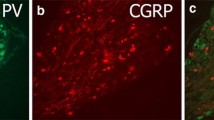
Abstract
Chronic constriction injury (CCI) and partial ligation (PSNL) of the sciatic nerve induce a similar neuropathic pain syndrome in rats. We examined calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), substance P (SP) and protein gene product (PGP) 9.5 immunoreactive (IR) axons in the footpad skin after the two types of injury. Four and 14 days after CCI, CGRP- and SP-IR axons in the ipsilateral footpad skin disappeared in most rats, but in one third, sparse CGRP- and SP-IR fibers remained. PGP-IR axons dramatically decreased, but some thick fiber fascicles appeared. At the ultrastructural level, these PGP-IR thick fiber fascicles were characterized as unmyelinated axons surrounded by non-IR Schwann cells. Some of these axons were swollen and irregular in shape. In contrast, 4 days after PSNL, CGRP-, SP-, and PGP-IR axons in the ipsilateral footpad skin were present, though significantly reduced in density, in all rats, and by 14 days all IR fiber densities in the footpad skin partially recovered. The loss of CGRP and SP axons in the footpad skin of the CCI model suggests that sensory nerves containing neuropeptides are not essential in transducing stimuli applied to the footpad skin into neuropathic pain, but the abnormal PGP-IR unmyelinated axons in thick fiber fascicles might play a role. The partial loss and rapid recovery of IR axons in the footpad skin after PSNL shows that the two injury models, causing similar behaviors, are associated with very different patterns of cutaneous innervation at the time when the pain syndrome is well developed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ALVAREZ, F. J., CERVANTES, C., BLASCO, I., VILLALBA, R., MARTINEZ-MURILLO, R., POLAK, J. M. & RODRIGO, J. (1988a) Presence of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P (SP) immunoreactivity in intraepidermal free nerve endings of cat skin. Brain Research 442, 391–395.
ALVAREZ, F. J., CERVANTES, C., VILLALBA, R., BLASCO, I., MARTINEZ-MURILLO, R., POLAK, J. M. & RODRIGO, J. (1988b) Immunocytochemical analysis of calcitonin gene-related peptide and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in Merkel cells and cutaneous free nerve endings of cats. Cell and Tissue Research 254, 429–437.
ATTAL, N., JAZAT, F., KAYSER, V. & GUILBAUD, G. (1990) Further evidence for 'pain-related' behaviours in a model of unilateral peripheral mononeuropathy. Pain 41, 235–251.
BASBAUM, A. I., GAUTRON, M., JAZAT, F., MAYES, M. & GUILBAUD, G. (1991) The spectrum of fiber loss in a model of neuropathic pain in the rat—an electron microscopic study. Pain 47, 359–367.
BENNETT, G. J. & XIE, Y. K. (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33, 87–107.
CAMERON, A. A., CLIFFER, K. D., DOUGHERTY, P. M., WILLIS, W. D. & CARLTON, S. M. (1991) Changes in lectin, GAP-43 and neuropeptide staining in the rat superficial dorsal horn following experimental peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience Letters 131, 249–252.
CARLTON, S. M., DOUGHERTY, P. M., POVER, C. M. & COGGESHALL, R. E. (1991) Neuroma formation and numbers of axons in a rat model of experimental peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience Letters 131, 88–92.
CUELLO, A. C., DEL FIACCO, M. & PAXINOS, G. (1978) The central and peripheral ends of the substance P-containing sensory neurons in the rat trigeminal system. Brain Research 152, 499–509.
DEVOR, M., SCHONFELD, D., SELTZER, Z. & WALL, P. D. (1979) Two modes of cutaneous reinnervation following peripheral nerve injury. Journal of Comparative Neurology 185, 211–220.
DIAMOND, J. & FOERSTER, A. (1992) Recovery of sensory function in skin deprived of its innervation by lesion of the peripheral nerve. Experimental Neurology 115, 100–103.
DIAMOND, J., HOLMES, M. & COUGHLIN, M. (1992) Endogenous NGF and nerve impulses regulate the collateral sprouting of sensory axons in the skin of the adult rat. Journal of Neuroscience 12, 1454–1466.
FAWCETT, D. W. (1986) Skin. In A Textbook of Histology (edited by FAWCETT, D. W.) pp. 543–558. Toronto: W. B. Saunders Company.
GAUWEILER, B., WEIHE, E., HARTSCHUH, W. & YANAIHARA, N. (1988) Presence and coexistence of chromogranin A and multiple neuropeptides in Merkel cells of mammalian oral mucosa. Neuroscience Letters 89, 121–126.
GUILBAUD, G., GAUTRON, M., JAZAT, F., RATINAHIRANA, H., HASSIG, R. & HAUW, J. J. (1993) Time-course of degeneration and regeneration of myelinated nerve-fibers following chronic loose ligatures of the rat sciatic-nerve—can nerve lesions be linked to the abnormal pain-related behaviors? Pain 53, 147–158.
HSIEH, S. T., CHOI, S., LIN, W. M., CHANG, Y. C., McARTHUR, J. C. & GRIFFIN, J. W. (1996) Epidermal denervation and its effects on keratinocytes and Langerhans cells. Journal of Neurocytolgy 25, 513–524.
ISHIDA-YAMAMOTO, A., SENBA, E. & TOHYAMA, M. (1989) Distribution and fine structure of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactive nerve fibers in the rat skin. Brain Research 491, 93–101.
KAJANDER, K. C. & XU, J. Y. (1995) Quantitative evaluation of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P levels in rat spinal cord following peripheral nerve injury. Neuroscience Letters 186, 184–188.
KINGERY, W. S., CASTELLOTE, J. M. & WANG, E. E. (1993) A loose ligature-induced mononeuropathy produces hyperalgesias mediated by both the injured sciatic nerve and the adjacent saphenous nerve. Pain 55, 297–304.
KINGERY, W. S., LU, J. D., ROFFERS, J. A. & KELL, D. R. (1994) The resolution of neuropathic hyperalgesia following motor and sensory functional recovery in sciatic axonotmetic mononeuropathies. Pain 58, 157–168.
KINGERY, W. S. & VALLIN, J. A. (1989) The development of chronic mechanical hyperalgesia, autotomy, and collateral sprouting following sciatic nerve section in rat. Pain 38, 321–332.
KINNMAN, E. & ALDSKOGIUS, H. (1986) Collateral sprouting of sensory axons in the glabrous skin of the hindpaw after chronic sciatic nerve lesion in adult and neonatal rats: A morphological study. Brain Research 377, 73–82.
KINNMAN, E., ALDSKOGIUS, H., JOHANSSON, O. & WIESENFELD-HALLIN, Z. (1992) Collateral reinnervation and expansive regenerative reinnervation by sensory axons into foreign denervated skin—an immunohistochemical study in the rat. Experimental Brain Research 91, 61–72.
LEE, Y., TAKAMI, K., KAWAY, Y., GIRGIS, S., HILLYARD, C. J., MACINTYRE, L., EMSON, P. C. & TOHYAMA, M. (1985) Distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat peripheral nervous system with reference to its coexistence with substance P. Neuroscience 16, 1227–1237.
LI, Y., HSIEH, S. T., CHIEN, H. F., ZHANG, X., McARTHUR, J. C. & GRIFFIN, J. W. (1997) Sensory and motor denervation influence epidermal thickness in rat foot glabrous skin. Experimental Neurology 147, 452–462.
LISNEY, S. J. & DEVOR, M. (1987) After discharge and interactions among fibers in damaged peripheral nerve in the rat. Brain Research 415, 122–136.
MA, W. & BISBY, M. A. (1998) Calcitonin gene related peptide, substance P and protein gene product 9.5 immunoreactive axons in the rat footpad skin following partial sciatic nerve injuries. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 24, 1391.
MEAROW, K. M., KRIL, Y. & DIAMOND, J. (1993) Increased NGF messenger RNA expression in denervated rat skin. NeuroReport 4, 351–354.
NAVARRO, X., VERDU, E., WENDELSCAFER-CRABB, G. & KENNEDY, W. R. (1995) Innervation of cutaneous structures in the mouse hind paw: A confocal microscopy immunohistochemical study. Journal of Neuroscience Research 41, 111–120.
NAVARRO, X., VERDU, E., WENDELSCHAFER-CRABB, G. & KENNEDY, W. R. (1997) Immunohistochemical study of skin reinnervation by regenerative axons. Journal of Comparative Neurology 380, 164–174.
NOGUCHI, K., KAWAI, Y., FUKUOKA, T., SENBA, E. & MIKI, K. (1995) Substance P induced by peripheral nerve injury in primary afferent sensory neurons and its effect on dorsal column nucleus neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 15, 7633–7643.
NUYTTEN, D., KUPERS, R., LAMMENS, M., DOM, R., VAN HEES, J. & GYBELS, J. (1992) Further evidence for myelinated as well as unmyelinated fiber damage in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Experimental Brain Research 91, 73–78.
RIBEIRO-DA-SILVA, A., PRIESTLEY, J. V. & CUELLO, A. C. (1993) Preembedding ultrastructural immunocytochemistry. In Immunocytochemistry II (edited by CUELLO, A. C.) pp. 181–227. Chichester: Wiley and Sons.
SELTZER, Z., DUBNER, R. & SHIR, Y. (1990) A novel behavioral model of neuropathic pain disorders produced in rats by partial sciatic nerve injury. Pain 43, 205–218.
SELTZER, Z., PARAN, Y., EISEN, A. & GINZBURG, R. (1991) Neuropathic pain behavior in rats depends on the afferent input from nerve-end neuroma including histamine-sensitive C-fiber. Neuroscience Letters 128, 203–206.
SHU, S., JU, G. & FAN, L. (1988) The glucose oxidase-DAB-nickel method in peroxidase histochemistry of the nervous system. Neuroscience Letters 85, 169–171.
STOLL, G., GRIFFIN, J. W., LI, C. Y. & TRAPP, B. D. (1989) Wallerian degeneration in the peripheral nervous system: Participation of both Schwann cells and macrophages in myelin degradation. Journal of Neurocytology 18, 671–683.
THOMPSON, R. J., DORAN, J. F., JACKSON, P., DHILLON, A. P. & RODE, J. (1983) PGP 9.5—a new marker for vertebrate neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Brain Research 278, 224–228.
WIESENFELD-HALLIN, Z., HOKFELT, T., LUNDBERG, J. M., FORSSMANN, W. G., REINECKE, M., TSCHOPP, F. A. & FISCHER, J. A. (1984) Immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P coexist in sensory neurons to the spinal cord and interact in spinal behavioral responses of the rat. Neuroscience Letters 52, 199–204.
WILKINSON, K. D., LEE, K., DESHPANDE, S., DUERKSENHUGHES, P., BOSS, J. M. & POHL, J. (1989) The neuron-specific protein PGP-9.5 is a ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase. Science 246, 670–673.
WILSON, P. O., BARBER, P. C., HAMID, Q. A., POWER, B. F., DHILLON, A. P., RODE, J., DAY, I. N., THOMPSON, R. J. & POLAK, J. M. (1988) The immunolocalization of protein gene product 9.5 using rabbit polyclonal and mouse monoclonal antibodies. British Journal of Experimental Pathology 69, 91–104.
WOOLF, C. J. & WIESENFELD-HALLIN, Z. (1986) Substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide synergistically modulate the gain of the nociceptive flexor withdrawal reflex in the rat. Neuroscience Letters 66, 226–230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W., Bisby, M.A. Calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P and protein gene product 9.5 immunoreactive axonal fibers in the rat footpad skin following partial sciatic nerve injuries. J Neurocytol 29, 249–262 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026519720352
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026519720352