Abstract
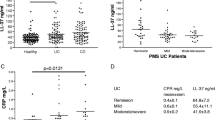
Trials of maintenance therapy in Crohn's disease are often underpowered, and there is need for objective markers of relapse. We assessed the relationship of whole gut lavage fluid cytokines to relapse in inactive Crohn's disease. Fifty-four patients with inactive Crohn's disease were prospectively assessed. Inactivity was determined as a Crohn's disease activity index of <150 and whole gut lavage fluid immunoglobulin G <10 μg/ml. All patients underwent whole gut lavage with analysis of IL-1β and IL-8. Follow up was for one year. Patients with elevated whole gut lavage fluid IL-1β (P < 0.004) and IL-8 (P < 0.02) had greater chance of relapse. Young age, short disease duration, and fistulating disease also relapsed more frequently. Multiple regression identified IL-1β as an independent variable. In conclusion, an elevated whole gut lavage fluid IL-1β in inactive Crohn's disease identifies patients at high risk of relapse.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFRENCES
O'Mahony S, Choudari CP, Barton JR, Walker S, Ferguson A: Gut lavage fluid proteins as markers of activity of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 26: 940–944, 1991
Choudari CP, O'Mahony S, Brydon G, Mwantembe O, Ferguson A: Gut lavage protein concentrations: Objective measures of disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 99:1380–1387, 1990
Troncone R, Caputo N, Campanozzi A, Cucciardi M, Esposito V, Russo R, De Vizia B, Greco L, Cucchiara S: Gut lavage IgG and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist:interleukin 1b ratio as markers of intestinal inflammation in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 41: 60–65, 1997
Arnott IDR, Drummond HE, Ghosh S, Ferguson A: Gut luminal neutrophil migration depends on the anatomical site of Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 114(part 2): G3786, 1998 (abstract)
Schreiber S, Nikolaus S, Hampe J, Hamling J, Koop I, Grossner B, Lochs H, Raedler A: Tumour necrosis factor a and interleukin 1b in relapse of Crohn's disease. Lancet 353: 459–461, 1999
Daig R, Andus T, Aschenbrenner E, Falk W, Scholmerich J, Gross V: Increased interleukin 8 expression in the colon mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 38: 216–222, 1996
Mitsuyama K, Toyonaga A, Sasaki E, Watanabe K, Tateishi H, Nishiyama T, Saiki T, Ikeda H, Tsuruta O, Tanikawa K: IL-8 as an important chemoattractant for neutrophils in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol 96: 432–436, 1994
Grimm MC, Elsbury SKO, Pavli P, Doe WF: Interleukin 8: Cells of origin in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 38: 90–98, 1996
Steinhardt HJ, Loeschke K, Kasper H, Holtermuller KH, Schafer H: European Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study (ECCDS): Clinical features and natural history. Digestion 31: 97–108, 1985
Mekhjian HS, Switz DM, Melnyk CS, Rankin GB, Brooks RK: Clinical features and natural history of Crohn's disease (NCCDS). Gastroenterology 77: 898–906, 1979
Sahmound T, Hoctin-Boes G, Modigliani R, Bitoun A, Colombel JF, Soule JC, Florent C, Gendre JP, Lerebours E, Sylvester R, Mary JY: Identifying patients with a high risk of relapse in quiescent Crohn's disease. Gut 37: 811–818, 1995
Andre C, Descos I, Vignal J, Gillon J: C-reactive protein as a predictor of relapse in asymptomatic patients with Crohn's disease. Scott Med J 28: 26–29, 1983
Boirivant M, Leoni M, Taricotti D, Fais S, Squarcia O, Pallone F: The clinical significance of serum C reactive protein levels in Crohn's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 10: 401–405, 1988
Wright JP: The differences in acute phase reactants to predict acute relapses of Crohn's disease. S Afr Med J 73: 666–666, 1988 (abstract)
Wyatt J, Vogelsang H, Hubl W, Waldhoer T, Lochs H: Intestinal permeability and the prediction of relapse in Crohn's disease. Lancet 341: 1437–1439, 1993
Louis E, Belaiche J, Van Kemseke C, Schaaf N, Mahieu P, Mary JY: Soluable interleukin-2 receptor in Crohn's disease, assessment of disease activity and prediction of relapse. Dig Dis Sci 40:1750–1756, 1994
Lennard-Jones JE: Classification of Inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 24: 2–6, 1989
Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F: Development of a Crohn's disease index: National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology 70: 439–444, 1976
Bayless TM, Tokayer AZ, Polito JMI, Quaskey SA, Mellits ED, Harris ML: Crohn's disease: Concordance for site and clinical type in affected family members-potential hereditary influences. Gastroenterology 111: 573–579, 1996
Ferguson A, Humphreys KA, Croft NM: Technical report: Results of immunological tests on faecal extracts are likely to be extremely misleading. Clin Exp Immunol 99:70–75, 1995
Croft NM, Marshall TG, Ferguson A: Gut inflammation in children with cystic fibrosis on high-dose enzyme supplements. Lancet 346: 1265–1267, 1995
Altman DG: Practical statistics for medical research, 1st ed. London, Chapman and Hall 1991, pp. 365–394
Bryman B, Cramer D: Quantitative data analysis with minitab: A guide for social scientists, 1st ed. London, Routledge; 1996, pp. 218–251
Ferguson A, Campieri M, Doe W, Persson T, Nygard G: Oral budesonide as maintenance therapy in Crohn's disease- results of a 12-month study. Global Budesonide Study Group. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 12: 175–183, 1998
Andre C, Descos I, Vignal J: C reactive protein predicts Crohn's disease relapses on quiesant patients. Gut A940(F2) 1988, (abstract)
Wright JP: Factors influencing first relapse in patients with Crohn's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 15: 12–16, 1992
Messori A, Brignola C, Trallori G, Rampazzo R, Bardazzi G, Belloli C, d'Albasio G, De Simone G, Martini N: Effectiveness of 5-aminosalicylic acid for maintaining remission in patients with Crohn's disease: A meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 89:692–698, 1994
Camma C, Giunta M, Rosselli M, Cottone M: Mesalamine in the maintenance treatment of Crohn's disease: A meta-analysis adjusted for confounding variables. Gastroenterology 113:1465–1473, 1997
McLeod RS, Wolff BG, Steinhart AH, Carryer PW, O'Rouke K, Andrews DF, Blair JE, Cangemi JR, Cohen Z, Cullen JB, Chaytor RG, Greenburg GR, Jaffer NM, Jeejeebhoy KN, MacCarty RL, Ready RL, Weiland LH: Risk and significance of endoscopic/radiographic evidence of recurrent Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 113: 1823–1827, 1997
Satsangi J, Wolstencroft RA, Cason J, Ainley CC, Dumonde DC, Thompson RP: Interleukin 1 in Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol 67: 594–605, 1987
Cominelli F, Pizarro TT: Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 10: 49–53, 1996
McAlindon ME, Mahida YR: Proinflammatory cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 10: 72–74, 1996
Ghosh S, Acciuffi S, Ferguson A: Prognostic value of whole gut lavage fluid analysis in Crohn's disease. Gut 38(suppl 1): F231, 1996 (Abstract)
Hussain F, Ajjan R, Grundman M, Bolton R, Riley S: Cytokine expression and relapse of ulcerative colitis. Gut 40: A28, 1997 (abstract)
Izzo RS, Witkon K, Chen AI, Hadjiyane C, Weinstein MI, Pellecchia C: Neutrophil-activating peptide (interleukin-8) in colonic mucosa from patients with Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 28: 296–300, 1993
Gomes P, du Boulay C, Smith CL, Holdstock G: Relationship between disease activity indices and colonoscopic findings in patients with colonic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 27: 92–95, 1986
Brydon WG, Ferguson A: Haemoglobin in gut lavage as a measure of gastrointestinal blood loss. Lancet 340: 1381–1382, 1992
O'Mahony S, Barton JR, Crichton S, Ferguson A: Appraisal of gut lavage in the study of intestinal immunity. Gut 31: 1341–1344, 1990
Brignola C, Campieri M, Bazzocchi G, Farruggia P, Tragnone A, Lanfranchi GA: A laboratory index for predicting relapse in asymptomatic patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 91:1490–1494, 1986
Farmer RG, Whelan G, Fazio VW: Long-term follow-up of patients with Crohn's disease. Relationship between clinical pattern and prognosis. Gastroenterology 88: 1818–1825, 1985
Siproudhis L, Mortaji A, Mary JY, Juguet F, Bretagne JF, Gosselin M: Anal lesions: Any significant prognosis in Crohn's disease? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:239–243, 1997
Wright JP, Young GO, Tigler-Wybrandi N: Predictors of acute relapse in Crohn's disease, a laboratory and clinical study. Dig Dis Sci 32: 164–170, 1987 PREDICTION OF RELAPSE IN CROHN's DISEASE 409 Digestive Diseases and Sciences, Vol. 46, No. 2 (February 2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arnott, I.D., Drummond, H.E. & Ghosh, S. Gut Mucosal Secretion of Interleukin 1β and Interleukin-8 Predicts Relapse in Clinically Inactive Crohn's Disease. Dig Dis Sci 46, 402–409 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005617302718
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005617302718