Abstract
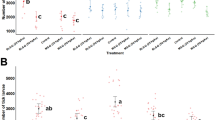
Our objective in this trial was to investigate the anti-tick effects of molasses grass (Melinis minutiflora) and gamba grass (Andropogon gayanus) against Boophilus microplus, using buffel grass (Cenchrus ciliaris) as a control. During a 3-year-period fieldwork was carried out in the tropical, subhumid climate at Progreso, Municipality of Jiutepec, Morelos, Mexico. Experimental plots were established for three treatments with six replicates under a random factorial design in order to evaluate each of the four seasons. Additional work was developed for two more consecutive autumn seasons to evaluate the anti-tick effects of these grasses. Once the plots were established they were infested with 5000 B. microplus larvae and sampled by dragging flannel cloths. The anti-tick effects were measured by counting the number of larvae recovered from each of the experimental plots. Both grasses, M. minutiflora and A. gayanus, demonstrated anti-tick effects; however, M. minutiflora grass had the greatest anti-tick effects through the seasons studied and in the three consecutive autumns evaluated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelson H.P. 1994. Chemical ecology. Science 264: 487.
Aycardi E., Benavides E., Garcia O., Mateus G., Henao F. and Zuluaga F. 1984. Boophilus microplus tick burdens on grazing cattle in Colombia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 16: 78–84.
Barnard D.R. 1986. Density perturbation in populations of Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) in beef cattle forage areas in response to two regimens of vegetation management. J. Econ. Entomol. 79: 122–127.
Brizuela C.M., Ortellano C.A., Sanchez T.I. and Walker A.R. 1996. Formulation of an integrated control of Boophilus microplus in Paraguay. Vet. Parasitol. 63: 95–108.
Cochran G.W. and Cox M.G. 1981. Diseños Experimentales. Ed. Trillas, Mexico.
Cruz-Vazquez C. and Fernández R.M. 2000. Anti-tick repellent effect of Andropogon gayanus grass on plots of different ages experimentally infested with Boophilus microplus larvae. Parasitol. Día 24: 88–91.
Cruz-Vazquez C., Fernández R.M., Solano V.J. and García V.Z. 1999. Anti-tick effect observed in mature plants of tropical legumes Stylosanthes humilis and Stylosanthes hamata. Parasitol. Día 23: 15–18.
Davey B.R., Garza J. and Thompson D.G. 1982. Seasonal observations on the development and ovipositional capability of B. annulatus and B. microplus reared on bovines. J. Med. Entomol. 19: 24–28.
De Castro J.J., James A.D., Minjauw B., Di Giulio G.U., Permin A., Pegram R.G., Chizyuka and Sinyangwe P. 1997. Long-term studies on the economic impact of ticks on Sanga cattle in Zambia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 21: 3–19.
Fernández R.M. 1996. Comparación de colecta de cuatro técnicas de colecta de larvas de Boophilus microplus bajo condiciones de campo en infestación controlada. Tec. Pecu. Mex. 34: 175–180.
Fernández R.M., Cruz-Vazquez C., Solano V.J. and García V.Z. 1999a. Anti-tick effects of Stylosanthes humilis and Stylosanthes hamata on plots experimentally infested with Boophilus microplus larvae in Morelos, Mexico. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 23: 171–175.
Fernández R.M., Cruz-Vazquez C., García-Vazquez Z. and Saltijeral O.J. 1999b. Estudio de seguimiento del efecto anti-garrapata de las leguminosas tropicales Stylosanthes humilis (L.) y Stylosanthes hamata (L.) de un año de edad. Tec. Pecu. Mex. 37: 51–56.
Frish E.J. 1999. Towards a permanent solution for controlling cattle ticks. Int. J. Parasitol. 29: 57–71.
George E.J. 1990. Summing-up of strategies for the control of ticks in regions of the world other than Africa. Parassitologia 32: 203–209.
Harborne B.J. 1987. Chemical signals in the ecosystem. Annal. Botan. 60(Suppl 4): 39–57.
Humpreys L.R. 1980. A Guide to Better Pastures for the Tropics and Subtropics. Wright Stephenson Co., Australia.
Jonsson N.N., Mayer D.G., Matschoss A.L., Green P.E. and Ansell J. 1998. Production effects of cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) infestation of high yielding dairy cows. Vet. Parasitol. 78: 65–77.
Kaaya G.P. 1992. Status and recent advances in tick management. Insect Sci. Appl. 13: 587–594.
Kaposhi C.K.M. 1992. The role of natural products in integrated tick management in Africa. Insect Sci. Appl. 13: 595–598.
Mwangi N.E., Essuman S., Kaaya P.G., Nyandat E., Munyinyi D. and Kimondo G.M. 1995. Repellence of the tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus by the grass Melinis minutiflora. Trop. Anim. Health. Prod. 27: 211–216.
Pegram G.R., Tatchell J.R., De Castro J.J., Chyzyuka B.G. and McCosker J.P. 1993. Tick control new concepts. Rev. Mund. Zoot. 74, 75: 1–11.
Solis S.S. 1986. Ecología de garrapatas en México. En: Memorias del Seminario Internacional de Parasitología Animal-AMPAVE, Cuernavaca, Mor. Mexico, 257 p.
Sutherst R.W., Jones J. and Schnitzerling H.J. 1982. Tropical legumes of the genus Stylosanthes immobilize and kill cattle ticks. Nature 295: 320–321.
Thadeu A.M., Barros De A. and Evans E.D. 1989. Acao de gramineas forrageiras em larvas infestantes do carrapato dos bovidos Boophilus microplus. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 9: 17–21.
Thompson K.C., Roa J.E. and Romero T.N. 1978. Anti-tick grasses as the basis for developing practical tropical tick control pastures. Trop. Anim. Health. Prod. 10: 179–182.
Wilkinson P.R. 1957. The spelling of pastures in cattle tick control. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 8: 414–423.
Zimmerman H.R. and Garris I.G. 1985. Sampling efficiency of three dragging techniques for the collection of nonparasitic Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) larvae in Puerto Rico. J. Econ. Entomol. 78: 627–631.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Ruvalcaba, M., Preciado-De-La Torre, F., Cruz-Vazquez, C. et al. Anti-tick effects of Melinis minutiflora and Andropogon gayanus grasses on plots experimentally infested with Boophilus microplus larvae. Exp Appl Acarol 32, 293–299 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPA.0000023233.63268.cc
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPA.0000023233.63268.cc