Abstract
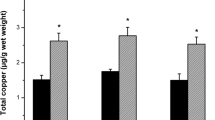
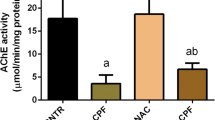
Neurodegenerative effects of MPP+, the main metabolite of MPTP include dopamine (DA) depletion and enhanced lipid peroxidation (LPO) in mice striata, both associated to free radicals overproduction. Since copper is related to several antioxidant enzymes, we tested its neuroprotective effect against MPP+-induced neurotoxicity (20 μg/3 μl). CuSO4 pretreatment was administrated by either acute (2.5 mg/kg, i.p) or chronic (350 or 700 mg/l doses through drinking water, for 30 days) schemes. Acute administration blocked MPP+-induced striatal LPO only when administered 16 or 24 hours before MPP+, and prevented the DA-depleting effect only at 24 hours. Chronic CuSO4 prevented the LPO increase, and blocked the DA depletion only at the higher dose used (700 mg/l). Neuroprotective effect of CuSO4 was dependent on the dose and the time of pretreatment, which suggest that this lag could be related with mechanisms of activation or synthesis of copper-dependent proteins responsible of cellular defense against MPP+.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Langston, J. W. 1985. MPTP neurotoxicity I: An overview and characterization of phases of toxicity. Life Sci. 36:201–206.
Rojas, P. and Rios, C. 1993. Increased striatal lipid peroxidation after intracerebroventricular MPP+ administration to mice. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 72:364–368.
Rios, C., Alvarez-Vega, R., and Rojas, P. 1995. Depletion of copper and manganese in brain after MPTP treatment of mice. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 76:348–352.
Linder, M. C. 1991. Nutrition and metabolism of the major minerals. in Linder, M. C. ed. Nutritional biochemistry and metabolism with clinical applications. Second Edition.
Prohaska, J. R. 1991. Changes in Cu, Zn-Superoxide Dismutase, Cytochrome c Oxidase, Glutathione Peroxidase and Glutathione Transferase Activities in Copper-Deficient mice and rats. J. Nutr. 121:355–363.
Miller, D. B., Reinhard, J. F., Daniels, A. J., and O'Callaghan, J. P. 1991. Diethyldithiocarbamate potentiates the neurotoxicity of in vivo 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine and of in vitro 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium. J. Neurochem. 57:541–549.
Hartmann, H. A. and Evenson, M. A. 1992. Deficiency of Copper can cause Neuronal Degeneration. Med. Hypot. 38:75–85.
Przedborski, S., Kostic, V., Jackson-Lewis, V., Naini, A. B., Simonetti, S., Stanley, F., Carlson, E., Epstein, C. J., and Cadet, J. L. 1992. Transgenic mice with increased Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase activity are resistant to N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 12:1658–1667.
Sorenson, J. R. J., Soderberg, L. S. F., and Chang, L. W. 1995. Radiation protection and radiation recovery with essential metalloelement chelates. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 210:191–204.
Linder, M. C. and Hazegh-Azam, M. 1996. Copper biochemistry and molecular biology. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 63:797S–811S.
Rojas, P., Alvarez-Vega, R., and Ríos, C. 1996. Copper supplementation blocks 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium neurotoxicity in mice. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 22:222.
Crowe, A. and Morgan, E. H. 1996. Iron and Copper Interact during Their Uptake and Deposition in the Brain and Other Organs of Developing Rats Exposed to Dietary Excess of the Two Metals. J. Nutr. 126:183–194.
Triggs, W. J. and Willmore, L. J. 1984. In vivo lipid peroxidation in rat brain following intracortical Fe+2 injection. J. Neurochem. 42:976–979.
Glowinski, J. and Iversen, L. L. 1966. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. Disposition of 3H-Norepinephrine, 3H-Dopamine and 3H-DOPA in various regions of the brain. J. Neurochem. 13:655–669.
Bonilla, E. 1978. Flameless atomic absorption spectrophotometric determination of manganese in rat brain and other tissues. Clin. Chem. 24:471–474.
Boll, M-C., Sotelo, J., Otero, E., Alcaraz-Zubeldia, M., and Rios, C. 1999. Reduced Ferroxidase activity in the cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurosc. Lett. 265:155–158.
Olivares, M. and Uauy, R. 1996. Copper as an essential nutrient. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 63:791S–796S.
Iwata, M., Irano, A., and French, J. H. 1979. Degeneration of the cerebellar system in X-chromosome-linked copper malabsorption. Ann. Neurol. 5:542–549.
Prohanska, J. R. and Bailey, W. R. 1994. Regional specificity in alterations of rat brain copper and catecholamines following perinatal copper deficiency. J. Neurochem. 63:1551–1557.
Dexter, D. T., Carayon, A., Javoy-Agid, F., Agid, Y., Wells, F. R., Daniel, S. E., Lees, A. J. Jenner, P., and Marsden, C. D. 1991. Alterations in the levels of iron, ferritin, and other trace metals in Parkinson's disease and other degenerative diseases affecting the basal ganglia. Brain 114:1953–1975.
Rojas, P., Hidalgo, J., Ebadi, M., and Rios, C. 2000. Changes of MT I y II proteins in the brain after 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium administration in mice. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol and Biol. Psychiat. 24:144–154.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alcaraz-Zubeldia, M., Rojas, P., Boll, C. et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Acute and Chronic Administration of Copper (II) Sulfate against MPP+ Neurotoxicity in Mice. Neurochem Res 26, 59–64 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007680616056
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007680616056