Abstract
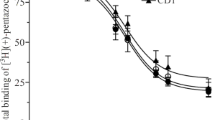
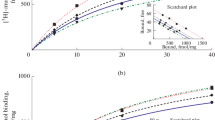
The binding of 125I-labeled substance P (SP) to rat brain cortex membranes has been studied Under control conditions and in the presence of ethanol. The binding of SP at low concentrations (20–1000 pM) gave two components, one with a K D value of 80 pM and another one with a K D of 500 pM. The higher-affinity component is due to NK1 receptors, as confirmed by the inhibition Of the SP binding by the rodent NK1 specific agonist [Sar9 Met(O2)11]SP. Ethanol (1.7 mM) added to the binding assays inhibited by more than 50% the specific binding at a very low SP concentration (20 pM); however, it had no effect at SP concentrations ranging from 50 to 120 pM. This suggests a decrease by ethanol of the affinity of SP to the NK1 receptors involved in this binding component. The ethanol effect disappeared at [EtOH] ≤ 0.17 mM.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
von Euler, U. S. and Gaddum, J. H. 1931. An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 72:74-87.
Hokfelt, T., Pernow, B., and Wahren, J. 2001. Substance P: A pioneer amongst neuropeptides. J. Internal Med. 249:27-40.
Saria, A. 1999. The tachykinin NK1 receptor in the brain: Pharmacology and putative functions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 375:51-60.
Maggi, C. A. 2000. The troubled story of tackykinins and neurokinins. Trends in Pharm. Sci. 21:173-175.
Beaujouan, J.-C., Saffroy, M., Torrens Y., and Glowinski, J. 2000. Different subtypes of tachykinin NK1 receptor binding sites are present in the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 75:1015-1026.
Kramer, M. S., Cutler, N., Feighner, J., Shrivastava, R., Carman, J., Sramek, J. J., Reines, S. A., Liu, G., Snavely, D., Wyatt-Knowles, E., Hale, J. J., Mills, S. G., MacCoss, M., Swain, C. J., Harrison, T., Hill, R. G., Hefti, F., Scolnick, E. M., Cascieri, M. A., Chicchi, G. C., Sadowski, S., Williams, A. R., Hewson, L., Smith, D., Carlson, E. J., Hargreaves, R. J., and Rupniak, N. M. J. 1998. Distinct mechanism for antidepressant activity by blockade of central substance P receptors. Science 281:1640-1645.
Davidson, D., Camara, P., and Swift, R. 1997. Behavioral effects and pharmacokinetics of low-dose intravenous alcohol in humans. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 21:1294-1299.
Minami, K., Shiraishi, M., Uezono, Y., Ueno, S., and Shigematsu, A. 2002. The inhibitory effects of anaesthetics and ethanol on substance P receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Anesth. Analg. 94:79-83.
Tousignant, C., Guillemette, G., Drapeau, G., Telemaque, S., Dion, S., and Regoli, D. 1990. 125I-BH[Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP, a new selective ligand for the NK-1 receptor in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 524:263-270.
Oku, R., Satoh, M., and Takagi, H. 1987. Release of substance P from the spinal dorsal horn is enhanced in polyarthrytic rats. Neurosci. Lett. 74:315-319.
Schaible, H.-G., Jarrot, B., Hope, P. J., and Duggan, A. W. 1990. Release of immunoreactive substance P in the spinal cord during development of acute arthrytis in the knee joint of the cat: A study with antibody microprobes. Brain Res. 529:214-223.
Duggan, A. W., Hendry, I. A., Morton, C. R., Hutchinson, W. D., and Zhao, Z. Q. 1988. Cutaneous stimuli releasing immunoreactive substance P in the dorsal horn of the cat. Brain Res. 451:261-273.
Krause, J. E., Di Maggio, D. A., and McCarson, K. E. 1995. Alterations in neurokinin 1 receptor gene expression in models of pain and inflammation. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 73:854-859.
Radhakrishnan, V., Iyengar, S., and Henry, J. L. 1998. The non-peptide NK-1 receptor antagonists LY-303,870 and LY-306,740 block the response of spinal dorsal horn neurons to substance P and to peripheral noxious stimuli. Neuroscience 83:1251-1260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scarrone, S., Cappelli, A., Cupello, A. et al. Ethanol Inhibits the Binding of Substance P to Rat Brain Cortex NK1 Receptors. Neurochem Res 28, 1159–1162 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024216109472
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024216109472