Abstract
Introduction: Current techniques for estimating catheter tip temperature in ablative therapy for cardiac arrhythmias rely on thermocouples or thermistors attached to or embedded in the tip electrode. These methods may reflect the electrode temperature rather than the tissue temperature during electrode cooling so that the highest temperature away from the ablation site may go undetected. A microwave radiometer is capable of detecting microwave radiation as a result of molecular motion. In this study, we evaluated microwave radiometric thermometry as a new technique to monitor temperature away from the electrode tip during ablative therapy utilizing a saline model.
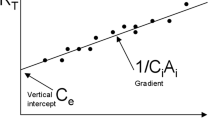
Methods and Results: A microwave radiometer antenna and fluoroptic thermometer were inserted in a test tube with circulating room temperature saline kept constant at 23.5°C while the surrounding saline bath was heated from 37°C to 70°C. For every degree rise in the warm saline bath placed either 5mm or 8mm from the radiometer antenna, the radiometer temperature changed 0.26°C and 0.14°C respectively while the fluoroptic temperature probe remained constant at 23.5°C. The radiometer temperature was highly correlated with the warm saline bath temperature (R2=0.997 for warm saline 5mm from the antenna, R2=0.991 for warm saline 8mm from the antenna).
Conclusions: Microwave radiometry can estimate distant temperatures by detecting microwave electromagnetic radiation. The sensitivity of the microwave radiometer is also distance-dependent. The microwave radiometer thus serves as a promising instrument for monitoring temperatures at depth away from the catheter-electrode tip in ablative therapy for cardiac arrhythmias.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jackman W, Xunzhang W, Friday KJ, et al. Catheter ablation of accessory pathways (Wolf-Parkinson-White Syndrome) by radiofrequency current. N Engl J Med 1991;324:1605–1611.
Kuck HK, Schlutter M, Geiger M, et al. Radiofrequency current catheter ablation of accessory pathways. Lancet 1991;337:1557–1561.
Jackman WM, Beckman KJ, McClelland JH, et al. Treatment of supraventricular tachycardia due to atrioventricular nodal reentry by radiofrequency catheter ablation of slow-pathway conduction. N Engl J Med 1992;327:313–318.
Calkins H, Langberg J, Sousa J, et al. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections in 250 patients. Circulation 1992;85:1337–1346.
Cosio FG, Lopez-Gil M, Goicolea A, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of the inferior vena cava-isthmus in common atrial flutter. Am J Cardiol 1993;71:705–709.
Morady F, Harvey M, Kalbfleisch SJ, et al. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of ventricular tachycardia in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 1993;87:363–373.
Calkins H, Prystowsky E, Carlson M, et al. Temperature monitoring during radiofrequency catheter ablation procedures using closed loop control. Circulation 1994;90:1279–1286.
Nakagawa H, Yamanashi WS, Pitha JV, et al. Comparison of in vivo tissue temperature profile and lesion geometry for radiofrequency ablation with a saline-irrigated electrode versus temperature control in a canine thigh muscle preparation. Circulation 1995;91:2264–2273.
Carter RG: Electromagnetic Waves: Microwave Components and Devices. Chapman and Hall, London, 1990, p. 264.
Pires LA, Huang SKS, Wagshal AB, et al. Temperature-guided radiofrequency catheter ablation of closedchest ventricular myocardium with a novel thermistortipped catheter. Am Heart J 1994;127:1614–1618.
Hartsgrove G, Kraszewski A, Surowiec A: Simulated biological materials for electromagnetic radiation absorption studies. Bioelectromagnetics 1987;8:29–36.
Stuchly MA, Stuchly SS: Dielectric properties of biological materials tabulated. J Microwave Power 1980;15:19–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S.S., VanderBrink, B.A., Regan, J. et al. Microwave Radiometric Thermometry and its Potential Applicability to Ablative Therapy. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 4, 295–300 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009842402357
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009842402357