Abstract
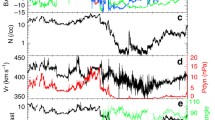
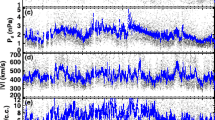
We examine the magnetic field in the martian magnetosheath due to solar wind draping. Mars Global Surveyor provided 3-D vector magnetic field measurements at a large range of altitudes, local times, and solar zenith angles as the spacecraft orbit evolved. We choose orbits with very clean signatures of draping to establish the nominal morphology of the magnetic field lines at local times of near-subsolar and near-terminator. Next, using a compilation of data from Mars Global Surveyor, we determine the average magnetic field morphology in the martian magnetosheath due to the solar wind interaction. The topology of the field is as expected from previous observations and predictions. The magnetic field magnitude peaks at low altitude and noon magnetic local time and decreases away from that point. The magnetic field has an inclination from the local horizontal of 5.6° on average in the dayside magnetosheath and 12.5° on the nightside. The inclination angle is closest to zero at noon magnetic local time and low altitude. It increases both upward and to later local times. The magnetic field in the induced magnetotail flares out from the Mars—Sun direction by 21°. Finally, we compare the observations to gasdynamic model predictions and find that the shocked solar wind flow in the martian magnetosheath can be treated as a gasdynamic flow with the magnetic pileup boundary as the inner boundary to the flow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña, M. H., Connerney, J. E. P., Wasilewski, P. et al.: 1998, ‘Magnetic Field and Plasma Observations at Mars: Initial Results of the Mars Global Surveyor Mission’, Science 279(5357), 1676–1680.
Albee, A. L., Arvidson, R. E., Pallucioni, F. and Thorpe, T.: 2001, ‘Overview of the Mars Global Surveyor Mission’, J. Geophys. Res. 106(E10), 23291–23316.
Alfvén, H.: 1957, ‘On the Theory of Comet Tails’, Tellus 9, 92–96.
Bertucci, C., Mazelle, C., Crider, D.H. et al.: 2003, ‘Magnetic Field Draping Enhancement at the Martian Magnetic Pileup Boundary from Mars Global Surveyor Observations’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 30(2), 1099, 10.1029/2002GL015713.
Brain, D. A., Bagenal, F., Crider, D. H., Acuña, M. H. and Connerney, J. E.: 2001, Martian Magnetic Topology: Evaluation of Crustal Magnetization and Solar Wind Interaction Models Using MGS MAG Data, American Geophysical Union Spring Meeting.
Brain, D. A., Bagenal, F., Acuña, M. H. and Connerney, J. E. P.: 2003, ‘Martian Magnetic Morphology: Contributions from the Solar Wind and Crust’, J. Geophys. Res. 108(A12), 1424, 10.1029/2002JA009482.
Brecht, S. H.: 1997, ‘Hybrid Simulations of the Magnetic Topology of Mars’, J. Geophys Res. 102(A3), 4743–4750.
Burlaga, L. F. and King, J. H.: 1979, ‘Intense Inter-Planetary Magnetic-Fields Observed by Geocentric Spacecraft During 1963–1975’, J. Geophys. Res. 84(NA11), 6633–6640.
Cloutier, P.A., Law, C. C., Crider, D. H. et al.: 1999, ‘Venus-Like Interaction of the Solar Wind with Mars’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 26(17), 2685–2688.
Connerney, J. E. P., Acuña, M. H., Wasilewski, P. J. et al.: 2001, ‘The Global Magnetic Field of Mars and Implications for Crustal Evolution’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 28(21), 4015–4018.
Crider, D. H., Acuña, M. H., Connerney, J. E. P. et al.: 2001, ‘Magnetic Field Draping around Mars: Mars Global Surveyor Results’, Adv. Space Res. 27(11), 1831–1836.
Crider, D. H., Acuña, M. H., Connerney, J. E. P. et al.: 2002, ‘Observations of the Latitude Dependence of the Location of the Martian Magnetic Pileup Boundary’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29(8), 10.1029/2001 GLO13860.
Dolginov, S. S., Yeroskenko, Y. G., Zhuzgov, L. N.: 1973, ‘The Magnetic Field in the Very Close Neighborhood of Mars According to Data from the Mars-2 and 3 Spacecraft’, J. Geophys. Res. 78(22), 4779–4786.
Dolginov, S. S.: 1978, ‘On the Magnetic-Field of Mars - Mars-5 Evidence’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 5(1), 93–95.
Dubinin, E., Sauer, K., Lundin, R. et al.: 1996, ‘Plasma Characteristics of the Boundary Layer in the Martian Magnetosphere’, J. Geophys. Res. 101(A12), 27061–27075.
Kallio, E. J. and Koskinen, H. E. J.: 2000, ‘A Semiempirical Magnetosheath Model to Analyze the Solar Wind-Magnetosphere Interaction’, J. Geophys. Res. 105(A12), 27469–27479.
Krymskii, A. M., Breus, T. K., Ness, N. F. et al.: 2002, ‘Structure of the Magnetic Field Fluxes Connected with Crustal Magnetization and Top-Side Ionosphere at Mars’, J. Geophys. Res. 107(A9), 1245, doi: 10.1029/2001 JA000239.
Liu, Y., Nagy, A. F., Gombosi, T. I., DeZeeuw, D. L. and Powell, K. G.: 2001, ‘The Solar Wind Interaction with Mars: Results of Three-Dimensional Three-Species MHD Studies’, Adv. Space Res. 27(11), 1837–1846.
Luhmann, J. G., Russell, C. T., Schwingenschuh, K. and Yeroshenko, Ye.: 1991, ‘A comparison of Induced Manetotails of Planetary Bodies: Venus, Mars, and Titan’, J. Geophys. Res. 96(A7), 11199–11208.
Marubashi, K., Grebowsky, J. M., Taylor, H. A. et al.: 1985, ‘Magnetic Field in the Wake of Venus and the Formation of Ionospheric Holes’, J. Geophys. Res. 90(NA2), 1385–1398.
Mazelle, C., Bertucci, C., Rème, H. et al.: 2002, ‘The Magnetic Pileup Boundary at Mars: a Comet-Like Feature in the Interaction of the Planet Atmosphere with the Solar Wind’ (in press).
McComas, D. J., Spence, H. E., Russell, C. T. et al.: 1986, ‘The Average Magnetic-field Draping and Consistent Plasma Properties of the Venus Magnetotail’, J. Geophys. Res. 91(A7), 7939–7953.
Mitchell, D. L., Lin, R. P., Mazelle, C. et al.: 2001, ‘Probing Mars' Crustal Magnetic Field and Ionosphere with the MGS Electron Reflectometer’, J. Geophys. Res. 106(E10), 23418–23427.
Ness, N. F., Hundhaus, A. J. and Bame, S. J.: 1971, ‘Observations of Interplanetary Medium - VELA 3 and IMP 3, 1965–1967’, J. Geophys. Res. 76(28), 6643.
Rosenbauer, H., Verigin, M., Kotova, G., Livi, S. et al.: 1994, ‘On the Correlation of the Magnetic Field in the Martian Magnetotail to the Solar Wind Parameters’, J. Geophys. Res. 99(A9), 17199–17204.
Russell, C. T., Luhmann, J. G., Spreiter, J. R. and Stahara, S. S.: 1984, ‘The Magnetic Field of Mars—Implications from Gas-Dynamic Modeling’, J. Geophys. Res. 89(NA5), 2997–3003.
Slavin, J. A., Holzer, R. E., Spreiter, J. R., Stahara, S. S. and Chausee, D. S.: 1983, ‘Solar-Wind Flow About the Terrestrial Planets 2. Comparison with Gas-Dynamic Theory and Implications Flor Solar-Planetary Interactions’, J. Geophys. Res. 88(NA1), 19–35.
Spreiter, J. R. and Stahara, S. S.: 1980, ‘A New Predictive Model for Determining Solar Wind-Terrestrial Planet Interactions’, J. Geophys. Res. 85(NA12), 6769–6777.
Spreiter, J.R. and Stahara, S. S.: 1992, in J. G. Luhmann, M. Tatrallyay and R. O. Pepin (eds), ‘Computer Modeling of the Solar Wind Interaction with Venus and Mars’, Venus and Mars: Atmospheres, Ionospheres, and Solar Wind Interactions, Geophysical Monograph 66, 345.
Tanaka, T.: 1993, ‘Configurations of the Soar-Wind Flow and Magnetic-Field Around the Planets with no Magnetic-Field - Calculation by a New MHD Simulation Scheme’, J. Geophys. Res. 98(A10), 17251–17262.
Verigin, M. I., Gringauz, K. I., Kotova, G. A. et al.: 1993, ‘The Dependence of the Martian Magnetopause Shape and Bow Shock on Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure According to Phobos 2 TAUS Ion Spectrometer Measurements’, J. Geophys. Res. 98(A2), 1303–1309.
Vignes, D., Mazelle, C., Rème, H. et al.: 2000, ‘The Solar Wind Interaction with Mars: Locations and Shapes of the Bow Shock and the Magnetic Pile-up Boundary from the Observations of the MAG/ER Experiment Onboard Mars Global Surveyor’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27(1), 49–52.
Vignes, D., Acuña, M. H., Connerney, J. E. P., Crider, D. H., Rème, H. and Mazelle, C.: 2004, ‘Magnetic Flux Ropes in the Martian Ionosphere: Global Characteristics’, Space Sci. Rev. 111(1–2).
Zhang, T. L., Luhmann, J. G. and Russell, C. T.: 1991, ‘The Magnetic Barrier at Venus’, J. Geophys. Res. 96(A7), 11145–11153.
Zhang, T. L., Schwingenschuh, K., Russell, C. T. et al.: 1994, ‘The Flaring of the Martian Magnetotail Observed by the Phobos-2 Spacecraft’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 21(12), 1121–1124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crider, D.H., Brain, D.A., Acuña, M.H. et al. Mars Global Surveyor Observations of Solar Wind Magnetic Field Draping Around Mars. Space Science Reviews 111, 203–221 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SPAC.0000032714.66124.4e
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SPAC.0000032714.66124.4e