Abstract
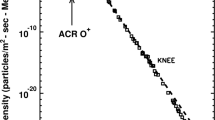
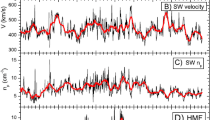
We review aspects of anomalous cosmic rays (ACRs) that bear on the solar modulation of energetic particles in the heliosphere. We show that the latitudinal and radial gradients of these particles exhibit a 22-year periodicity in concert with the reversal of the Sun's magnetic field. The power-law index of the low energy portion of the energy spectrum of ACRs at the shock in 1996 appears to be ≤ -1.3, suggesting that the strength of the solar wind termination shock at the helioequatorial plane is relatively weak, with s ≤ 2.8. The rigidity dependence of the perpendicular interplanetary mean free path in the outer heliosphere for particles with rigidities between ∼ 0.2 and 0.7 GV varies approximately as R2, where R is particle rigidity. There is evidence that ACR oxygen is primarily multiply charged above ∼ 20 MeV/nuc and primarily singly-charged below ∼ 16 MeV/nuc. The location of the termination shock was at ∼ 65 AU in 1987 and ∼ 85 AU in 1994.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bieber, J. W., Burger, R. A., and Matthaeus, W. H.: 1995, 'The diffusion tensor throughout the heliosphere', Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Ray 24th 4, 694.
Christian, E. R., Cummings, A. C., and Stone, E. C.: 1988, 'Evidence for anomalous cosmic ray hydrogen', Astrophys. J. Lett. 334, L77.
Christian, E. R., Cummings, A. C., and Stone, E. C.: 1995, 'Observations of anomalous cosmic ray hydrogen from the Voyager spacecraft', Astrophys. J. Lett. 446, L105.
Cummings, A. C., and Stone, E. C.: 1988, 'Composition, gradients, and temporal variations of the anomalous cosmic-ray component', Proc. Sixth Internat. Solar Wind Conference (Boulder, CO), Pizzo, V. J., Holzer, T. E., and Sime, D. G., eds., NCAR Technical Note 306 2, 599.
Cummings, A. C., and Stone, E. C.: 1990, 'Elemental composition of the very local interstellar medium as deduced from observations of anomalous cosmic rays', Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Ray 21st 6, 202.
Cummings, A. C., and Stone, E. C.: 1996, 'Composition of anomalous cosmic rays and implications for the heliosphere', Space Sci. Rev. 78, 117.
Cummings, A. C., Stone, E. C., and Webber, W. R.: 1984, 'Evidence that the anomalous cosmic-ray component is singly ionized', Astrophys. J. Lett. 287, L99.
Cummings, A. C., Stone, E. C., and Webber, W. R.: 1987, 'Latitudinal and radial gradients of anomalous and galactic cosmic rays in the outer heliosphere', Geophys. Res. Lett. 14, 174.
Cummings, A. C., Stone E. C., and Webber W. R.: 1993, 'Estimate of the distance to the solar wind termination shock from gradients of anomalous cosmic ray oxygen', J. Geophys. Res. 98, 15,165.
Cummings, A. C., Stone E. C., and Webber W. R.: 1994, 'Distance to the solar wind termination shock and the source flux of anomalous cosmic rays during 1986-1988', J. Geophys. Res. 99, 11,547.
Cummings, A. C., Mewaldt, R. A., Blake, J. B., Cummings, J. R., Fränz, M., Hovestadt, D., Klecker, B., Mason, G. M., Mazur, J. E., Stone, E. C., von Rosenvinge, T. T., and Webber, W. R.: 1995a, 'Anomalous cosmic ray oxygen gradients throughout the heliosphere', Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 341.
Cummings, A. C., Blake, J. B., Cummings, J. R., Fränz, M., Hovestadt, D., Klecker, B., Mason, G. M., Mazur, J. E., Mewaldt, R. A., Stone, E. C., and Webber, W. R.: 1995b, 'Radial and latitudinal gradients of anomalous cosmic ray oxygen throughout the heliosphere', Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Ray 24th 4, 800.
Fisk, L. A.: 1971, 'Solar modulation of galactic cosmic rays, 2.', J. Geophys. Res. 76, 221.
Fisk, L., Kozlovsky, B., and Ramaty, R.: 1974, 'An interpretation of the observed oxygen and nitrogen enhancements in low-energy cosmic rays', Astrophys. J. Lett. 190, L35.
Garcia-Munoz, M., Mason, G. M., and Simpson, J. A.: 1973, 'A new test for solar modulation theory: The 1972 May-July low-energy galactic cosmic ray proton and helium spectra', Astrophys. J. Lett. 182, L81.
Geiss, J., Gloeckler, G., Mall, U., von Steiger, R., Galvin, A. B., and Ogilvie, K. W.: 1994, 'Interstellar oxygen, nitrogen, and neon in the heliosphere', Astron. Astrophys. 282, 924.
Gloeckler, G.: 1996, 'The abundance of 1 H, 4 H, and 3 He in the local interstellar cloud from pickup ion observations with SWICS on Ulysses', Space Sci. Rev. 78, 335.
Hovestadt, D., Vollmer, O., Gloeckler, G., and Fan, C. Y.: 1973, 'Differential energy spectra of low-energy (<8.5 MeV per nucleon) heavy cosmic rays during solar quiet times', Phys. Rev. Lett. 31, 650.
Jokipii, J. R.: 1990, 'The anomalous component of cosmic rays', in Physics of the Outer Heliosphere, eds. S. Grzedzielski and D. E. Page (Oxford: Pergamon), 169.
Jokipii, J. R: 1996, 'Theory of multiply-charged anomalous cosmic rays', Astrophys. J. Lett. 466, L47.
Jokipii, J. R., Kóta, J., and Merényi, E.: 1993, 'The gradient of galactic cosmic rays at the solar-wind termination shock', Astrophys. J. 405, 782.
Klecker, B., McNab, M. C., Blake, J. B., Hamilton, D. C., Hovestadt, D., Kästle, H., Looper, M. D., Mason, G. M., Mazur, J. E., and Scholer, M.: 1995, 'Charge state of anomalous cosmic-ray nitrogen, oxygen, and neon: SAMPEX observations', Astrophys. J. Lett. 442, L69.
Levy, E. H.: 1978, 'Origin of the solar-magnetic-cycle dependent semiannual variation in galactic cosmic-ray flux', J. Geophys. Res. 5, 969.
McDonald, F. B., Teegarden, B. J., Trainor, J. H., and Webber, W. R.: 1974, 'The anomalous abundance of cosmic-ray nitrogen and oxygen nuclei at low energies', Astrophys. J. Lett. 187, L105.
McDonald, F.B., Lukasiak, A., and Webber, W.R.: 1995, 'Pioneer 10 and Voyager 1 observations of anomalous cosmic ray hydrogen in the outer heliosphere', Astrophys. J. Lett. 446, L101.
McKibben, R. B., Connell, J. J., Lopate, C., Simpson, J. A., and Zhang, M.: 1995, 'Cosmic ray modulation in the 3-D heliosphere', Space Sci. Rev. 72, 367.
Mewaldt, R. A., Selesnick, R. S., Cummings, J. R., and Stone, E. C.: 1996, 'Evidence for multiply charged anomalous cosmic rays', Astrophys. J. Lett. 466, L43.
Möbius, E.: 1996, 'The local interstellar medium viewed through pickup ions, recent results and future perspectives', Space Sci. Rev. 78, 375.
Pesses, M. E., Jokipii, J. R., and Eichler, D.: 1981, 'Cosmic ray drift, shock wave acceleration, and the anomalous component of cosmic rays', Astrophys. J. Lett. 246, L85.
Potgieter, M. S., and Le Roux, J. A.: 1994, 'The long-term heliospheric modulation of galactic cosmic rays according to a time-dependent drift model with merged interaction regions', Astrophys. J. 423, 817.
Potgieter, M. S., and Moraal, H.: 1985, 'A drift model for the modulation of galactic cosmic rays', Astrophys. J. 294, 425.
Potgieter, M. S., and Moraal H.: 1988, 'Acceleration of cosmic rays in the solar wind termination shock, I. A steady state technique in a spherically symmetric model', Astrophys. J. 330, 445.
Richardson, J. D., Belcher, J. W., Lazarus, A. J., Paulerena, K. I., Gazis, P. R., and Barnes, A.: 1996, 'Plasmas in the outer heliosphere', Proc. Eighth Internat. Solar Wind Conference (Dana Point, CA), Winterhalter, D., Gosling, J. T., Habbal, S. R., Kurth, W. S., Neugebauer, M., eds., AIP Conference Proceedings 382, 586.
Simpson, J. A., Connell, J. J., Lopate, C., McKibben, R. B., and Zhang, M.: 1995, 'The latitude gradients of galactic cosmic rays and anomalous helium fluxes measured on Ulysses from the Sun's south polar region to the equator', Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 3337.
Stone, E. C., Cummings, A. C., and Webber, W. R.: 1995, 'Radial and latitudinal gradients of anomalous cosmic rays in the outer heliosphere', Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Ray 24th 4, 796.
Stone, E. C., Cummings, A. C., and Webber, W. R.: 1996, 'The distance to the solar wind termination shock in 1993 and 1994 from observations of anomalous cosmic rays', J. Geophys. Res. 101, 11,017.
Trattner, K. J., Marsden, R. G., Sanderson, T. T., Wenzel, K.-P., Klecker, B., and Hovestadt, D.: 1995, 'The anomalous component of cosmic rays: oxygen latitudinal gradient', Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 337.
Whang, Y. C., and Burlaga, L. F.: 1993, 'Termination shock: solar cycle variations of location and speed', J. Geophys. Res. 98, 15,221.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cummings, A.C., Stone, E.C. Anomalous Cosmic Rays and Solar Modulation. Space Science Reviews 83, 51–62 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005057010311
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005057010311