Abstract
The behavioral activity of some trifluoromethyl ketones (TFMKs) as inhibitors of the pheromone activity of the corn stalk borer Sesamia nonagrioides (Lef.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) is reported. The most closely-related analogue to the pheromone tested, (Z)-11-hexadecenyl trifluoromethyl ketone (Z11-16:TFMK), elicited a significant decrease in the number of male catches in traps baited with mixtures with the pheromone in 1:1 and 10:1 ratios in comparison to the pheromone alone. The E isomer of the analogue as well as two highly hydrated ketones, 3-octylthio-1,1,1-trifluoropropan-2-one (OTFP) and 1,1-difluoropentadecyl trifluoromethyl ketone, were inactive. Conversely, the saturated TFMKs n-dodecyl trifluoromethyl ketone and, particularly, n-hexadecyl trifluoromethyl ketone induced a synergistic effect when mixed with the synthetic pheromone in 10:1 ratio. However, in a wind tunnel these chemicals did not elicit any differential effect on flying moths attracted to a source containing a 10:1 blend of the analogue and the pheromone. In a dual choice bioassay with two dispensers, containing the pheromone alone, and mixtures of Z11-16:TFMK and the pheromone and separated 5 cm apart, males showed no particular preference for either dispenser. The ketone mixture, however, induced moths to execute erratic flights with frequent crosswind counter-turns and intersections with plume boundaries. The total number of contacts with the source were reduced when a control dispenser was paired with a dispenser containing Z11-16:TFMK and pheromone. Z11-16:TFMK and OTFP showed little toxicity on mice with a LD50 of 1 g/kg after the 6th day of treatment. For comparitive purposes, the major component of the pheromone, Z11-16:Ac, displayed a LD50 of 5 g/kg 6 days after application. Our results provide additional information about the activity of the TFMKs, which might be useful for the utilization of these chemicals in future pest control studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
ABDEL-AAL, Y. A. I., ROE, R. M., and HAMMOCK, B. D. 1984. Kinetic properties of the inhibition of juvenile hormone esterase by two trifluoromethyl ketones and O-ethyl-Sphenylphosphoramidothiolate. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 21:232–241.
ANONYMOUS. 1979. Distribution maps of pests. Series A (Agricultural), Map No. 399 Pest: Sesamia nonagrioides (Lef.). Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau, London.
ASHOUR, M.-B. A., and HAMMOCK, B. D. 1987. Substituted trifluoroketones as potent selective inhibitors of mammalian carboxylesterases. Biochem. Pharm. 36:1869-1879.
BAKER, T. C., FADAMIRO, H. Y., and COSSé, A. A. 1998. Moth uses fine tuning for odour resolution. Nature 393:530.
BAU, J. (2000). Activitat electrofisiològica i comportamental de feromones sexuals de Lepidòpters i dels seus inhibidors. PhD Thesis. University of Barcelona, 230 pp.
BAU, J., MARTíNEZ, D., RENOU, M., and GUERRERO, A. 1999. Pheromone-triggered orientation flight of male moths can be disrupted by trifluoromethyl ketones. Chem. Senses 24:473-480.
BONNING, B. C., HOOVER, K., BOOTH, T. F., DUFFEY, S., and HAMMOCK, B. D. 1995. Development of a recombinant baculovirus expressing a modified juvenile hormone esterase with potential for insect control. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 30:177-194.
CAMPS, F., FABRIàS, G., GASOL, V., GUERRERO, A., HERNáNDEZ, R., and MONTOYA, R. 1988. Analogs of the sex pheromone of processionary moth Thaumetopoea pityocampa: Synthesis and biological activity. J. Chem. Ecol. 14:1331-1346.
CARPENTER, J. E., and SPARKS, A. N. 1982. Effects of vision on mating behavior of the male corn earworm. J. Econ. Entomol. 75:248-250.
DURáN, I., PARRILLA, A., FEIXAS, J., and GUERRERO, A. 1993. Inhibition of antennal esterases of the Egyptian armyworm Spodoptera littoralis by trifluoromethyl ketones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 3:2593-2598.
FEIXAS, J., PRESTWICH, G. D., and GUERRERO, A. 1995. Ligand specificty of pheromone-binding proteins of the processionary moth. Eur. J. Biochem. 234:521-526.
FRéROT, B., GUILLON, M., BERNARD, P., MADRENNES, L., SCHEPPER, B., MATHIEU, F., and COEUR, A. 1997. Mating disruption of corn stalk borer, Sesamia nonagrioides Lef. (Lep. Noctuidae), pp. 119-128, in P. Witzgall and H. Arn (eds.). Technology Transfer in Mating Disruption. IOBC, Montpellier.
GELB, M. H., SVAREN, J. P., and ABELES, R. H. 1985. Fluoroketone inhibitors of hydrolytic enzymes. Biochemistry 24:1813-1817.
HAMMOCK, B. D., and PHILPOTT, M. L. 1992. Juvenile hormone esterase for insect control. US Patent US 5,098,706.
HAMMOCK, B. D., WING, K. D., McLAUGHLIN, J., LOVELL, V. M., and SPARKS, T. C. 1982. Trifluoromethyl ketones as possible transition state analog inhibitors of juvenile hormone esterase. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 17:76-88.
HATHAWAY, D. O., McGOVERN, T. P., BEROZA, M., MOFFITT, H. R., MCDONOUGH, L. M., and BUTT, B. A. 1974. An inhibitor of sexual attraction of male codling moths to a synthetic sex pheromone and virgin females in traps. Environ. Entomol. 3:522-524.
KASANG, G., NICHOLLS, M., and VON PROFF, L. 1989. Sex pheromone conversion and degradation in antennae of the silkworm moth Bombyx mori L. Experientia 45:81-87.
KLUN, J. A., SCHWARZ, M., and UEBEL, E. C. 1991. European corn borer: Pheromonal catabolism and behavioral response to sex pheromone. J. Chem. Ecol. 17:317-334.
LINDERMAN, R. J., LEAZER, J., ROE, R. M., VENKATESH, K., SELINSKY, B. S., and LONDON, R. E. 1988. 19F NMR Spectral evidence that 3-octylthio-1,1,1-trifluoropropan-2-one, a potent inhibitor of insect juvenile hormone esterase, functions as a transition state analog inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 31:187-194.
MAFRA-NETO, A., and CARDé, R. T. 1994. Fine-scale structure of pheromone plumes modulates upwind orientation of flying moths. Nature 369:142-144.
MARSH, D., KENNEDY, J. S., and LUDLOW, A. R. 1978. An analysis of anemotactic zigzagging flight in male moths stimulated by pheromone. Physiol. Ent. 3:221-240.
MAZOMENOS, B. E. 1989. Sex pheromone components of corn stalk borer Sesamia nonagrioides (Lef.). J. Chem. Ecol. 15:1241-1247.
MAZOMENOS, B. E., BARDAS, D., and PANTAZIMAZOMENOU, A. 1989. Sesamia nonagrioides sex pheromone: Field attactiveness use of pheromone traps for monitoring and control. Acta Phytopatol. Entomol. Hungar. 24:153-156.
MURLIS, J., and JONES, C. D. 1981. Fine-scale structure of odour plumes in relation to insect orientation to distant pheromone and other attractant sources. Physiol. Entomol. 6:71-86.
PARRILLA, A., and GUERRERO, A. 1994. Trifluoromethyl ketones as inhibitors of the processionary moth sex pheromone. Chem. Senses 19:1-10.
PERDIGUER, A., GIMENO, F., AGUILAR, L., EIZAGUIRRE, M., RIBA, M., and SANS, A. 1992. Ensayos de confusión sexual en Sesamia nonagrioides. Inv. Agr. Prot. Veg. 7:253-260.
POITOUT, S., and BUES, R. 1974. Élevage des chenilles de vingt-huit espèces de lepidoptères Noctuidae et deux espèces d'Arctiidae sur milieu artificiel simple. Particularités de l'élevage selon les espèces. Ann. Zool. Ecol. Anim. 6:431-441.
POPHOF, B. 1998. Inhibitors of sensillar esterase reversibly block the responses of moth pheromone receptor cells. J. Comp. Physiol. A 183:153-164.
POPHOF, B., GEBAUER, T., and ZIEGELBERGER. 2000. Decyl-thio-trifluoropropanone, a competitive inhibitor of moth pheromone receptors. J. Comp. Physiol. 186:315-323.
PREISS, R., and PRIESNER, E. 1988. Responses of male codling moths (Laspeyresia pomonella) to codlemone and other alcohols in a wind tunnel. J. Chem. Ecol. 14:797-813.
PRESTWICH, G. D. 1986. Fluorinated sterols, hormones and pheromones: Enzyme-targeted disruptants in insects. Pest. Sci. 37:430-440.
PRESTWICH, G. D. 1987. Chemical studies of pheromone reception and catabolism, pp. 473-527, in G. D. Prestwich and G. J. Blomquist (eds.). Pheromone Biochemistry. Academic Press, New York.
PRESTWICH, G. D., and STREINZ, L. 1988. Haloacetate analogs of pheromones: Effects on catabolism and electrophysiology in Plutella xylostella. J. Chem. Ecol. 14:1003-1021.
QUERO, C., CAMPS, F., and GUERRERO, A. 1995. Behavior of processionary males (Thaumetopoea pityocampa) induced by sex pheromone and analogs in a wind tunnel. J. Chem. Ecol. 21:1957-1969.
RENOU, M., and GUERRERO, A. 2000. Insect parapheromones in olfaction research and semiochemicalbased pest control strategies. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 48:605-630.
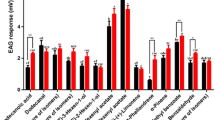
RENOU, M., LUCAS, P., MALO, E., QUERO, C., and GUERRERO, A. 1997. Effects of trifluoromethyl ketones and related compounds on the EAG and behavioural responses to pheromones in male moths. Chem. Senses 22:407-416.
RIBA, M., EIZAGUIRRE, M., SANS, A., QUERO, C., and GUERRERO, A. 1994. Inhibition of pheromone action in Sesamia nonagrioides by haloacetate analogues. Pest. Sci. 41:97-103.
RIDGWAY, R. L., SILVERSTEIN, R. M., and INSCOE, M. N., (eds.) (1990). Behavior-Modifying Chemicals for Insect Management. New York, Marcel Dekker.
ROSELL, G., HERRERO, S., and GUERRERO, A. 1996. New trifluoromethyl ketones as potent inhibitors of esterases: 19F NMR spectroscopy of transition state analog complexes and structure-activity relationships. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 226:287-292.
SANS, A., RIBA, M., EIZAGUIRRE, M., and LOPEZ, C. 1997. Electroantennogram, wind tunnel and field responses of male Mediterranean corn borer, Sesamia nonagrioides, to several blends of its sex pheromone components. Ent. Exp. Appl. 82:121-127.
SHOREY, H. H., and GASTON, L. K. 1970. Sex pheromones of noctuid moths. XX. Short-range visual orientation by pheromone-stimulated males of Trichoplusia ni. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 63:829-832.
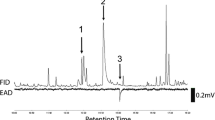
SRENG, I., MAUME, B., and FRéROT, B. 1985. Analyse de la sécretion phéromonale produite par les femelles vierges de Sesamia nonagrioides (Lef.) (Lepidoptère, Noctuidae). C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris III 301:439-442.
VALEUR, P. G., and LöFSTEDT, C. 1996. Behaviour of male oriental fruit moth, Grapholita molesta, in overlapping sex pheromone plumes in a wind tunnel. Ent. Exp. Appl. 79:51-59.
VILLUENDAS, I., PARRILLA, A., and GUERRERO, A. 1994. An efficient and expeditious synthesis of functionalized trifluoromethyl ketones through lithium-iodine exchange reaction. Tetrahedron 50:12673-12684.
VOGT, R. G., RIDDIFORD, L. M., and PRESTWICH, G. D. 1985. Kinetic properties of a pheromonedegrading enzyme: The sensillar esterase of Antheraea polyphemus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:8827-8831.
WEATHERSTON, I., and MINKS, A. K. 1995. Regulation of semiochemicals-global aspects. Pest Manage. Rev. 1:1-13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riba, M., Sans, A., Bau, P. et al. Pheromone Response Inhibitors of the Corn Stalk Borer Sesamia nonagrioides. Biological Evaluation and Toxicology. J Chem Ecol 27, 1879–1897 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010468911352
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010468911352