Abstract
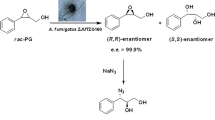
(R)-2-Phenylpropanoic acid was synthesized from the racemic acid through an isomerization reaction involving resting cells of Nocardia diaphanozonaria JCM3208. The isomerization activity of the cells was enhanced 25-fold by adding 5.5 mM racemic 2-phenylpropanoic acid to the culture medium. When 5 mM racemic 2-phenylpropanoic acid was included in the reaction mixture (4 ml) containing resting cells (100 mg dry cell wt) in 25 mM K2HPO4/KH2PO4 buffer (pH 7.0) at 30 °C for 8 h, 4.56 mM (R)-2-phenylpropanoic acid (95.8% e.e.) was formed with a 91% molar conversion yield.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arroyo M, Sinisterra JV (1994) High enantioselective esterification of 2-arylpropionic acids catalyzed by immobilized lipase from Candida antarctica: a mechanistic approach. J. Org. Chem. 59: 4410–4417.
Battistel E, Bianchi D, Cesti P, Pina C (1991) Enzymatic resolution of (S)-(+)-naproxen in a continuous reactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 38: 659–664.
Chen CS, Shieh WR, Lu PH, Harriman S, Chen CY (1991) Metabolic stereoisomeric inversion of ibuprofen in mammals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1078: 411–417.
Gandolfi R, Gualandris R, Zanchi C, Molinari F (2001) Resolution of (RS)-2-phenylpropanoic acid by enantioselective esterification with dry microbial cells in organic solvent. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 12: 501–504.
Gu QM, Chen CS, Sih CJ (1986) A facile enzymatic resolution process for the preparation of (+)-S-2-(6-methoxy-2-naphthyl)propionic acid (Naproxen). Tetrahedron Lett. 27: 1763–1766.
Hall SD, Xiaotao Q (1994) The role of coenzyme A in the biotransformation of 2-arylpropionic acid. Chem. Biol. Interact. 90: 235–251.
Hanlon GW, Kooloobandai A, Hutt AJ (1994) Microbial metabolism of 2-arylpropionic acid: effect of environmental on the metabolism of ibuprofen by Verticillum lecanii. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 76: 442–447.
Hung YF, ThomasonMJ, Rhys-WilliamsW, Lloyd AW, Hanlon GW (1996) Chiral inversion of 2-phenylpropionic acid by Cordyceps militalis. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 81: 242–250.
Hutt AJ, Kooloobandai A, Hanlon GW (1993) Microbial metabolism of 2-arylpropionic acids: chiral inversion of ibuprofen and 2-phenylpropionic acid. Chirality 5: 596–601.
Kato D, Mitsuda S, Ohta H (2002) Microbial deracemization of alpha-substituted carboxylic acids. Org. Lett. 4: 371–373.
Kato K, Gong Y, Tanaka S, Katayama M, Kimoto H (1999) Optical resolution of 2-(3-indolyl)propionic acid with Mucor javanicus and α-chymotrypsin. Biotechnol. Lett. 21: 457–461.
Knihinicki RD, Day RO, Williams KM (1991) Chiral inversion of 2-arylpropionic acid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-II. Racemization and hydrolysis of (R)-and (S)-ibuprofen-CoA thioesterase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 42: 1905–1911.
Knights KM, Talbot, UM, Baillie TA (1992) Evidence of multiple forms of rat liver microsomal coenzyme A ligase catalyzing the formation of 2-arylpropionyl-coenzyme A thioesters. Biochem. Pharmacol. 44: 2415–2417.
Landoni MF, Soraci A (2001) Pharmacology of chiral compounds: 2-arylpropionic acid derivatives. Curr Drug. Metab. 2: 37–51.
Lee EDJ, Williams KM, Graham GG, Day RO, Champion GD (1984) Liquid chromatographic determination and plasma concentration profile of optical isomers of ibuprofen in mammals. J. Pharm. Sci. 73: 1542–1544.
López-Belmonte MT, Alcántara AR, Sinisterra JV (1997) Enantioselective esterification of 2-arylpropionic acids catalyzed by immobilized Rhizomucor miehei lipase. J. Org. Chem. 62: 1831–1840.
Morrone R, Nicolosi G, Patti A, Piatelli M (1995) Resolution of racemic flurbiprofen by lipase-mediated esterification in organic solvent. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 6: 1773–1178.
Mustranta A (1992) Use of lipases in the resolution of racemic ibuprofen. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38: 61–66.
Phillips GT (1990) Biotransformations and their role in industrial synthesis. In: Proceeding of the Chiral 90 Symposium, pp. 17–22.
Rantakylä M, Aaltonen O (1994) Enantioselective esterification of ibuprofen in supercritical carbon dioxide by immobilized lipase. Biotechnol. Lett. 16: 825–830.
Reichel C, Bang H, Brune K, Geisslinger G, Menzel S (1995) 2-Arylpropionyl-CoA epimerase, partial peptide sequences and tissue localization. Biochem. Pharmacol. 50: 1803–1806.
Reichel C, Brugger R, Bang H, Geisslinger G, Brune K (1997) Molecular cloning and expression of a 2-arylpropionyl coenzyme A epimerase: a key enzyme in the inversion metabolism of ibuprofen. Mol. Pharmacol. 51: 576–582.
Rhys-Williams W, Thomason MJ, Lloyd AW, Hanlon GW (1996) Demonstration of the chiral inversion of 2-phenylpropionic acid by cell free extract from Verticilium lecanii. Pharm. Sci. 2: 537–540.
Rhys-Williams W, McCarthy J, Baker JA, Hung YF, Thomason MJ, Lloyd AW, Hanlon GW (1998) A mechanistic inversion into the microbial chiral inversion of 2-arylpropionic acids using deuterated derivatives of 2-phenylpropionic acid. J. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 22: 281–287.
Rhys-Williams W, Thomason MJ, Hanlon GW, Lloyd AW (1998) Extent of chiral inversion of 2-arylpropionic acids by Cordyceps millitaris. Chirality 10: 528–534.
Sánchez A, Valero F, Lafuente R, Sola C (1998) Enantioselective esterification of 2-arylpropionic acids and trans-2-phenyl-1-cyclohexanol: comparison between immobilized lipases from Candida rugosa and Rhizomucor miehei. Biotechnol. Lett. 20: 1145–1148.
Sánchez A, Ferrer P, Serrano A, Valero F, Sola C, Pernas M, Rua ML, Fernandez-Lafuente, R, Guisan JM, de la Casa R, Sinisterra JV, Sánchez-Montero JM (1999) A controlled fed-batch cultivation for the production of new crude lipase from Candida rugosa with improved properties in fine chemistry. J. Biotechnol. 69: 169–182.
Sevoz C, Benoit E, Buronfosse T (2000) Thioesterification of 2-arylpropionic acid by recombinant acyl-coenzyme A synthetases (ACS1 and ACS2). Drug Metab. Dispos. 28: 398–402.
Shieh WR, Chen CS (1993) Purification and characterization of novel 2-arylpropionyl-CoA epimerase from rat liver and mitochondria. J Biol. Chem. 268: 3487–3493.
Thomason MJ, Rhys-Williams W, Lloyd AW, Hanion GW (1997) Optimization of the chiral inversion of 2-phenylpropionic acid by Verticillum lecanii. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 49: 263–269.
Thomason MJ, Rhys-Williams W, Hung YF, Baker JA, Hanlon GW, Lloyd AW (1997) A mechanistic investigation into the microbial chiral inversion of 2-phenylpropionic acid by Verticillum lecanii. Chirality 9: 254–260.
Thomason MJ, Rhys-Williams W, Lloyd AW, Hanlon GW (1998) The stereoinversion of 2-arylpropionic acid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and structurally related compounds by Verticillium lecanii. J. Appl. Microbiol. 85: 155–163.
Tracy TS, Hall SD (1991) Determination of the epimeric composition of ibuprofenyl-CoA. Anal. Biochem. 195: 24–29.
Tracy TS, Hall SD (1992) Metabolic inversion of (R)-ibuprofen, epimerization and hydrolysis of ibuprofenyl-CoA. Drug Metat. Dispos. 20: 322–327.
Tsai SW, Wei HJ (1994) Enantioselective esterification of racemic naproxen by lipases in organic solvent. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 16: 328–333.
Tsai SW, Lin BY, Chang CS (1996) Enhancement of (S)-naproxen ester productivity from racemic naproxen by lipase in organic solvents. J. Chem. Tech. Biotechnol. 65: 156–162.
Wechter WJ (1994) Drug chirality: on the mechanism of Rarylpropionic acid class NSAIDs epimerization in humans and the clinical implications for the use of racemates. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 34: 1036–1042.
Yang H, Henke E, Bornscheuer UT (1999) The use of vinyl esters significantly enhanced enantioselectivities and reaction rates in lipase-catalyzed resolutions of arylaliphatic carboxylic acids. J. Org. Chem. 64: 1709–1712.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitsukura, K., Yoshida, T. & Nagasawa, T. Synthesis of (R)-2-phenylpropanoic acid from its racemate through an isomerase-involving reaction by Nocardia diaphanozonaria . Biotechnology Letters 24, 1615–1621 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020353631566
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020353631566