Abstract
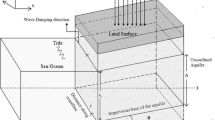
Cross-shore interactions between the ocean and a coastal aquifer have been studied extensively, whereas the corresponding along-shore case has seldom been examined. This paper presents a numerical model that simulates two-dimensional groundwater flow averaged over the thickness of a coastal aquifer. The model is used to examine the essential features of tide-induced, along-shore effects on an aquifer adjacent to a cross-shore river. The results show that the tide, which fluctuates the water level in the river, induces groundwater table fluctuations and oscillating flows in the along-shore direction. This occurs even at locations much further inland than tidal cross-shore fluctuations can propagate. However, the magnitude of along-shore water table fluctuations and flow velocity at a given cross-shore distance decreases with the distance from the river in the same manner as cross-shore tidal fluctuations. The along-shore groundwater flow, together with the cross-shore flow, forms horizontal circulation and increases mixing of solute in the aquifer. Over a tidal period, a large amount of water exchange occurs at the river-aquifer and ocean-aquifer interfaces, leading to increased transfer of chemicals between the three water bodies. These results have implications for the management of waste discharge in estuaries and coastal aquifers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.A. Barry, S.J. Barry and J.-Y. Parlange, Capillarity correction to periodic solutions of the shallow flow approximation, in: Mixing Processes in Estuaries and Coastal Seas, ed. C.B. Pattiaratchi, Coastal and Estuarine Studies, Vol. 50 (American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 1996) pp. 496–510.
J. Bear, Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media (Elsevier, New York, 1972).
N.J. Ericksen, Measurement of tide induced change to water table profiles in coarse and fine sandy beaches along Pegasus, Canterbury, Earth Sci. 4 (1970) 24–31.
H.B. Fischer, R.C.Y. Koh, J. Imberger, N.H. Brooks and E.J. List, Mixing in Inland and Coastal Waters (Academic Press, New York, 1979).
A.T. Ippen and D.R.F. Harleman, Tidal dynamics in estuaries, in: Estuary and Coastline Hydrodynamics, ed. A.T. Ippen (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1966).
G. Jacobson, P. Biewirth and T. Graham, Major environmental issues associated with coastal groundwater systems in Australia, in: Proceeding of 1st International Conference on LOICZ, Moscow, Russia (July 1996).
J.A. Lanyon, I.G. Eliot and D.J. Clarke, Groundwater level variation during semi-diurnal spring tidal cycles on a sandy beaches, Austr. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 33 (1982) 377–400.
L. Lapidus and G.F. Pinder, Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations in Science and Engineering (Wiley, New York, 1982).
L. Li, D.A. Barry and C.B. Pattiaratchi, Numerical modelling of tide-induced beach water table fluctuations, Coastal Eng. 30 (1997) 105–123.
W.S. Moore, Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by 226Ra enrichments, Nature 380 (1996) 612–614.
P. Nielsen, Tidal dynamics of the water table in beaches, Water Resour. Res. 26 (1990) 2127–2134.
J.-Y. Parlange, F. Stagnitti, J.L. Starr and R.D. Braddock, Free-surface flow in porous media and periodic solution of the shallow-flow approximation, J. Hydrol. 70 (1984) 251–263.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Barry, D., Stagnitti, F. et al. Tidal along-shore groundwater flow in a coastal aquifer. Environmental Modeling & Assessment 4, 179–188 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019043729455
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019043729455