Abstract
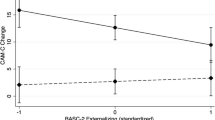
The predictive power of age and IQ at time of admission to an intensive treatment program using applied behavior analysis were examined in a 4- to 6-year follow-up of educational placement. Twenty-seven children with autistic disorder who were between the ages of 31 and 65 months and had IQs on the Stanford Binet between 35 and 109 at time of admission to the Douglass Developmental Disabilities Center were followed up 4 to 6 years after they left the preschool. The results showed that having a higher IQ at intake (M = 78) and being of younger age (M = 42 months) were both predictive of being in a regular education class after discharge, whereas having a lower IQ (M = 46) and being older at intake (M = 54 months) were closely related to placement in a special education classroom. The results are interpreted as pointing to the need for very early intervention for children with Autistic Disorder. It is also emphasized that older children and those with lower IQs in the present study showed measurable gains in IQ from treatment. The data should not be taken to suggest that children older than 4 years of age do not merit high quality treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
American Psychiatric Association. (1987). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (3rd ed., Rev.). Washington DC: Author.
Anderson, S. R., Campbell, S., & Cannon, B. O. (1994). The may center for early childhood education. In S. L. Harris & J. S. Handleman (Eds.), Preschool education programs for children with autism (pp. 15–36). Austin TX: Pro-ed.
Birnbrauer, J. S., & Leach, D. J. (1993) The Murdoch early intervention program after 2 years. Behaviour Change, 10, 63–74.
Fenske, E. C., Zalenski, S., Krantz, P. J., & McClannahan, L. E. (1985). Age at intervention and treatment outcome for autistic children in a comprehensive intervention program. Analysis and Intervention for Developmental Disabilities, 5, 49–58.
Gresham, F. M., & MacMillan, D. L. (1998) Early intervention project: Can its claims be substantiated and its effects replicated? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 28, 5–13.
Harris, S. L., Handleman, J. S., & Burton, J. L. (1990) The Stanford-Binet profiles of young children with autism. Special Services in the Schools, 6, 135–143.
Harris, S. L., Handleman, J. S., Gordon, R., Kristoff, B., & Fuentes, F. (1991). Changes in cognitive and language functioning of preschool children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 21, 281–290.
Lord, C., & Schopler, E. (1994). TEACCH services for preschool children. In S. L. Harris & J. S. Handleman (Eds.), Preschool education programs for children with autism (pp. 87–106). Austin TX: Pro-ed.
Lovaas, O. I. (1987). Behavioral treatment and normal educational and intellectual functioning in young autistic children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 55, 3–9.
McClannahan, L. E., & Krantz, P. J. (1994). The princeton child development institute. In S. L. Harris & J. S. Handleman (Eds.), Preschool education programs for children with autism (pp. 107–126). Austin TX: Pro-ed.
Sheinkopf, S. J., & Siegel, B. (1998). Home based behavioral treatment of young autistic children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 28, 1524.
Schopler, E. (1998). Preface. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 28, 3–4.
Schopler, E., Reichler, R. J., & Renner, B. R. (1986). The Childhood Autism Rating Scale. New York: Irvington.
Thorndike, R. L., Hagen, E. R., & Sattler, J. M. (1986). The Stanford-Binet intelligence scale (4th ed.) Chicago: Riverside.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harris, S.L., Handleman, J.S. Age and IQ at Intake as Predictors of Placement for Young Children with Autism: A Four- to Six-Year Follow-Up. J Autism Dev Disord 30, 137–142 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005459606120
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005459606120