Abstract
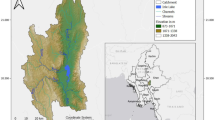
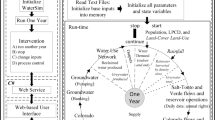
Studies of future management and policy options based on different assumptions provide a mechanism to examine possible outcomes and especially their likely benefits and consequences. The San Pedro River in Arizona and Sonora, Mexico is an area that has undergone rapid changes in land use and cover, and subsequently is facing keen environmental crises related to water resources. It is the location of a number of studies that have dealt with change analysis, watershed condition, and most recently, alternative futures analysis. The previous work has dealt primarily with resources of habitat, visual quality, and groundwater related to urban development patterns and preferences. In the present study, previously defined future scenarios, in the form of land-use/land-cover grids, were examined relative to their impact on surface-water conditions (e.g., surface runoff and sediment yield). These hydrological outputs were estimated for the baseline year of 2000 and predicted twenty years in the future as a demonstration of how new geographic information system-based hydrologic modeling tools can be used to evaluate the spatial impacts of urban growth patterns on surface-water hydrology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, J.G., Williams, J.R., Srinivasan, R., King, K.W. and Griggs, R.H.: 1994, 'SWAT: Soil Water Assessment Tool', U. S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Grassland, Soil and Water Research Laboratory, Temple, TX, USA.
CEC: 1998, 'Advisory Panel Report on the Upper San Pedro River Initiative: Recommendations and Findings presented to the Commission for Environmental Cooperation', Commission for Environmental Cooperation, Montreal, Canada.
Ebert, D.W. and Wade, T.G.: 2000, Analytical tools interface for landscape assessments (ATtILA) User Guide Version 2.0, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Las Vegas, NV, USA.
ESRI: 2001, ArcView Version 3.2a Software and User Manual, Environmental Systems Research Institute, Redlands, CA, USA.
Hernandez, M., Kepner, W.G., Semmans, D.J., Ebert, D.W., Goodrich, D.C. and Miller S.N.: 2003, 'Integrating a Landscape/Hydrologic Analysis for Watershed Assessment,' in K.G. Renard, S.A. McElroy, W.J. Gburek, E.H.Canfield and R.L. Scott (eds.), Proceedings of the First Interagency Conference on Research in the Watersheds Agricultural Research Service, Benson, AZ, USA, pp. 461-466.
Houghton, R.A., Hobbie, J.E., Melillo, J.M., Moore, B., Peterson, G.J., Shaver, G.R. and Woodwell, G.M.: 1983, 'Changes in the carbon content of terrestrial biota and soil between 1860 and 1980: a net release of CO2 to the atmosphere', Ecol. Monogr. 53, 235-262.
Kepner, W.G., Semmens, D.J., Heggem, D.T., Evanson, E.J., Edmonds, C.M., Scott, S.N. and Ebert, D.W.: 2003, The San Pedro River Geo-Data Browser and Assessment Tools. CD-ROM (EPA/600/C-03/008 and ARS/152432) U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Las Vegas, NV, USA; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Tucson, AZ, USA.
Kepner, W.G., Watts, C.J., Edmonds, C.M., Maingi, J.K., Marsh, S.E. and Luna, G.: 2000, 'A landscape approach for detecting and evaluating change in a semi-arid environment', Environ. Monit. Assess. 64, 179-195.
Kepner, W.G., Edmonds, C.M. and Watts, C.J.: 2002, 'Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems for Decision Analysis in Public Resource Administration: A Case Study of 25 Years of Landscape Change in a Southwestern Watershed', EPA/600/R-12/039, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Las Vegas, NV, USA, p. 23.
Lahlou, M., Shoemaker, L., Choudry, S., Elmer, R., Hu, A., Manguerra, H. and Parker, A.: 1998, 'Better assessment science integrating point and nonpoint sources: BASINS 2.0 User's Manual', EPA-823-B-98-006 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Washington, DC, USA.
Miller, S.N., Semmens, D.J., Miller, R.C., Hernandez, M., Goodrich, D.C., Miller, W.P., Kepner, W.G. and Ebert, D.: 2002, 'GIS-based Hydrologic Modeling: The Automated Geospatial Watershed Assessment Tool', Proceedings of the 2nd Federal Interagency Hydrologic Modeling Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, p. 12.
McDonnell, M.J. and Pickett, S.T.A. (eds.): 1993, Humans as Components of Ecosystems, Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, USA.
Schwartz, P.: 1996, The art of the long view: paths to strategic insight for yourself and your company, Currency Doubleday, New York, NY, USA, p. 272.
Smith, R.E., Goodrich, D.C., Woolhiser, D.A. and Unkrich, C.L.: 1995, 'KINEROS-A kinematic runoff and erosion model', in V.P. Singh (ed.), Computer Models of Watershed Hydrology, Water Resources Publications, Highlands Ranch, CO, USA, p. 1130.
Steinitz, C.: 1990, 'A framework for the theory applicable to the education of landscape architects (and other environmental design professionals)', Landscape Journal. 9 (2), 136-143.
Steinitz, C.: 1993, 'A framework for theory and practice in landscape planning', GIS Europe. July (1993), 42-45.
Steinitz, C., Binford, M., Cote, P., Edwards, T. Jr., Ervin, S., Forman, R.T.T., Johnson, C., Kiester, R., Mouat, D., Olson, D., Shearer, A., Toth, R. and Wills, R.: 1996, 'Biodiversity and Landscape Planning: Alternative Futures for the Region of Camp Pendleton California', Graduate School of Design, Harvard University for the Biodiversity Research Consortium, Cambridge, MA, USA, p. 142.
Steinitz, C., Anderson, R., Arias, H., Bassett, S., Cablk, M., Flaxman, M., Goode, T., Lozar, R., Maddock, T., Mouat, D., Rose, W., Peiser, R. and Shearer, A.: 2000, 'Summary Report: Alternative Futures for the Upper San Pedro River Basin Arizona, U.S.A. and Sonora, Mexico', Harvard University, Graduate School of Design, Cambridge, MA, USA, p. 19.
Steinitz, C., Arias, H., Bassett, S., Flaxman, M., Goode, T., Maddock T. III, Mouat, D., Peiser, R. and Shearer, A.: 2003, Alternative Futures for Changing Landscapes. The Upper San Pedro River Basin in Arizona and Sonora, Island Press, Washington, DC, USA.
Tellman, B., Yarde, R. and Wallace, M.G.: 1997, 'Arizona's Changing Rivers: How People Have Affected the Rivers', Water Resources Research Center Issue Paper 19, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA.
Turner, B.L. (ed.): 1990, The Earth as Transformed by Human Action, Cambridge University Press with Clark University, Cambridge, MA, USA.
USEPA: 2000, 'Environmental Planning for Communities. A Guide to the Environmental Visioning Process Utilizing a Geographic Information System (GIS)', EPA/625/R-98/003, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Cincinnati, OH, USA, p. 49.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kepner, W.G., Semmens, D.J., Bassett, S.D. et al. Scenario Analysis for the San Pedro River, Analyzing Hydrological Consequences of a Future Environment. Environ Monit Assess 94, 115–127 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EMAS.0000016883.10110.15
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EMAS.0000016883.10110.15