Abstract
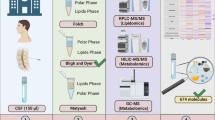
Free fatty acids (FFA) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are well-recognized markers of brain damage in animal studies. Information is limited regarding human CSF in both normal and pathological conditions. Samples of CSF from 73 patients, who had undergone lumbar puncture for medically indicated reasons, came from a core laboratory upon completion of ordered tests. Using high performance liquid chromatography, mean FFA concentrations (μg/L ± SEM) were: arachidonic 26.14 ± 3.44; docosahexaenoic 60.74 ± 5.70; linoleic 105.07 ± 10.98; myristic 160.38 ± 16.17; oleic 127.91 ± 10.13; and palmitic 638.34 ± 37.27. No differences in FFA concentrations were seen with gender, race, age, and/or indication for lumbar puncture. This is the first study to document normal human CSF FFA concentrations in a large series. Further characterization of FFA in pathological conditions may provide markers for evaluating clinical treatments and assisting in prognostication of neurological disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bazan, N. G. 1970. Effects of ischemia and electroconvulsive shock on free fatty acid pool in the brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 218:1–10.
Gardiner, M., Nilsson, B., Rehncrona, S., and Siesjo, B. K. 1981. Free fatty acids in the brain in moderate and severe hypoxia. J. Neurochem. 52:946–951.
Rehncrona, S., Westerberg, E., Akesson, B., and Siesjo, B. K. 1982. Brain cortical fatty acids and phospholipids during and following complete and severe ischemia. J. Neurochem. 38:84–93.
Yasuda, H., Kishiro, K., Izumi, N., and Nakanishi, M. 1985. Biphasic liberation of arachidonic and stearic acids during cerebral ischemia. J. Neurochem. 45:168–172.
Siesjo, B. K. 1992. Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia. Part II: Mechanisms of damage and treatment. J. Neurosurg. 77:337–354.
Dhillon, H. S., Dose, J. M., Scheff, S. W., and Prasad, M. R. 1997. Time course of changes in lactate and free fatty acids after experimental brain injury and relationship to morphologic damage. Exp. Neurol. 146:240–249.
Zamir, I., Grushka, E., and Cividalli, G. 1991. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of free palmitic and stearic acid in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Chromatogr. 565:424–429.
Berry, J. F., Bovis, M., and Logothetis, J. 1965. Determination of the fatty acid composition of cerebrospinal fluid by gas-liquid chromatography. Neurology 15:1089–1094.
Illingsworth, D. R. and Glover, J. 1971. The composition of lipids in cerebrospinal fluid of children and adults. J. Neurochem. 18:769–776.
Schippling, S., Kontush, A., Arlt, S., Buhmann, C., Sturenburg, H. J., Mann, U., Muller-Thomsen, T., and Beisiegel, U. 2000. Increased lipoprotein oxidation in Alzheimer's disease. Free Rad. Bio. Med. 28:351–360.
Estevez, A. Y. and Phillis, J. W. 1997. The phospholipase A2 inhibitor, quinacrine, reduces infarct size in rats after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Brain Res. 52:203–208.
Phillis, J. W. 1996. Cerebroprotective action of the phospholipase inhibitor quinacrine in the ischemia/reperfused gerbil hippocampus. Life Sci. 58:97–101.
Powers, W. J. 1981. Cerebrospinal fluid to serum glucose ratios in diabetes mellitus and bacterial meningitis. Am. J. Med. 71:217–220.
Bailey, E. M., Domenico, P., and Cunha, B. A. 1990. Bascterial or viral meningitis? Measuring lactate in CSF can help you know quickly. Postgrad. Med. 88:217–219.
Wood, R. and Lee, T. 1983. High performance liquid chromatography of fatty acids: quatitative analysis of saturated monoenoic, polyenoic, and geometrical isomers. J. Chromatogr. 254:237–246.
Mehta, A., Oeser, A., and Carlson, M. G. 1998. Rapid quantitation of free fatty acids in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 719:9–23.
Dhillon, H. S., Carman, H. M., Zhang, D., Scheff, S. W., and Prasad, M. R. 1999. Severity of experimental brain injury on lactate and free fatty acid accumulation and Evans blue extravasation in the rat cortex and hippocampus. J. Neurotrauma 16:455–469.
Sun, D. and Gilboe, D. D. 1994. Ischemia-induced changes in cerebral mitochondrial free fatty acids, phospholipids, and respiration in the rat. J. Neurochem. 62:1921–1928.
Homayoun, P., Parkins, N. E., Soblosky, J., Carey, M. E., Rodriguez de Turco, E. B., and Bazan, N. G. 2000. Cortical impact injury in rats promotes a rapid and sustained increase in polyunsaturated free fatty acids and diacylglycerols. Neurochem. Res. 25:269–276.
Pilitsis, J. G., Diaz, F. G., O'Regan, M. H., and Phillis, J. W. 2001. Inhibition of Na+/H+ exchange by SM-20220 attenuates free fatty acid efflux in rat cerebral cortex during ischemiareperfusion injury. Brain Res. 913:156–158.
Pilitsis, J. G., Diaz, F. G., O'Regan, M. H., and Phillis, J. W. 2001. Inhibition of Na+/Ca++ exchange by KB-R7943, a novel selective antagonist, attenuates phosphoethanolamine and free fatty acid efflux in rat cerebral cortex during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Res. 916:192–198.
Kubota, M., Nakane, M., Narita, K., Nakagomi, T., Tamura, A., Hisaki, H., Shimasaki, H., and Ueta, N. 1998. Mild hypothermia reduces the rate of metabolism of arachidonic acid following postischemic reperfusion. Brain Res. 779:297–300.
Westcott, J. Y., Murphy, R. C., and Stenmark, K. 1987. Eicosanoids in human ventricular cerebrospinal fluid following severe brain injury. Prostaglandins 34:877–887.
Fitzpatrick, F. A. and Soberman, R. 2001. Regulated formation of eicosanoids. J. Clin. Invest. 107:1347–1351.
Tetzloff, S. U. and Bizzozero, O. A. 1998. Palmitoylation of proteolipid protein from rat brain myelin using endogenously generated 18O-fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 273:279–285.
Kokoglu, E., Tuter, Y., Yazici, Z., Sandikci, K. S., Sonmez, H., Ulakoglu, E. Z., and Ozyurt, E. 1998. Profiles of the fatty acids in the plasma membrane of human brain tumors. Cancer Biochem. Biophys. 16:301–312.
Hanai, T., Hashimoto, T., Nishiwaki, K., Ono, M., Akomo, Y., Tanaka, M., Mizuno, I., and Yura, J. 1993. Comparison of prostanoids and their precursor fatty acids in human hepatocellular carcinoma and noncancerous reference tissues. J. Surg. Res. 54:57–60.
Pontiroli, A. E., Manzoni, M. F., Malighetti, M. E., and Lanzi, R. 1996. Restoration of growth hormone response to GH-releasing hormone in elderly and obese subjects by acute pharmacological reduction of plasma free fatty acids. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81:3998–4001.
Nam, S. Y., Kim, K. R., Lee, H. C., Nam, M. S., Cho, J. H., and Huh, K. B. 1996. Long-term administration of acipomox potentiates growth hormone response to growth hormone-releasing hormone by decreasing serum free fatty acid in obesity. Metabolism 45:594–597.
Spector, A. A. 2001. Plasma free fatty acid and lipoproteins as sources of polyunsaturated fatty acid for the brain. J. Mol. Neurosci. 16:159–165.
Reiber, H. and Peter, J. B. 2001. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: disease-related data patterns and evaluation programs. J. Neurol. Sci. 184:101–122.
Roine, R., Somer, H., Kaste, M., Viinikka, L., and Karonen, S. L. 1989. Neurological outcome after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Arch. Neurol. 46:753–756.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pilitsis, J.G., Diaz, F.G., Wellwood, J.M. et al. Quantification of Free Fatty Acids in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid. Neurochem Res 26, 1265–1270 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014227231130
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014227231130