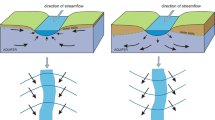
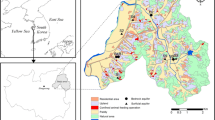
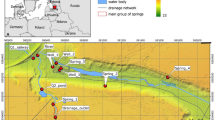
Abstract
In French Brittany, water pollution with nitrate due tointensive agriculture has become one of the major environmentalconcerns. In this article, the nitrate, sulfate and chlorideconcentrations from the groundwater and the stream of a first-order agricultural watershed, are analyzed to infer the mechanisms responsible for the distribution and transfer of nitrate within the watershed. The aquifer is constituted by three layers: the thin soil cover, the weathered shale and thefissured shale. The weathered shale groundwater appears to bea large reservoir of nitrate in the watershed. Indeed the amount of nitrate is estimated at about 450 kg N ha-1, 5 to 9 times the total annual nitrate flux in the stream. In the upslope zones, this groundwater exhibited high nitrate concentrations (up to 138.4±10.5 mg NO3 - L-1), which decreased along the flow paths towards the stream (77.1±13.8 mg NO3 - L-1). Unlike nitrate, sulfate concentrations showed an increase from uphillto downhill (from 6.1±0.8 to 12.5±5.4 mg SO4 2- L-1) with little change in chloride concentrations. These patterns are presumed to result from upward flows from fissured shale groundwater where denitrification by oxidation of pyrite occurs with sulfate as end product. A scheme of nitrate transfer is proposed where stream discharge would result from the mixing of three end members which are: uphill weathered groundwater, deep groundwater and water in the uppermost soil horizons ofthe bottomlands. Temporal variability of nitrate concentrationsin base flow reflects changes in the relative contribution of each end member.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrassart, J. and Garon, F.: 1995, ‘Flux de nutriments dans le BVRE du Coet-Dan’, Rapport d’activité du Contrat de Plan Etat-Region Bretagne, CEMAGREF, 33 pp.
Bouraoui, F., Turpin, N. and Boerlen, P.: 1999, ‘Trend Analysis of Nutrient Concentrations and Loads in Surface Water in an Intensive Fertilized Watershed’, J. Environ. Qual. 28, 1878–1885.
Böhlke, J. K. and Denver, J. M.: 1995, ‘Combined Use of Groundwater Dating, Chemical, and Isotopic Analyses to Resolve the History and Fate of Nitrate Contamination in Two Agricultural Watershed, Atlantic Coastal Plain, Maryland’, Wat. Resour. Res. 31, 2319–2339.
BRGM, 1998, ‘Capacités épuratrices des zones humides ‘Etude hydrogéologique et géochimique des zones humides ‘Relations avec les nappes d’eau souterraine’, BRGM Report 40694, 43 pp.
Burt, T. P. and Arkell, B. P.: 1987, ‘Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Nitrate Losses from an Agricultural Watershed’, Soil Use and Management 3, 138–142.
Burt, T. P., Arkell, B. P., Trudgill, S. T. and Walling, D. E.: 1988, ‘Stream Nitrate Levels in a Small Watershed in South West England over Period of 15 yr (1970-1985)’, Hydrol. Process. 2, 267–284.
Cann, C.: 1994, ‘Factors of Transfer of Nitrate to Water and Their Ways of Action’, J. Europ. Hydrol. 25, 153–167.
Crave, A. and Gascuel-Odoux, C.: 1997, ‘The Influence of the Topography on Time and Space Distribution of Soil Surface Water Content’, Hydrol. Process. 11, 203–210.
Creed, I. F. and Band, L. E.: 1998, ‘Export of Nitrogen from Watersheds Within a Temperate Forest: Evidence for a Unifying Mechanism Regulated by Variable Source Area Dynamics’, Wat. Resour. Res 34, 3105–3120.
Curmi, P., Durand, P., Gascuel-Odoux, C., Hallaire, V., Mérot, P., Robin, P., Trolard, F., Walter, C. and Bourrié, G.: 1995, ‘Le programme CORMORAN-INRA: de l’importance du milieu physique dans la régulation biogéochimique de la teneur en nitrate des eaux superficielles’, J. Europ. Hydrol. 26, 37–56.
Curmi, P., Durand, P., Gascuel-Odoux, C., Mérot, P., Walter, C. and Taha, A.: 1998, ‘Hydromorphic Soils, Hydrology and Water Quality: Spatial Distribution and Functional Modelling at Different Scales’, Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 50, 127–147.
Durand, P. and Juan-Torres, J. L.: 1996, ‘Solute Transfer in Agricultural Watersheds: The Interest and Limits of Mixing Models’, J. Hydrol. 81, 1–22.
Gineste, P., Puech, C. and Mérot, P.: 1998, ‘Radar Remote Sensing of the Source Areas from the Coet-Dan Catchment’, Hydrol. Process. 12, 267–284.
Grimaldi, C. and Chaplot V.: 2000, ‘Nitrate Depletion During Within Catchment: Effects of Exchange Processes Between Streamwater, the Hyperheic and Riparian Zone’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. (in press).
Hill, A. R.: 1996, ‘Nitrate Removal in Stream Riparian Zones’, J. Environ. Qual. 25, 743–755.
IFEN: 1997, L’environnement en France: Approche Régionale, La Découverte, Paris, France.
Larsson, U., Elmgren, R. and Wulff, F.: 1985, ‘Eutrophication of the Baltic Sea: Causes and Consequences’, Ambio 14, 9–14.
Mariotti, A.: 1997, ‘Quelques réflexions sur le cycle biogéochimique de l’azote dans les agrosystèmes’, in G. Lemaire and B. Nicolardot (eds), Maîtrise de l’azote dans les agrosystèmes, Reims, France, pp. 9–22.
Mariotti, A.: 1986, ‘La dénitrification dans les eaux souterraines, principes et méthodes de son identification: Une revue’, J. Hydrol. 88, 1–23.
Mason, J. W., Wegner, G. D., Quinn, G. I and Lange, E. L.: 1990, ‘Nutrient Loss via Groundwater Discharge from Small Watersheds in Southwestern and South-Central Wisconsin’, Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 327–331.
Mattikalli, N. M.: 1996, ‘Time Series Analysis of Historical Surface Water Quality Data of the River Glen Catchment, U.K.’, Journal of Environmental Management 46, 149–172.
Mérot, P. and Durand, P.: 1995, ‘Assessing the Representativity of Catchments According to their Size from Hydrochemical Observations’, in Effects of Scale on Interpretation and Management of Sediment and Water Quality, IAHS Publ. 226, pp. 105–112.
Molénat, J.: 1999, ‘Rôle de la nappe sur les transferts d’eau et de nitrate dans un bassin versant agricole. Etude expérimentale et modélisation’, Ph.D. Diss., Université de Rennes 1, France, 272 pp.
Molénat, J., Davy, P., Gascuel-Odoux, C. and Durand. P.: 1999, ‘Study of Three Subsurface Hydrologic Systems Based on Spectral and Cross-Spectral Analysis of Time Series’, J. Hydrol. 222, 152–164.
Morand, P. and Briand, X.: 1996, ‘Excessive Growth of Macroalgae: A Symptom of Environmental Disturbance’, Bot. Mar. 39, 491–516.
Pauwels, H.: 1994, ‘Natural Denitrification in Groundwater in the Presence of Pyrite: Preliminary Results Obtained at Naizin (Brittany, France)’, Mineralogical Magazine 58A, 696–697.
Pauwels, H., Kloppman, W., Foucher, J. C., Martelat, A. and Fritsche, V.: 1998, ‘Field Tracer Test for Denitrification in Pyrite-Bearing Schist Aquifer’, Applied Geochem. 6, 767–778.
Pionke, H. B. and DeWalle, D. R.: 1994, ‘Streamflow Generation in a Small Agricultural Catchment During Autumn Recharge: I. Nonstormflow Periods, J. Hydrol. 163, 1–22.
Somlette, L.: 1998, ‘Contribution à l’étude hydrogéologique de la distribution et du devenir des nitrates dans les nappes de fissures, de l’échelle du périmétre expérimental à celle du bassin versant côtier. Conséquences sur les ressources en eaux et la protection du littoral en Bretagne’, Ph.D. Diss., Université de Bretagne Occidentale, France, 236 pp.
Steinheimer, T. R., Scoggin, K. D. and Kramer, L. A.: 1998a, ‘Agricultural Chemical Movement Through a Field-Size Watershed in Iowa: Subsurface Hydrology and Distribution of Nitrate in Groundwater’, Environ. Sci. Tech. 32, 1039–1047.
Steinheimer, T. R., Scoggin, K. D. and Kramer, L. A.: 1998b, ‘Agricultural Chemical Movement Through a Field-Size Watershed in Iowa: Surface Hydrology and Nitrate Losses in Discharge’, Environ. Sci. Tech. 32, 1048–1052.
Widiatmaka: 1994, ‘Analyse structurale et fonctionnement hydrique d’un système pédologique li-moneux acide sur granite et sur schiste du Massif Armoricain’, Ph.D. Diss., Ecole Supérieure d’Agronomie de Rennes, France, 334 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molénat, J., Durand, P., Gascuel-Odoux, C. et al. Mechanisms of Nitrate Transfer from Soil to Stream in an Agricultural Watershed of French Brittany. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 133, 161–183 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012903626192
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012903626192