Abstract
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SR) is being used with increasing frequency in the treatment of brain metastases. This study provides data from a clinical experience with radiosurgery in the treatment of cases with multiple metastases and identifies parameters that may be useful in the proper selection and therapy of these patients. From January 1993 to April 1997, 97 patients (43 women and 54 men; median age 58 years) suffering from multiple brain metastases (median 3; range 2–4) in MRI scans, received SR with the Gamma Knife. The median dose at the tumor margin was 20 Gy (range 17–30 Gy). Median tumor volume was 3900 cmm (range 100–10 000). Different forms of hemiparesis, focal and generalized seizures, cognitive deficit, headache, dizziness and ataxia had been the predominant neurological symptoms. Major histologies included lung carcinoma (44%), breast cancer (21%), renal cell carcinoma (10%), colorectal cancer (8%), and melanoma (7%).
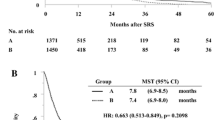
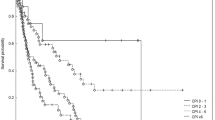
The median survival time was 6 months after SR. The actual one-year survival rate was 26%. In univariate and multivariate analysis, a higher Karnofsky performance rating and absence of extracranial metastases had a significantly positive effect on survival. Local tumor control was achieved in 94% of the patients. Complications included the onset of peritumoral edema (n=5) and necrosis (n=1).
SR induces a significant tumor remission accompanied by neurological improvement and, therefore, provides the opportunity for prolonged high quality survival. We conclude that radiosurgical treatment of multiple brain metastases leads to an equivalent rate of survival when compared to the historic experience of patients treated with whole brain radiotherapy. Patients presenting initially with a higher Karnofsky performance rating and without extracranial metastases had a median survival time of nine months. Each such case should therefore be evaluated based on these factors to determine an optimal treatment regimen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cairncross JG, Kim JH, Posner JB: Radiation therapy for brain metastases. Ann Neurol 7: 529–541, 1980
Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT, et al.: Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol 45: 741–744, 1988
Patchell RA: Brain metastases. Neurol Clin 9: 817–824, 1991
Bindal RK, Sawaya R, Leavens ME, et al.: Surgical treatment of multiple metastases. J Neurosurg 79: 210–216, 1993
Nussbaum ES, Djalilian HR, Cho KH, et al.: Brain metastases: histology, multiplicity, surgery, and survival. Cancer 78: 1781–1788, 1996
Amer MH, Al-Sarraf M, Baker LH, et al.: Malignant melanoma and central nervous system metastases. Incidence, diagnosis, treatment and survival. Cancer 42: 660–668, 1978
Chason JL, Walker FB, Landers JW: Metastatic carcinoma in the central nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. A prospective autopsy study. Cancer 16: 781–787, 1963
Davis PC, Hudgins PA, Peterman SB, et al.: Diagnosis of cerebral metastases: double-dose delayed CT vs contrast enhanced MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 12: 293–300, 1991
Sze G, Milano E, Johnson C, et al.: Detection of brain metastases: comparison of contrast-enhanced MR with unenhanced MR and enhanced CT. Am J Neuroradiol 11: 785–791, 1990
Adler JR, Cox RS, Kaplan I, et al.: Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of brain metastases. J Neurosurg 76: 444–449, 1992
Alexander E III, Moriarty TM, Davis RB, et al.: Stereotactic radiosurgery for the definitive, non invasive treatment of brain metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 87: 34–40, 1995
Black P, Alexander E III, Loeffler JS: New treatment for metastatic brain tumors; in Salcman M (ed): Current Techniques in Neurosurgery. Philadelphia. Current Medicine. 151–156, 1995
Breneman JC, Warnick RE, Albright RE Jr, et al.: Stereotactic Radiosurgery for the treatment of brain metastases. Cancer 79: 551–557, 1997
Caron J, Southami L, Podgorsak E: Dynamic stereotactic radiosurgery in the palliative treatment of cerebral metastatic tumors. J Neurooncol 12: 173–179, 1992
Gerosa M, Nicolato A, Severi F, et al.: Gamma knife radiosurgery for intracranial metastases: from local tumor control to increased survival. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 66(suppl 1): 184–192, 1996
Joseph J, Adler JR, Cox RS, et al.: Linear Acceleator-based radiosurgery for brain metastases: The influence of number of lesions on survival. J Clin Oncol 14: 1085–1092, 1996
Kihlström L, Karlsson B, Lindquist C: Stereotactic radiosurgery for single and multiple cerebral metastases. Acta Neurochir 122: 158–164, 1993
Loeffler JS, Kooy HM, Wen PY, et al.: The treatment of recurrent brain metastases with stereotactic radiosurgery. J Clin Oncol 8: 576–582, 1990
Shu HKG, Sneed PK, Shiau CY, et al.: Factors influencing survival after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for patients with single and multiple brain metastases. Cancer J Sci Am 2: 335–342, 1996
Sturm V, Kimming B, Wowra B, et al.: Radiosurgery in malignant intracranial tumors; in Steiner L (ed): Radiosurgery Baseline and Trends. New York, Raven Press, 155–160, 1992
Karnofsky DA, Burcheval JH: The clinical evaluation of chemotherapeutic agents in cancer, in MacLeod CM (ed): Evaluation of chemotherapeutic agents. New York: Columbia University Press. 191–205, 1949
Horton J, Baxter DH, Olson KB: The management of metastases to the brain by irradiation and corticosteroids. AJR Am J Roentgenol 3: 334–335, 1971
Markesbery WR, Brooks WH, Gupta GD, et al.: Treatment for patients with cerebral metastases. Arch Neurol 35: 754–756, 1978
Ruderman NB, Hall TC: Use of glucocorticosteroids in the palliative treatment of metastatic brain tumors. Cancer 18: 298–306, 1965
Kurtz JM, Gelber R, Brady LW, et al.: The palliation of brain metastases in a favorable patient population: a randomized clinical trial by the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 7: 891–895, 1981
Zimm S, Wampler GL, Stablein D, et al.: Intracerebral metastases in solid-tumor patients: natural history and results of treatment. Cancer 48: 384–394, 1981
Hazuka MB, Burleson WD, Stroud DN, et al.: Multiple brain metastases are associated with poor survival in patients treated with surgery and radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 11: 369–373, 1993
Engenhart R, Kimmig BN, Höver KH, et al.: Long-term follow-up for brain metastases treated by percutaneous stereotactic single high-dose irradiation. Cancer 71: 1353–1361, 1993
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, et al.: A multiinstitutional experience with stereotactic radiosurgery for solitary brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 28: 797–802, 1994
Fuller BG, Kaplan ID, Adler J, et al.: Stereotaxic radiosurgery for brain metastases: The importance of adjuvant whole brain irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23: 413–418, 1992
Loeffler JS, Alexander E III: Radiosurgery for the treatment of intracranial metastases; in Alexander E III, Loeffler JS, Lunsford LD (eds): Stereotactic Radiosurgery. New York, McGraw-Hill, 197–206, 1993
Schoeggl A, Kitz K, Ertl A, et al.: Gamma-Knife radiosurgery for brain metastases of renal cell carcinoma: results in 23 patients. Acta Neurochir 140(6): 549–555, 1998
Crossen JR, Garwood D, Glatstein E, et al.: Neurobehavioral sequelae of cranial irradiation in adults: a review of radiation induced encephalopathy. J Clin Oncol 12: 627–642, 1994
Rutigliano M, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, et al.: The cost effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery versus surgical resection in the treatment of solitary metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurgery 37: 445–455, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schoeggl, A., Kitz, K., Ertl, A. et al. Prognostic Factor Analysis for Multiple Brain Metastases After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: Results in 97 Patients. J Neurooncol 42, 169–175 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006110631704
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006110631704