Abstract
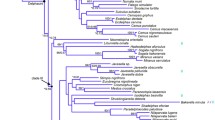
We have sequenced the complete mitochondrial DNA cytochrome b gene from 18 species of the subfamily Caprinae and two outgroup taxa. Additional sequences retrieved from the literature were used to constitute a data set of 32 cytochrome b sequences comprising all genera usually included within the Caprinae. Phylogenetic relationships were assessed by PAUP using three new weighting schemes based on homoplasy analyses. Each type of substitution considered at each of the three codon positions was weighted according to its homoplasy level, as measured by the consistency index (CI), the slope of saturation (S), or their product (CIS). These differentially weighted parsimony analyses indicate that (1) the subfamily Caprinae is monophyletic, but only with the exclusion of Saiga from the group; (2) there is no support for monophyly of the four tribes currently recognized (Caprini, Rupicaprini, Ovibovini, and Saigini), suggesting relationships different from those traditionally accepted; (3) the caprine group consists of three major clades corresponding to (a) Budorcas and Ovis, (b) Capricornis, Ovibos, and Naemorhedus, and (c) Capra, Hemitragus, and Pseudois; and (4) the basal branching pattern is very weakly supported by bootstrap or branch support values except for the sister-group relationship of Pantholops with all other caprines, and the phylogenetic positions of Ammotragus, Oreamnos, and Rupicapra remain unclear.
Similar content being viewed by others
LITERATURE CITED
Anderson, S., Bankier, A. T., Barrell, B. G., De Bruijn, M. H. L., Coulson, A. R., Drouin, J., Eperon, I. E., Nierlich, D. P., Roe, B. A., Sanger, F., Schreier, P. H., Smith, A. J. H., Staden, R., and Young, I. G. (1981). Sequence and organisation of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 290: 457–465.
Anderson, S., De Bruijn, M. H. L., Coulson, A. R., Eperson, I. E., Sanger, F., and Young, I. G. (1982). Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J. Mol. Biol. 156: 683–717.
Arai, K., Munechika, I., Ito, I., Kikkawa, A., Nakamura, K., Kanazawa, T., and Kosugiyama, M. (1997). Phylogenetic relationship of Caprini estimated by cytochrome b gene sequence analysis. Anim. Sci. Technol. (Jpn.) 68: 148–155.
Benecke, N. (1994). Der Mensch und seine Haustiere. Die Geschichte einer jahrtausendealten Beziehung, KTV, Theiss.
Bökönyi, S. (1988). History of Domestic Mammals in Central and Eastern Europe, Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest.
Bremer, K. (1988). The limits of amino acid sequence data in angiosperm phylogenetic reconstruction. Evolution 42: 795–803.
Bremer, K. (1994). Branch support and tree stability. Cladistics 10: 295–304.
Chikuni, K., Mori, Y., Tabata, T., Saito, M., Momma, M., and Kosugiyama, M. (1995). Molecular phylogeny based on the k-casein and cytochrome b sequences in the mammalian suborder Ruminantia. J. Mol. Evol. 41: 859–866.
Cronin, M. A., Stuart, R., Pierson, B. J., and Patton, J. C. (1996). K-casein gene phylogeny of higher ruminants (Pecora, Artiodactyla). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 6: 295–311.
Ellerman, J. R., and Morrisson-Scott, T. C. S. (1966). Checklist of Palaearctic and Indian Mammals, British Museum, London.
Eriksson, T. (1996). AutoDecay Version 2.9.5, Distributed by the author, Department of Botany, University of Stockholm, Stockholm, Sweden.
Felsenstein, J. (1978). Cases in which parsimony and compatibility methods may be positively misleading. Syst. Zool. 27: 401–410.
Felsenstein, J. (1985). Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39: 783–791.
Gatesy, J., Amato, G., Vrba, E., Schaller, G., and DeSalle, R. (1997). A cladistic analysis of mitochondrial ribosomal DNA from the Bovidae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 7: 303–319.
Gentry, A. W. (1992). The subfamilies and tribes of the family Bovidae. Mammal Rev. 22: 1–32.
Gentry, A. W. (1994). The Miocene differentiation of Old World Pecora (Mammalia). Hist. Biol. 7: 115–158.
Groves, P., and Shields, G. (1996). Phylogenetics of the Caprinae based on cytochrome b sequence. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 5: 467–476.
Groves P., and Shields, G. F. (1997) Cytochrome b sequences suggest convergent evolution of the Asian takin and Arctic muskox. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 8: 363–374.
Grubb, P. (1993). Family Bovidae. In: Mammal Species of the World. A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, D. E. Wilson and D. M. Reeder, eds., pp. 393–414, Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC.
Gustafsson, M. H. G., and Bremer, K. (1995). Morphology and phylogenetic interrelationships of the Asteraceae, Calyceraceae, Campanulaceae, Goodeniaceae, and related families (Asterales). Am. J. Bot. 82: 250–265.
Hagelberg, E., and Clegg, J. B. (1991). Isolation and characterization of DNA from archaeological bone. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 244: 45–50.
Hassanin, A., Lecointre, G., and Tillier, S. (1998). The “evolutionary signal” of homoplasy in protein-coding gene sequences and its consequences for a priori weighting in phylogeny. C.R. Acad. Sci. Ser. III 321: 611–620.
Irwin, D. M., Kocher, T. D., and Wilson, A. C. (1991). Evolution of the cytochrome b gene of mammals. J. Mol. Evol. 32: 128–144.
Kingdon, J. (1997). The Kingdon Field Guide to African Mammals, Academic Press, London.
Kluge, A. G., and Farris, J. S. (1969). Quantitative phyletics and the evolution of anurans. Syst. Zool. 30: 1–32.
McKenna, M. C., and Bell, S. K. (1997). Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level, Columbia University Press, New York.
Nowak, R. M. (1991). Walker's Mammals of the Word, Vol. II, 5th ed., The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore and London.
Pfeffer, P. (1967). Le mouflon de Corse (Ovis ammon musimon Schreber, 1782). Position systématique écologie et éthologie comparées. Mammalia S31: 1–262.
Philippe, H., Sorhannus, U., Baroin, A., Perasso, R., Gasse, F., and Adoutte, A. (1994). Comparison of molecular and paleontological data in diatoms suggests a major gap in the fossil record. J. Evol. Biol. 7: 247–265.
Randi, E., Fusco, G., Lorenzini, R., Toso, S., and Tosi, G. (1991). Alloenzyme divergence and phylogenetic relationships among Capra, Ovis and Rupicapra (Artiodactyla, Bovidae). Heredity 67: 281–286.
Schaller, G. B. (1977). Mountains Monarchs. Wild Sheep and Goats of the Himalayas, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Shackleton, D. M. (1997). Wild Sheep and Goats and Their Relatives, Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan for Caprinae, Caprinae Specialist Group, IUCN-SSC, Gland.
Simpson, G. G. (1945). The principles of classification and a classification of mammals. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 85: 1–350.
Swofford, D. L. (1993). PAUP: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony, Version 3.1.1, Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign.
Valdez, R. (1985). Lords of the Pinnacles. Wild Goats of the World, Wild Sheep and Goat International, Mesilla, New Mexico.
Van Gelder, R. G. (1977). Mammalian hybrids and generic limits. Am. Mus. Novit. 2535: 1–25.
Vigne, J.-D. (1988). Les grandes étapes de la domestication de la chèvre: une proposition d'explication de son statut en Europe occidentale. Ethnozootechnie 41: 1–13.
Winnepenninckx, B., Backeljau, T., and Dewachter, R. (1993). Extraction of high molecular weight DNA from molluscs. Trends Genet. 9: 407.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassanin, A., Pasquet, E. & Vigne, JD. Molecular Systematics of the Subfamily Caprinae (Artiodactyla, Bovidae) as Determined from Cytochrome b Sequences. Journal of Mammalian Evolution 5, 217–236 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020560412929
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020560412929