Abstract
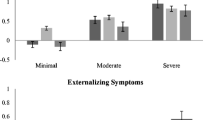
A mild deficit in executive functions has been hypothesized to be associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), with externalizing problem behaviors such as conduct disorder (CD) and with the vulnerability to alcoholism in sons of multi-generational alcoholics (SOMGAs). These three categories overlap, which raises concerns about the specificity of the hypothesized associations. In the present study, measures of executive functions (EFs) were tested in seventy-six 7- to 11-year-old boys: boys with ADHD but without a family history of addiction, SOMGAs, and controls. Specific deficits in EFs were found for boys with ADHD but not for SOMGAs. The association between a deficit in EFs and attention problems remained after controlling for externalizing problem behaviors, but not for the reverse. These results suggest that a mild deficit in EFs is specifically related to ADHD and that the deficits reported in boys with CD and in SOMGAs are due to relatively high attentional problems in these groups or due to other factors such as motivation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Integrative guide for the 1991 CBCL/4-18 YSR, and TRF profiles. Burlington: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry.
American Psychiatric Association. (1987). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (3rd ed., rev.). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, D.C.: Author.
Babor, T. F., Hofmann, M., DelBoca, F. K., Hesselbrock, V., Meyer, R. E., Dolinsky, Z. D., & Rounsaville, B. (1992). Types of alcoholics, I. Evidence for an emperically derived typology based on indications of vulnerability and severity. Archives of General Psychiatry, 49, 599–608.
Baker, S. C., Rogers, R. D., Owen, A. M., Frith, C. D., Dolan, R. J., Frackowiak, R. S. J., & Robbins, T. W. (1996). Neural systems engaged by planning: A PET study of the Tower of London task. Neuropsychologia, 34, 515–526.
Barkley, R. A. (1997). Behavioral inhibition, susained attention, and executive funtions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychological Bulletin, 121, 65–94.
Barkley, R. A., Grodzinsky, G., & DuPaul, G. (1992). Frontal lobe functions in attention deficit disorder with and without hyperactivity: A review and research report. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 20, 163–188.
Bates, M. E., & Pandina, R. J. (1992). Familial alcoholism and premorbid cognitive deficit: A failure to replicate subtype differences. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 53, 320–327.
Biederman, J., Wilens, T., Mick, E., Faraone, S., Weber, W., Curtis, S., Thornell, A., Pfister, K., Garcia Jetton, J., & Soriano, J. (1997). Is ADHD a risk factor for psychoactive substance use disorders? Findings from a four-year prospective follow-up study. Journal of the American Acedemy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36, 21–29.
Clarren, S. K., Sampson, P. D., Larsen, J., Donnell, D. J., Barr, H. M., Bookstein, F. L., Martin, D. C., & Streissguth, A. P. (1987). Facial effects of fetal alcohol exposure: Assessment by photographs and morphometric analysis. American Journal Medical Genetics, 26, 651–666.
Cloninger, C. R. (1987). Neurogenetic adaptive mechanisms in alcoholism. Science, 236, 410–416.
Cooper, L., Russell, M., & George, W. (1988). Coping, expectancies, and alcohol abuse: A test of social learning formulations. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 97, 218–230.
Damasio, A. R. (1994). Descartes' error. Emotion, reason, and the human brain. New York: Avon.
Daugherty, T. K., & Quay, H. C. (1991). Response perseveration and delayed responding in childhood behavior disorders. Journal Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 32, 453–461.
Dobkin, P. L., Tremblay, R. E. & Sacchitelle, C. (1997). Predicting boys' early-onset substance abuse from father's alcoholism, son's disruptiveness, and mother's parenting behavior. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 86–92.
Eslinger, P. J. (1996). Conceptualizing, describing, and measuring components of executive function, a summary. In G. R. Lyon & N. A. Krasnegor (Eds.), Attention, memory and executive function (pp. 367–396). London: Paul H. Brookes.
Fergusson, D. M., & Horwood, L. J. (1995). Early disruptive behavior, IQ, and later school achievement and delinquent behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 23, 183–199.
Fergusson, D. M., Lynskey, M. T., & Horwood, L. J. (1997). Attentional difficulties in middle childhood and psychosocial outcomes in young adulthood. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 38, 633–644.
Finn, P. R., Kessler, D. N., & Hussong, A. M. (1994). Risk for alcoholism and classical conditioning to signals for punishment: Evidence for a weak behavioral inhibition system? Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 103, 293–301.
Fuster, J. M. (1989). The prefrontal cortex: Anatomy, Physiology, and Neuropsychology of the Frontal Lobe. (2nd. Ed.), New York: Raven Press.
Giancola, P. R., Peterson, J., & Pihl, R. O. (1993). Risk for alcoholism, antisocial behavior, and response perseveration. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 49, 423–428.
Giancola, P. R., & Zeichner, A. (1994). Neuropsychological performance on tests of frontal-lobe funcioning and aggressive behavior in men. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 103, 832–835.
Gorenstein, E. E. (1987). Cognitive-perceptual deficit in an alcoholism spectrum disorder. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 48, 310–318.
Gorenstein, E. E., & Newman, J. P. (1980). Disinhibitory psychopathology: A new perspective and a model for research. Psychological Review, 87, 301–315.
Grafman, J. (1989). Plans, actions and mental sets: Managerial knowledge units in the frontal lobes. In E. Perecman (Ed.), Integrating theory and practice in clinical neuropsychology (pp. 93–138). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Gray, J. A. (1982). The neuropsychology of anxiety: An enquiry into the function of the septo-hippocampal system. New York: Oxford University Press.
Groth-Marnat, G. (1990). Handbook of psychological assessment. 2nd Ed. NY: Wiley.
Gunning, W. B., Pattiselanno, W. E. Van der Stelt, O., & Wiers, R. W. (1994). Children of alcoholics: Predictors for psychopathology and addiction. Acta Pediatrica Supplement, 404, 7–8.
Harden, P. W., & Pihl, R. O. (1995). Cognitive function, cardiovascular reactivity, and behavior in boys at high risk for alcoholism. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 104, 94–103.
Hare, R. D. (1993). Without conscience: The disturbing world of the psychopaths among us. New York: Pocket Books.
Hinshaw, S. P. (1987). On the distinction between attentional deficits/hyperactivity and conduct problems/aggression in child psychopathology. Psychological Bulletin, 101, 443–463.
Hill, S. Y., & Smith, T. R. (1991). Evidence for genetic mediation of alcoholism in women. Journal of Substance Abuse, 3, 159–174.
Huberty, C. J., & Morris, J. D. (1989). Multivariate analysis versus multiple univariate analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 105, 302–308.
Huberty, C. J., & Smith, J. D. (1982). The study of effect in MANOVA. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 17, 417–432.
Hughes, C., Russell, J., & Robbins, T. W. (1992). Evidence for executive dysfunction in autism. Neuropsychologia, 32, 477–492.
Iaboni, F., Douglas, V. I., & Baker, A. G. (1995). Effects of reward and response cost on inhibition in ADHD children. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 104, 232–240.
Iaboni, F., Douglas, V. I., & Ditto, B. (1997). Psychophysiological response of ADHD children to reward and extinction. Psychophysiology, 34, 116–123.
Iversen, S. D., & Dunnett, S. B. (1990). Functional organization of striatum as studied with neural graphs. Neuropsychologia, 28, 601–626.
Kagan, J., Rosman, B. L., Day, D., Albert, J., & Phillips, W. (1964). Information processing in the child, significance of analytic and reflective attitudes. Psychological Monographs (1, Whole No. 578).
Kasius, M. (1997). Interviewing children: Development of the Dutch version of the semistructured Clinical Interview for Children and Adolescents (SCICA) and testing the psychometric properties. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Erasmus Universiteit, Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
Kendler, K. S., Neale, M. C., Heath, A. C., Phil, R. O., Kessler, R. C., & Eaves, L. J. (1994). A twin study on alcoholism in women. American Journal of Psychiatry, 151, 707–715.
Kokkevi, A., & Hartgers, C. (1995). EuropASI: European adapatation of a multidimensional assessment instrument for drug and alcohol dependence. European Addiction Research, 1, 208–210.
Krikorian, R., Bartok, J., & Gay, N. (1994). Tower of London procedure: A standard method and developmental data. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 16, 840–850.
Lilienfield, S. O., & Waldman, I. D. (1990). The relation between childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and adult antisocial behavior re-examined: The problem of heterogeneity. Clinical Psychology Review, 10, 699–725.
Lynam, D. R. (1996). Early identification of chronic offenders: Who is the fledgling psychopath? Psychological Bulletin, 120, 209–234.
Martin, C. S., Earleywine, M., Blackson, T. C., Vanyukov, M. M., Moss, H. B., & Tarter, R. E. (1994). Aggressivity, Inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity in boys at high and low risk for substance abuse. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22, 177–203.
McCord, J. (in press). “He did it because he wanted to....” In W. Osgood (Ed.), Nebraska Symposium on Motivation (pp. 1–43). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
McGue, M. (1993). From proteins to cognitions: The behavioral genetics of alcholism. In R. Plomin & G. E. McClearn (Eds.), Nature, Nurture and Psychology (pp. 245–268). Washington DC: American Psychological Association.
McGue, M., Pickens, R. W., & Svikis, D. S. (1992). Sex and age effects on the inheritance of alcohol problems: A twin study. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 101, 3–17.
Meehl, P. E. (1970). Nuisance variables and the ex post facto design. In M. Radner & S. Winoku (Eds.), Minnesota studies in the philosophy of science (pp. 373–402). Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Moffit, T. E. (1993). The neuropsychology of conduct disorder. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 135–151.
Myers, J. L., & Well, A. D. (1991). Research design and statistical analysis. New York: HarperCollins.
Newlin, D. B., & Thomson, J. B. (1990). Alcohol challenge with sons of alcoholics: A critical review and analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 108, 383–402.
Newman, J. P., Patterson, C. M., & Kosson, D. S. (1987). Response perseveration in psychopaths. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 96, 145–148.
Newman, J. P., & Wallace J. F. (1993). Diverse pathways to deficient self-regulation: Implications for disinhibitory psychopathology in children. Clinical Psychology Review, 13, 699–720.
Oosterlaan, J., Logan, G. D., & Sergeant, J. A. (1998). Response inhibition in ADHD, CD, comorbid ADHD + CD, anxious, and normal children: A meta-analysis of studies with the stop task. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 39, 411–425.
Oosterlaan, J., & Sergeant, J. A. (1998). Response inhibition and the effects of reward and response cost: A comparison between ADHD, disruptive, anxious and normal children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology.
Ozkaragoz, T. Z., & Noble, E. P. (1995). Neuropsychological differences between sons of active alcoholic and non-alcoholic fathers. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 30, 115–123.
Ozkaragoz, T. Z., Satz, P., & Noble, E. P. (1997). Neuropsychological functioning in sons of active alcoholic, recovering alcoholic, and social drinking fathers. Alcohol, 14, 31–37.
Patterson, C. M., & Newman, J. P. (1993). Reflectivity and learning from aversive events: Toward a psychological mechanism for syndromes of disinhibition. Psychological Review, 100, 716–736.
Pennington, B. F. (1994). The working memory function of the prefrontal cortices: Implications for developmental and individual differences in cognition. In M. M. Haith, J. Benson, R. Roberts, & B. F. Pennington (Eds.), The development of future oriented processes (pp. 243–289). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Pennington, B. F., & Ozonoff, S. (1996). Executive funtions and developmental psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 37, 51–87.
Peterson, J., Finn, P., & Pihl, R. (1992). Cognitive dysfunction and the inherited predisposition to alcoholism. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 53, 154–160.
Petrides, M., Aliviasatos, B., Evans, A. C., & Meyer, E. (1993). Dissociation of human mid-dorsolateral from posterio dorsolateral frontal cortex in memory processing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 90, 873–877.
Petrides, M., Aliviasatos, B., Meyer, E., & Evans, A. C. (1993). Functional activation of the human frontal cortex during performance of verbal working memory tasks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 90, 878–882.
Petrides, M., & Milner, B. (1982). Deficits on subject-ordered tasks after frontal-and temporal-lobe lesions in man. Neuropsychologia, 20, 249–262.
Pihl, R. O., & Bruce, K. R. (1995). Cognitive impairments in children of alcoholics. Alcohol Health and Research World, 19, 142–147.
Pihl, R. O., Peterson, J., & Finn, P. (1990a). An heuristic model for the inherited predispostion to alcoholism. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 4, 12–25.
Pihl, R. O., Peterson, J., & Finn, P. (1990b). Inherited predisposition to alcoholism: Characteristics of sons of male alcoholics. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 99, 291–301.
Quay, H. C. (1988). Attention-deficit disorder and the behavioral inhibition system: The relevance of the neuropsychological theory of Jeffrey Gray. In L. M. Bloomingdale & J. A. Sergeant (Eds.), Attention deficit disorder: Criteria, cognition, intervention. (pp. 117–125). Oxford, England: Pergamon Press.
Quay, H. C. (1993). The psychobiology of undersocialized aggressive conduct disorder: A theoretical perspective. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 165–180.
Robins, L. N., Wing, J. K., Wittschen, H. U., Helzer, J. E., Babor, T. F., Burke, J., Farmer, A., Jablenski, A., Pickens, R., Regier, D. A. Sartorius, N., & Towle, L. H. (1988). The Composite International Diagnostic Interview: An epidemiologic instrument suitable for use in conjunction with different diagnostic systems and in different cultures. Archives of General Psychiatry, 38, 1069–1077.
Sattler, J. M. (1992). Assessment of children. (3rd ed., rev. and updated). San Diego: J. M. Sattler.
Schaffer, D. (1992). Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children (DISC 2.3) Parent Version. New York: Columbia University Press. (Translation into Dutch by F. C. Verhulstand M.Kasius)
Schuckit, M. A., & Smith, T. L. (1996). An 8-year follow-up of 450 sons of alcoholic and control subjects. Archives General Psychiatry, 53, 202–210.
Sergeant, J. A., Oosterlaan, J., & Van der Meere, J. (1999). Information processing and energetic factors in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. In H. C. Quay & A. E. Hogan (Eds.), Handbook of disruptive behaviors (pp. 95–104). New York: Plenum Press.
Shallice, T. (1982). Specific impairments of planning. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 298, 199–209.
Sher, K. J. (1991). Children of alcoholics: A critical appraisal of theory and research. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Sher, K. J., Walitzer, K. S., Wood, P. K., & Brent, E. E. (1991). Characteristics of children of alcoholics: Putative risk factors, substance use and abuse and psychopathology. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 100, 427–448.
Shue, K. L., & Douglas, V. I. (1992). Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and the frontal lobe syndrome. Brain and Cognition, 20, 104–124.
Smith, G. T., Goldman, M. S., Greenbaum, P. E., & Christiansen, B. A. (1995). Expectancy for social facilitation from drinking: The divergent paths of high-expectancy and low-expectancy adolescents. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 104, 32–40.
Stuss, D. T. (1992). Biological and psychological development of executive functions. Brain and Cognition, 20, 8–23.
Stuss, D. T., & Benson, D. F. (1984). Neuropsychological functions of the frontal lobes. Psychological Bulletin, 95, 3–28.
Tarter, R. E., Alterman, A. I., & Edwards, K. L. (1985). Vulnerability to alcoholism in men: A behavior genetic perspective. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 46, 329–356.
Tarter, R. E., Jacob, T., & Bremer, D. A. (1989a). Cognitive status of sons of alcoholic men. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 13, 232–235.
Tarter, R. E., Jacob, T., & Bremer, D. A. (1989b). Specific cognitive impairments in sons of early onset alcoholics. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 13, 786–789.
Van Haasen, P. P., De Bruyn, E. E. J., Pijl, Y. J., Poortinga, Y. H. Lutje Spelberg, H. C., Vander Steene, G., Coetsier, P., Spoelders-Claes, R., & Stinissen, J. (1986). Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children — Revised. Nederlandstalige Uitgave [Dutch Edition]. Lisse, The Netherlands: Swets & Zeitlinger.
Van Westerlaak, J. M., Kropman, J. A., & Collaris, J. W. M. (1975). Beroepenklapper. Nijmegen, The Netherlands: Instituut voor Toegepaste Sociologie.
Verhulst, F. C., Koot, J. M., Akkerhuis, G. W., & Veerman, J. W. (1990). Practische Handleiding voor de CBCL (Child Behavior Checklist) [Manual for the CBCL]. Assen, The Netherlands: Van Gorcum.
Verhulst, F. C., Van der Ende, J., & Koot, H. M. (1996). Handleiding voor de CBCL/4-18. Rotterdam: Afd. Kinder-en Jeugdpsychiatrie Sophia Kinderziekenhuis, The Netherlands.
West, M. O., & Prinz, R. J. (1987). Parental alcoholism and childhood psychopathology. Psychological Bulletin, 102, 204–218.
Whipple, S. C., Parker, E. S., & Noble, E. P. (1988). An atypical neurocognitive profile in alcoholic fathers and their sons. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 49, 240–244.
White, J. L., Moffit, T. E., Caspi, A., Bartusch, D. J., Needless, D. J., & Stouthamer-Loeber, M. (1994). Measuring impulsivity and examining its relationship to delinquency. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 103, 192–205.
Wickelgren, I. (1997). Getting the brain's attention. Science, 278, 35–37.
Wiegersma, S., Van der Scheer, E., & Hijman, R. (1990). Subjective ordering, short-term memory, and the frontal lobes. Neuropsychologia, 28, 95–98.
Wiers, R. W., Hoogeveen, K. J., Sergeant, J. A., & Gunning, W. B. (1997). High and low dose expectancies and the differential associations with drinking in male and female adolescents and young adults. Addition, 92, 871–888.
Wiers, R. W., Sergeant, J. A. & Gunning, W. B. (1994). Psychological mechanisms of enhanced risk of addiction: A dual pathway? Acta Pediatrica Supplement, 404, 9–13.
Workman-Daniels, K. L., & Hesselbrock, V. M. (1987). Childhood problem behavior and neuropsychological functioning in persons at risk for alcoholism. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 48, 187–193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiers, R.W., Gunning, W.B. & Sergeant, J.A. Is a Mild Deficit in Executive Functions in Boys Related to Childhood ADHD or to Parental Multigenerational Alcoholism?. J Abnorm Child Psychol 26, 415–430 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022643617017
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022643617017