ionization and complexation with chemically modified cyclodextrins. J. Pharm. Sci. 83:1142–1146 (1994).
K. Okimoto, R. A. Rajewski, K. Uekama, J. A. Jona, and V. J. Stella. The interaction of charged and uncharged drugs with neutral (HP-β-CD) and anionically charged (SBE7-β-CD) β-cyclodextrins. Pharm. Res. 13:256–264 (1996).
T. Loftsson, T. K. Gudmundsdóttir, and H. Fridriksdóttir. The influence of water-soluble polymers and pH on hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complexation of drugs. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 22:401–405 (1996).
L. S. Goodman and A. Gilman. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, Pergamon Press, New York, 1990.
K. Uekama, S. Narisawa, F. Hirayama and M. Otagiri. Improvement of dissolution and absorption characteristics of benzodiazepines by cyclodextrin complexation. Int. J. Pharm. 16:327–338 (1983).
T. Järvinen, K. Järvinen, N. Schwarting, and V. J. Stella. β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives, SBE4-β-CD and HP-β-CD, Increase the oral bioavailability of cinnarizine in beagle dogs. J. Pharm. Sci. 84:295–299 (1995).
C. J. Betlach, M. A. Gonzalez, B. C. McKiernan, C. Neff-Davis, and N. Bodor. Oral pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine in dogs from commercial tablets and a cyclodextrin complex. J. Pharm. Sci. 82:1058–1060 (1993).
M. E. Brewster, W. R. Anderson, D. Meinsma, D. Moreno, A. I. Webb, L. Pablo, K. S. Estes, H. Derendorf, N. Bodor, R. Sawchuk, B. Cheung, and E. Pop. Intravenous and oral pharmacokinetic evaluation of a 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin based formulation of carbamazepine in the dog: comparison with commercially available tablets and suspensions. J. Pharm. Sci. 86:335–339 (1997).
J. K. Kristinsson, H. Fridriksdóttir, S. Thórisdóttir, A. M. Sigurdardóttir, E. Stefánsson, and T. Loftsson. Dexamethasone-cyclodextrin-polymer co-complexes in aqueous eye drops. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 37:1199–1203 (1996).
H. Fridriksdóttir, T. Loftsson, J. A. Gudmundsson, G. J. Bjarnason, M. Kjeld, and T. Thorsteinsson. Desing and in vivo testing of 17β-estradiol-HPβCD sublingual tablets. Pharmazie 51:39–42 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savolainen, J., Järvinen, K., Taipale, H. et al. Co-Administration of a Water-Soluble Polymer Increases the Usefulness of Cyclodextrins in Solid Oral Dosage Forms. Pharm Res 15, 1696–1701 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011900527021
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011900527021