Abstract
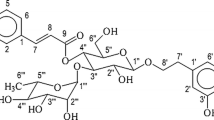
Liquid-cultivated compact callus aggregates (CCA) of Rhodiola sachalinensis were initiated from the explant of stems. Microscopic analysis showed that CCA displayed some level of cellular/tissue differentiation, which was perhaps responsible for the increased salidroside production. A higher ratio of cytokinin/auxin was found to be beneficial both for CCA growth and salidroside accumulation. Sucrose (> 100 g l-1) had a positive effect on salidroside synthesis, which was not due to an osmotic effect of the medium. The medium containing 40 g l-1 sucrose, 1.5 μM naphthaleneacetic acid and 15 μM 6-benzylaminopurine yielded ca. 120 mg l-1 salidroside after 24 days of culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellis DD, Zeldin EL, Brodhagen M, Russin WA & McCown BH (1996) Taxol production in nodule cultures of Taxus. J. Nat. Prod. 59: 246-250
Feder N & O'Brien TP (1968) Plant microtechnique: some principles and new methods. Am. J. Bot. 55: 123-142
Gertlowski C & Petersen M (1993) Influence of the carbon source on growth and rosmarinic acid production in suspension cultures of Coleus blumei. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 34: 183-190
Kurkin VA (1986) The chemical composition and pharmacological properties of Rhodiola plants. J. Pharm. Chem. 20(10): 1231-1235
Lindsey K & Yeoman MM (1983) The relationship between growth rate, differentiation and alkaloid accumulation in cell cultures. J. Exp. Bot. 34: 1055-1065
Mantell SH, Pearson DW, Hazell LP & Smith H (1983) The effect of initial phosphate and sucrose levels on nicotine accumulation in batch suspension cultures of Nicotiana tabacum L. 2: 73-77
McCown BH, Zeldin EL, Pinkalla HA & Dedolph RR (1988) Nodule culture: A developmental pathway and high potential for regeneration, automated micropropagation and plant metabolite production from woody plants. In: Hanover JW & Keathley DE (eds) Genetic Manipulation of Woody Plants (pp 149-166). Plenum Press, New York
Ming HQ, Xia GC & Zhang RD (1988) Advanced research on Rhodiola. Chin Traditional and Herbal Drugs. 19(5): 229-234
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473-497
Panda AK, Saroj M & Bisaria VS (1992) Alkaloid production by plant cell suspension culture of Holarrhena antidysenterica: I. Effect of Major Nutrients. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 39: 1043-1051
Saratikov AS (1968) Rhodioloside, a new glycoside from Rhodiola rosea and its pharmacological properties. Die Pharmazie. 69: 394-398
Selles M, Bergonon S, Viladomat F, Bastida J & Codina C (1997) Effect of sucrose on growth and galanthamine production in shoot-clump cultures of Narcissus confusus in liquid shake medium—shoot culture, for use in galanthamine production. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 49: 129-136
Tal B, Gressel J & Goldberg I (1982) The effect of medium constituents on growth and diosgenin production by Dioscorea deltoidea cells grown in batch culture. Planta Med. 44: 111-115
Tsoulpha P & Doran PM (1991) Solasodine production from self-immobilized Solanum aviculare cells. J. Biotechnol. 19: 99-100
Xu JF, Han AM & Feng PS (1996) Studies on kinetics and technique characteristics of Rhodiola sachalinensis A. Bor callus suspension culture. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 12(4): 460-465
Zenk MH, El-Shagi H & Ulbrich B(1977) Production of rosmarinic acid by cell suspension cultures of Coleus blumei. Naturwissenschaften. 64: 585-586
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J.F., Ying, P.Q., Han, A.M. et al. Enhanced salidroside production in liquid-cultivated compact callus aggregates of Rhodiola sachalinensis: manipulation of plant growth regulators and sucrose. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 55, 53–58 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026489515174
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026489515174