Abstract
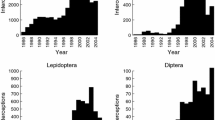
Since 1985, the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service has maintained the 'Port Information Network' (PIN) database for plant pests intercepted at the U.S. ports of entry. As of August 2001, PIN contained 6825 records of beetles (Coleoptera) in the family Scolytidae that had been intercepted during the years 1985–2000 from countries outside of North America. Of the 6825 scolytid interceptions, 2740 (40%) were identified to the species level, 2336 (34%) to only the genus level, and 1749 (26%) were identified to only the family level. Of the 49 identified scolytid genera, the 10 most common were Hypothenemus (821 interceptions), Pityogenes (662), Ips (544), Coccotrypes (520), Orthotomicus (461), Hylurgops (327), Hylurgus (266), Tomicus (194), Dryocoetes (166), and Hylastes (142). The 10 most common identified species were Pityogenes chalcographus (565 interceptions), Orthotomicus erosus (385), Hylurgops palliatus (295), Ips typographus (286), Hylurgus ligniperda (217), Ips sexdentatus (157), Tomicus piniperda (155), Hylastes ater (75), Hypothenemus hampei (62), and Polygraphus poligraphus (48). Of these 10 species, H. palliatus, H. ligniperda, and T. piniperda are known to be established in the continental U.S. The scolytids were intercepted from 117 different countries; the top 12 countries were Italy (1090 interceptions), Germany (756), Spain (457), Mexico (425), Jamaica (398), Belgium (352), France (261), China (255), Russia (247), India (224), U.K. (151), and Portugal (150). The scolytids were intercepted in 35 U.S. states and 97 port cities. In general, there was a positive relationship between the number of scolytid interceptions from individual countries and the value of the imports from those countries. Overall, 73% of the scolytids were found in solid wood packing materials, 22% in food or plants, and 5% in other or unspecified materials. The products most commonly associated with scolytid-infested wood packing materials were tiles, marble, machinery, steel, parts, ironware, granite, aluminum, slate, and iron. The food products and plants that were commonly infested with scolytids included nutmeg, palms, coffee beans, kola nuts, and macadamia nuts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, T.H. and Peck, S.B. (1994) Annotated checklist of the bark and ambrosia beetles (Coleoptera: Platypodidae and Scolytidae) of tropical southern Florida. Florida Entomologist 77, 313–29.
Atkinson, T.H., Rabaglia, R.J. and Bright, D.E. (1990) Newly detected exotic species of Xyleborus (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) with a revised key to species in eastern North America. Can. Entomologist 122, 93–104.
Atkinson, T.H., Rabaglia, R.J., Peck, S.B. and Foltz, J.L. (1991) New records of Scolytidae and Platypodidae from the U.S. and Bahamas. Coleopterists Bull. 45, 152–64.
Bain, J. (1977) Overseas wood-and bark-boring insects intercepted at New Zealand ports. New Zealand Forest Service Technical Paper No. 63.
Beeche-Cisternas, M.A. (2000) Riesgos cuarentenarios de insectos asociados a embalajes de madera y maderas de estiba de cargas de internacion en Chile. In Proc.: Int. Conf. on Quarantine Pests for the Forestry Sector and their Effects on Foreign Trade, 27–28 June 2000, Concepcion, Chile. Concepcion, Chile, CORMA.
Bevan, D. and King, C.J. (1983) Dendroctonus micans Kug., a new pest of spruce in U.K. Commonwealth Forest Rev. 62, 41–51.
Bright, D.E. (1968) Review of the tribe Xyleborini in America north of Mexico (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Can. Entomologist 100, 1288–323.
Bright, D.E. and Rabaglia, R.J. (1999) Dryoxylon, a new genus for Xyleborus onoharaensum Murayama, recently established in the southeastern United States (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). The Coleopterists Bull. 53, 333–7.
Britton, K.O. and Sun, J.H. (2002) Unwelcome guests: exotic forest pests. Acta Entomologica Sinica 45, 121–30.
Browne, F.G. (1968) Pests and Diseases of Forest Plantation Trees. Oxford, UK: Clarendon Press.
Campbell, F.T. (2001) The science of risk assessment for phytosanitary regulation and the impact of changing trade regulations. BioScience 51, 148–53.
Ciesla, W.M. (1993) Recent introductions of forest insects and their effects: a global overview. FAO Plant Protection Bull. 41, 3–13.
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (2002) International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures: Guidelines for RegulatingWood Packaging Material in International Trade. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Publication No. 15.
Francke-Grosmann, H. (1966) Some investigations on the hazard of intercontinental spread of forest and timber insects. In FAO/IUFRO Symposium on Internationally Dangerous Forest Diseases and Insects, 20–30 July 1964, Oxford.
Gibbs, J.N. and Wainhouse, D. (1986) Spread of forest pests and pathogens in the northern hemisphere. Forestry 59, 141–53.
Gregoire, J.C. (1988) The greater European spruce beetle. In A.A. Berryman (ed.) Dynamics of Forest Insect Populations, pp. 455–78. New York: Plenum.
Haack, R.A. (2001) Exotic scolytids of the Great Lakes region. Newsletter of the Michigan Entomol. Soc. 46 (3), 6–7.
Haack, R.A. (2002) Intercepted bark-and wood-boring insects in the United States: 1985–2000. Newsletter Michigan Entomol. Soc. 47(3–4), 14–15.
Haack, R.A. and Byler, J.W. (1993) Insects and pathogens: Regulators of forest ecosystems. J. Forestry 91(9), 32–7.
Haack, R.A. and Cavey, J.F. (1997) Insects intercepted on wood articles at ports-of-entry in the United States: 1985–1996. Newsletter Michigan Entomol. Soc. 42(2–4), 1–7.
Haack, R.A. and Cavey, J.F. (2000) Insects intercepted on solid wood packing materials at United States ports-of-entry: 1985–1998. In Proc.: Int. Conf. on Quarantine Pests for the Forestry Sector and their Effects on Foreign Trade, 27–28 June 2000, Concepcion, Chile. Concepcion, Chile, CORMA.
Haack, R.A., Jendek, E., Liu, H., Marchant, K.R., Petrice, T.R., Poland, T.M. and Ye, H. (2002) The emerald ash borer: a new exotic pest in North America. Newsletter of the Michigan Entomol. Soc. 47(3–4), 1–5.
Haack, B. and Kucera, D. (1993) New introduction-common pine shoot beetle, Tomicus piniperda (L.). USDA Forest Service, Northeastern Area, Pest Alert NA-TP-05–93. p. 2.
Haack, R.A., Law, K.R., Mastro, V.C., Ossenbruggen, H.S. and Raimo, B.J. (1997) New York's battle with the Asian longhorned beetle. J. Forestry 95(12), 11–15.
Haack, R.A. and Poland, T.M. (2001) Evolving management strategies for a recently discovered exotic forest pest: Tomicus piniperda (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Biol. Invasions 3, 307–22.
Haack, R.A. and Slansky, F. (1987) Nutritional ecology of wood-feeding Coleoptera, Lepidoptera, and Hymenoptera. In F. Slansky and J.G. Rodriguez (eds) Nutritional Ecology of Insects, Mites, and Spiders, pp. 449–86. NewYork: John Wiley.
Hobson, K.R. and Bright, D.E. (1994) A key to the Xyleborus of California, with faunal comments (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Pan-Pacific Entomologist 70, 267–8.
Hoebeke, E.R. (1989) Pityogenes bidentatus (Herbst), a European bark beetle new to North America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). J. NY Entomol. Soc. 97, 305–8.
Hoebeke, E.R. (1991) An Asian ambrosia beetle, Ambrosiodmus lewisi, new to North America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Proc. Entomol. Soc. Washington 93, 420–4.
Hoebeke E.R. (2001) Hylurgus ligniperda: a newexotic pine bark beetle in the United States. Newsletter Michigan Entomol. Soc. 46(1–2), 1–2.
Humble, L.M. (2001) Invasive bark and wood-boring beetles in British Columbia, Canada. In E. Alfaro, K. Day, S. Salom, K.S.S. Nair, H. Evans, A. Liebhold, F. Lieutier, M. Wagner, K. Futai and K. Suzuki (eds) Protection of World Forests from Insect Pests: Advances in Research, pp. 69–77. Papers presented at the XXI IUFRO World Congress, IUFRO World Series, Vol. 11. Vienna, Austria.
Humble, L.M. and Allen, E.A. (2001) Implications of nonindigenous introductions in forest ecosystems. In A.M. Liebhold, M.L. McManus, I.S. Otvos, and S.L.C. Fosbroke (eds) Proceedings: Integrated Management and Dynamics of Forest Defoliating Insects, pp. 45–55. USDA Forest Service, Northeastern Research Station, General Technical Report NE-277.
Jones, T. (1967) The present world situation in regard to the spread of internationally dangerous forest insects. East African Agricultural and Forestry J. 32, 484–92.
Kahn, R.P. (1989) Plant Protection and Quarantine, Vol. 1. Biological Concepts. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Kirkendall, L.R. (1983) The evolution of mating systems in bark and ambrosia beetles (Coleoptera: Scolytidae and Platypodidae. Zoologic. J. Linnean Soc. 77, 293–352.
Kirkendall, L.R. (1993) Ecology and evolution of biased sex ratios in bark and ambrosia beetles (Scolytidae). In D.L. Wrensch and M.A. Ebbert (eds) Evolution and Diversity of Sex Ratio: Insects and Mites, pp. 235–345. New York: Chapman and Hall.
Liebhold, A.M., MacDonald, W.L., Bergdahl, D. and Mastro, V.C. (1995) Invasion by exotic forest pests: a threat to forest ecosystems. Forest Sci. Monograph 41, 1–49.
Marchant, K.R. and Borden, J.H. (1976) Worldwide introduction and establishment of bark and timber beetles (Coleoptera: Scolytidae and Platypodidae). Burnaby, BC, Canada: Simon Fraser University, Pest Management Papers No. 6.
Mattson, W.J., Niemela, P., Millers, I. and Inguanzo, Y. (1994) Immigrant phytophagous insects onwoody plants in the United States and Canada: an annotated list. USDA Forest Service, North Central Forest Experiment Station, General Technical Report NC-169.
Milligan, R.H. (1970) Overseas wood-and bark-boring insects intercepted at New Zealand ports. New Zealand Forest Service Technical Paper No. 57.
Morrell, J.J. (1995) Importation of unprocessed logs into North America: a review of pest mitigation procedures and their efficacy. Forest Products J. 45(9), 41–50.
Morrell, J.J. and Filip, G. (eds) (1996) ImportingWood Products: Pest Risks to Domestic Industries. Proceedings, 4–6 March 1996, Portland, OR. Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR.
Mudge, A.D., LaBonte, J.R., Johnson, K.J.R. and LaGasa, E.H. (2001) Exotic woodboring Coleoptera (Micromalthidae, Scolytidae) and Hymenoptera (Xiphydriidae) new to Oregon andWashington. Proc. Entomol. Soc.Washington 103, 1011–19.
National Research Council, Committee on the Scientific Basis for Predicting the Invasive Potential of Nonindigenous Plants and Plant Pests in the United States, Board on Agriculture and Natural Resources (2002) Predicting Invasions of Nonindigenous Plants and Plant Pests. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Niemela, P. and Mattson,W.J. (1996) Invasion of North America by European phytophagous insects: legacy of the European crucible? BioScience 46, 740–52.
Nowak, D.J., Pasek, J.E., Sequeira, R.A., Crane, D.E. and Mastro, V.C. (2001) Potential effect of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) on urban trees in the United States. J. Econom. Entomol. 94, 116–22.
Pimentel, D., Lach, L., Zuniga, R., and Morrison, D. (2000) Environmental and economic costs of nonindigenous species in the United States. BioScience 50, 53–65.
Rabaglia, R.J. (2002) Scolytinae Latreille 1807. In R.H. Arnett, M.C. Thomas, P.E. Skelley and J.H. Frank (eds) American Beetles, Vol. 2, pp. 792–815. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Rabaglia, R.J. and Cavey, J.F. (1994) Note on the distribution of the immigrant bark beetle, Hylastes opacus, in North America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Entomol. News 105, 277–9.
Rabaglia, R.J. and Williams, G.L. (2002) Two species of western North American Hylesinus Fabricius (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) new to the eastern United States. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Washington 104, 1058–60.
Schroeder, L.M. (1990) Occurrence of insects in coniferous roundwood imported to Sweden from France and Chile. EPPO Bull. 20, 591–6.
Siitonen, J. (2000) Beetles (Coleoptera) imported to Finland on Russian roundwood. In B. Okland (ed.) Invasive Species and Timber Imports from Russia: Review of Current Knowledge by Nordic Experts, pp. 11–18. Aktuelt fra Skogforskningen 4–00.
Tkacz, B.M., Burdsall, H.H., DeNitto, G.A., Eglitis, A., Hanson, J.B., Kliejunas, J.T., Wallner, W.E., O'Brien, J.G. and Smith, E.L. (1998) Pest risk assessment of the importation into the United States of unprocessed Pinus and Abies logs from Mexico. USDA Forest Service, General Technical Report FPL-GTR-104.
US Census Bureau (2001) Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2001. Washington, DC.
US Congress (1993) Harmful Non-indigenous Species in the United States. Washington, DC: US Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, OTA-F-565.
USDA Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) (1982) List of Intercepted Plant Pests: Fiscal Years 1980 and 1981. Hyattsville, MD: USDA APHIS, Plant Protection and Quarantine, APHIS 82–8.
USDA APHIS (1995) 7 CFR Parts 300 and 319–Importation of logs, lumber, and other unmanufactured wood articles. Federal Register, 25 May 1995, 60(101), 27665–82.
USDA APHIS (1998) 7 CFR Parts 319 and 354–Solid wood packing material from China. Federal Register, 18 September 1998, 63(181), 50100–11.
USDA APHIS (2002) Pest Risk Assessment for Importation of Solid Wood Packing Materials into the United States. Washington, DC: USDA APHIS, APHIS 81–35–008.
USDA Forest Service (1992) Pest Risk Assessment of the Importation of Pinus radiata and Douglas-fir logs from New Zealand.Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Miscellaneous Publication No. 1508.
USDA Forest Service (1993) Pest Risk Assessment of the Importation of Pinus radiata, Nothofagus dombeyi, and Laurelia philippiana logs from Chile. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Miscellaneous Publication No. 1517.
USDA Forest Service (2003) Pest Risk Assessment of the Importation of Unprocessed Eucalypt logs and chips from Australia into the United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Miscellaneous Publication (in press).
Vandenberg, N.J., Rabaglia, R.J. and Bright, D.E. (2000) New records of two Xyleborus (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) in North America. Proc. Entomol. Soc. Washington 102, 62–8.
Wallenmaier, T. (1989) Wood-boring insects. In R.P. Kahn (ed.) Plant Protection and Quarantine. Vol. 2, pp. 99–108. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Wallner, W.E. (1996) Invasive pests ('biological pollutants') and US forests: whose problem, who pays? EPPO Bulletin 26, 167–80.
Wood, S.L. (1975) New synonymy and new species of American bark beetles (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), Part II. Great Basin Naturalist 35, 391–401.
Wood, S.L. (1977) Introduced and exported American Scolytidae (Coleoptera). Great Basin Naturalist 37, 67–74.
Wood, S.L. (1982) The bark and ambrosia beetles of North and Central America (Coleoptera: Scolytidae), a taxonomic monograph. Great Basin Naturalist Memoirs 6, 1–1359.
Wood, S.L. (1992) Nomenclatural changes and new species in Platypodidae and Scolytidae (Coleoptera), Part II. Great Basin Naturalist 52, 78–88.
Wood, S.L. and Bright, D.E. (1992) A catalog of Scolytidae and Platypodidae (Coleoptera), Part 2: Taxonomic index. Great Basin Naturalist Memoirs 13, 1–1553.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haack, R.A. Intercepted Scolytidae (Coleoptera) at U.S. ports of Entry: 1985–2000. Integrated Pest Management Reviews 6, 253–282 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025715200538
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025715200538