Abstract
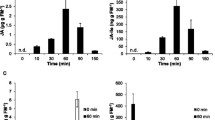
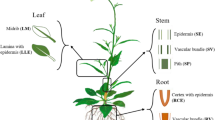
We investigated the impact of leaf vascular connections on systemically transmitted herbivore-induced gene expression in Nicotiana attenuata. Although systemic signaling is clearly associated with the plant vascular system, few studies consider vascular architecture when measuring systemically induced defenses. N. attenuata is a plant with dispersed phyllotaxis approximating 3/8 in the rosette stage of growth. We mimicked Manduca sexta herbivory by introducing larval regurgitant to wounds produced with a standardized continuous mechanical wounding and investigated mRNA accumulation of genes. Herbivory in N. attenuata induces the expression of genes coding for a proteinase inhibitor protein (PI), threonine deaminase (TD, EC 4.3.1.19), a luminal-binding protein (BiP), and an α-dioxygenase (α-DOX). We measured the systemic response of sink leaves when orthostichous (growing at an angular distance of 0 degrees) source leaves were treated, and vice versa, and compared it to the systemic response of leaves growing at the maximum angular distance of 180 degrees. Vascular architecture clearly controlled the intensity of systemic mRNA accumulation within the 4-hr time frame of the experiment. In addition, we found signal translocation to be bidirectional, travelling from source to sink as well as from sink to source leaves, which argues against a phloem-based assimilate-linked signal identity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alarcon, J-J. and Malone, M. 1994. Substantial hydraulic signals are triggered by leaf-biting insects in tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 45:953–957.
Allard, H. A. 1942. Some aspects of the phyllotaxy of tobacco. J. Agric. Res. 64:49–55.
Azevedo, R. A., Arrud, P., Turner, W. L., and Lea, P. J. 1997. The biosynthesis and metabolism of the aspartate derived amino acids in higher plants. Phytochemistry 46:395–419.
Baldwin, I. T. 2001. An ecologically-motivated analysis of plant-herbivore interactions in native tobacco. Plant Physiol. 127:1449–1458.
Baldwin, I. T. and Schmelz, E. A. 1994. Constraints on an induced defense: the role of leaf area. Oecologia 97:424–430.
Baldwin, I. T., Staszak-kozinski, L., and Davidson, R. 1994. Up in smoke: I. Smoke-derived germination cues for postfire annual, Nicotiana attenuata Torr. Ex. Watson. J. Chem. Ecol. 20:2345–2371.
Bowles, D. 1998. Signal transduction in the wound response of tomato plants. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B 353:1495–1510.
Davis, J. M., Gordon, M. P., and Smit, B. A. 1991. Assimilate movement dictates remote sites of wound-induced gene expression in poplar leaves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88:2393–2396.
De Bruxelles, G. L. and Roberts, M. R. 2001. Signals regulating multiple responses to wounding and herbivores. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 20:487–521.
De Leon, I. P., Sanz, A., Hamberg, M., and Castresana, C. 2002. Involvement of the Arabidopsis alpha-DOX1 fatty acid dioxygenase in protection against oxidative stress and cell death. Plant J. 29:61–72.
Denno, R. F. and McClure, M. S. 1983. Variable Plants and Herbivores in Natural and Managed Systems. Academic Press, New York.
Duffey, S. S. and Stout, M. J. 1996. Antinutritive and toxic components of plant defense against insects. Arch. Insect Biochem. Phys. 32:3–37.
Hamberg, M., Sanz, A., and Castresana, C. 1999. Alpha-oxidation of fatty acids in higher plants-Identification of a pathogen-inducible oxygenase (PIOX) as an alpha-dioxygenase and biosynthesis of 2–hydroperoxylinolenic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 274:24503–24513.
Halitschke, R., Schittko, U., Pohnert, G., Boland, W., and Baldwin, I. T. 2001. Molecular interactions between the specialist herbivore Manduca sexta (Lepidoptera, Sphingidae) and its natural host Nicotiana attenuata. III. Fatty acid-amino acid conjugates in herbivore oral secretions are necessary and sufficient for herbivore-specific plant responses. Plant Physiol. 125:711–717.
Hermsmeier, D., Schittko, U., and Baldwin, I. T. 2001. Molecular interactions between the specialist herbivore Manduca sexta (Spodoptera, Sphingidae) and its natural host Nicotiana attenuata. I. Large-scale changes in the accumulation of growth-and defense-related plant mRNAs. Plant Physiol. 125:683–700.
Jelitto-Van Dooren, E., Vidal, S., and Denecke, J. 1999. Anticipating endoplasmic reticulum stress: A novel early response before pathogenesis-related gene induction. Plant Cell 11:1935–1943.
Jones, C. G., Hopper, R. F., Coleman, J. S., and Krischik, V. A. 1993. Control of systemically induced herbivore resistance by plant vascular architecture. Oecologia 93:452–456.
Jones, H., Martin, R. V., and Porter, H. K. 1959. Translocation of 14carbon in tobacco following assimilation of 14carbon dioxide by a single leaf. Ann. Bot. London 23:493–510.
Karban, R. and Baldwin, I. T. 1997. Induced Responses to Herbivory. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Malone, M. and Alarcon, J. J. 1995. Only xylem-borne factors can account for systemic wound signaling in the tomato plant. Planta 196:740–746.
Malone, M., Alarcon, J. J., and Palumbo, L. 1994. An hydraulic interpretation of rapid, long-distance wound signaling in the tomato. Planta 193:181–185.
Murray, B. J., Mauk, C., and Nooden, L. D. 1982. Restricted vascular pipelines (and orthostichies) in plants. What's new? Plant Physiol. 13:33–36.
Orians, C. M. and Jones, C. G. 2001. Plants as resource mosaics: a functional model for predicting patterns of within-plant resource heterogeneity to consumers based on vascular architecture and local environmental variability. Oikos 94:493–504.
Orians, C. M., Pomerleau, J., and Ricco, R. 2000. Vascular architecture generates fine scale variation in systemic induction of proteinase inhibitors in tomato. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:471–485.
Pawlowski, K., Kunze, R., De Vries, S., Bisseling, T. 1994. Isolation of total, poly(A), and polysomal RNA from plant tissue, Section D, pp. 1–4, in S. B. Gelvin, and R. A. Schilperoort, (Eds.). Plant Molecular Biology Manual. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Rhodes, J. D., Thain, J. F., and Wildon, D. C. 1999. Evidence for physically distinct systemic signalling pathways in the wounded tomato plant. Ann. Bot. London 84:109–116.
Ryan, C. A. 2000. The systemin signaling pathway: differential activation of plant defensive genes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1477:112–121.
Samach, A., Hareven, D., Gutfinger, T., Ken-Dror, S., and Lifschitz, E. 1991. Biosynthetic threonine deaminase gene of tomato: isolation, structure and upregulation in floral organs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88:2678–2682.
Sanz, A., Moreno, J. I., and Castresana, C. 1998. PIOX, a new pathogen-induced oxygenase with homology to animal cyclooxygenase. Plant Cell 10:1523–1537.
Shirova, M., Lister, G. R., Nelson, C. D., and Krotkov, G. 1961. Translocation of C14 in tobacco at different stages of development following assimilation of C14O2 by a single leaf. Can. J. Bot. 39:855–864.
Shulaev, V., Leon, J., and Raskin, I. 1995. Is salicylic-acid a translocated signal of systemic acquired-resistance in tobacco. Plant Cell 7:1691–1701.
Stankovic, B, and Davies, E. 1996. Both action potentials and variation potentials induce proteinase inhibitor gene expression in tomato. FEBS 390:275–279.
Stratmann, J. W. and Ryan, C. A. 1997. Myelin basic protein kinase activity in tomato leaves is induced systemically by wounding and increases in response to systemin and oligosaccharide elicitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94:11085–11089.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schittko, U., Baldwin, I.T. Constraints to Herbivore-Induced Systemic Responses: Bidirectional Signaling Along Orthostichies in Nicotiana attenuata . J Chem Ecol 29, 763–770 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022833022672
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022833022672