Abstract
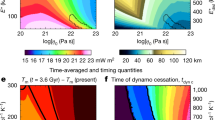
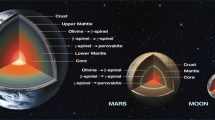
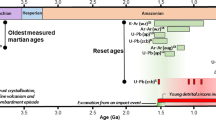
The evolution of Mars is discussed using results from the recent Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) and Mars Pathfinder missions together with results from mantle convection and thermal history models and the chemistry of Martian meteorites. The new MGS topography and gravity data and the data on the rotation of Mars from Mars Pathfinder constrain models of the present interior structure and allow estimates of present crust thickness and thickness variations. The data also allow estimates of lithosphere thickness variation and heat flow assuming that the base of the lithosphere is an isotherm. Although the interpretation is not unambiguous, it can be concluded that Mars has a substantial crust. It may be about 50 km thick on average with thickness variations of another ±50 km. Alternatively, the crust may be substantially thicker with smaller thickness variations. The former estimate of crust thickness can be shown to be in agreement with estimates of volcanic production rates from geologic mapping using data from the camera on MGS and previous missions. According to these estimates most of the crust was produced in the Noachian, roughly the first Gyr of evolution. A substantial part of the lava generated during this time apparently poured onto the surface to produce the Tharsis bulge, the largest tectonic unit in the solar system and the major volcanic center of Mars. Models of crust growth that couple crust growth to mantle convection and thermal evolution are consistent with an early 1 Gyr long phase of vigorous volcanic activity. The simplest explanation for the remnant magnetization of crustal units of mostly the southern hemisphere calls for an active dynamo in the Noachian, again consistent with thermal history calculations that predict the core to become stably stratified after some hundred Myr of convective cooling and dynamo action. The isotope record of the Martian meteorites suggest that the core formed early and rapidly within a few tens of Myr. These data also suggest that the silicate rock component of the planet was partially molten during that time. The isotope data suggest that heterogeneity resulted from core formation and early differentiation and persisted to the recent past. This is often taken as evidence against vigorous mantle convection and early plate tectonics on Mars although the latter assumption can most easily explain the early magnetic field. The physics of mantle convection suggests that there may be a few hundred km thick stagnant, near surface layer in the mantle that would have formed rapidly and may have provided the reservoirs required to explain the isotope data. The relation between the planform of mantle convection and the tectonic features on the surface is difficult to entangle. Models call for long wavelength forms of flow and possibly a few strong plumes in the very early evolution. These plumes may have dissolved with time as the core cooled and may have died off by the end of the Noachian.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña, M.H., et al.:1998, 'Magnetic Field and Plasma Observations at Mars: Initial Results of the Mars Global Surveyor Mission', Science 279, 1676-1680.
Acuña, M.H., et al.:1999, 'Global Distribution of Crustal Magnetism Discovered by the Mars Global Surveyor MAG/ER Experiment', Science 284, 790-793.
Anderson, R.C., et al.:2000, 'Primary Centers and Secondary Concentrations of Tectonic Activity Through Time in the Western Hemisphere of Mars', J. Geophys. Res., in press.
Bandfield, J.L., Hamilton, V.E., and Christensen, P.R.: 2000, 'A Global View of Martian Surface Compositions from MGS-TES', Science 287, 1626-1630.
Banerdt, W.B., Golombek, M.P., and Tanaka, K.L.:1992, 'Stress and Tectonics on Mars', in H.H. Kieffer, B.M. Jakosky, C.W. Snyder, and M.S. Matthews (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 249-297.
Banerdt, W.B., and Golombek, M.P.: 2000, 'Tectonics of the Tharsis Region, Insights from MGS Topography and Gravity', Proc. 31 st Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 2038.
Bertka, C. M. and Fei, Y.: 1997, 'Mineralogy of the Martian Interior up to Core-Mantle Boundary Pressures', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 5251-5264.
Bertka, C. M. and Fei, Y.: 1998, 'Density Profile of an SNC Model Martian Interior and the Moment of Inertia Factor of Mars', Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 157, 79-88.
Benz, W., and Cameron, A.G.W.: 1990, 'Terrestrial Effect of the Giant Impact', in H.E. Newsom and J.H. Jones (ed.), Origin of the Earth, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 61-67.
Braginsky, S. I.: 1964, 'Magnetohydrodynamics of the Earth's Core', Geomag. Aeron. 4, 698-712.
Breuer, D., and Spohn, T.: 1993, 'Cooling of the Earth, Urey Ratios, and the Problem of Potassium in the Core', Geophys. Res. Lett. 20, 1655-1658.
Breuer, D., Spohn, T., and Wüllner, U.: 1993. 'Mantle Differentiation and the Crustal Dichotomy of Mars', Planet. Space Sci. 41, 269-283.
Breuer, D., Zhou, H., Yuen, D.A., and Spohn, T.: 1996, 'Phase Transitions in the Martian Mantle: Implications for the Planet's Volcanic Evolution', J. Geophys. Res. 101, 7531-7542.
Breuer, D., Yuen, D.A., and Spohn, T.: 1997, 'Phase Transitions in the Martian Mantle: Implications for Partially Layered Convection', Earth Planet. Sci Lett. 148, 457-469.
Breuer, D., Yuen, D.A., Spohn, T., and Zhang, S.: 1998, 'Three Dimensional Models of Martian Mantle Convection with Phase Transitions', Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 229-232.
Breuer, D., and Spohn, T.: 2001a, 'Thermal, Volcanic, and Magnetic Field History of Mars', Planet. Space Sci., submitted.
Breuer, D., and Spohn, T.: 2001b, 'Plate Tectonics Versus one-Plate Tectonics on Mars: Constraints From the Crustal Evolution', J. Geophys. Res., submitted.
Bruhn, D., Groebner, N., and Kohlstedt, D. L.: 2000, 'An Interconnected Network of Core-forming Melts Produced by Shear Deformation', Nature 403, 883-886.
Carr, M.H.: 1996, 'Water on Mars', Oxford Univ. Press, New York.
Chen, J.H., and Wasserburg, G.J.: 1986, 'Formation Ages and Evolution of Shergotty and its Parent Planet From U-Th-Pb Systematics', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 955-968.
Chopelas, A., Boehler, R., and Ko, T.: 1994, 'Thermodynamics and Behavior of γ-Mg2SiO4 at High Pressure: Implications for Mg2SiO4 Phase Equilibrium', Phys. Chem. Min. 21, 351-359.
Connerney, J.E.P., et al.: 1999, 'Magnetic Lineations in the Ancient Crust of Mars', Science 284, 794-798.
Curtis, S.A., and Ness, N.F.: 1988, 'Remanent Magnetism at Mars', Geophys. Res. Lett. 15, 737-739.
Davaille, A., and Jaupart, C.: 1993, 'Transient High-Rayleigh-Number Thermal Convection With Large Viscosity Variations', J. Fluid Mech. 253, 141-166.
Davies, G.F., and Arvidson, R.E.: 1981, 'Martian Thermal History, Core Segregation, and Tectonics', Icarus 45, 339-346.
Dreibus, G., and Wänke, H.: 1985, 'Mars: A Volatile Rich Planet', Meteoritics 20, 367-382.
Fei, Y., Prewitt, C.T., Mao, H.K., and Bertka, C.M.:1995, 'Structure and Density of FeS at High Pressure and High Temperature and the Internal Structure of Mars', Science 268, 1892-1894.
Folkner, W.M., Yoder, C.F., Yuan, D.N., Standish, E.M., and Preston, R.A.:1997, 'Interior Structure and Seasonal Mass Redistribution of Mars From Radio Tracking of Mars Pathfinder, Science 278, 1749-1752.
Grasset, O., and Parmentier, E.M.:1998, 'Thermal Convection in a Volumetrically Heated, Infinite Prandtl Number Fluid With Strongly Temperature-Dependent Viscosity:Implications for Planetary Thermal Evolution, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 18,171-18,181.
Greeley, R., and Spudis, N.F.:1978, 'Volcanism in the Cratered Terrain Hemisphere of Mars', Geophys. Res. Lett. 5, 453-455.
Greeley, R., and Schneid, B.D.:1991, 'Magma Generation on Mars: Amounts/Rates, and Comparisons With Earth, Moon, and Venus', Science 254, 996-998.
Greeley, R., Bridges, N.T., Crown, D.A., Crumpler, L.S., Fagents, S.A., Mouginis-Mark, P.J., and Zimbleman, J.R.:2000, 'Volcanism on the Red Planet: Mars', in J.R. Zimbelmann and T.K.P. Gregg (eds.), Environmental Effects on Volcanic Eruptions: from Deep Oceans to Deep Space, Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publ., New York, pp. 75-112.
Halliday, A.N., and Lee, D.-C.:1999, 'Tungsten Isotopes and the Early Development of the Earth and Moon', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 63, 4157-4179.
Halliday, A.N., Birck, J.L., Clayton, R.N., and Wänke, H.:2001, 'The Accretion, Composition and Early Differentiation of Mars', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Harder, H.:2000, 'Mantle Convection and the Dynamic Geoid of Mars', Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 301-304.
Harder, H., and Christensen, U.:1996, 'A One-Plume Model of Martian Mantle Convection, Nature 380, 507-509.
Harper, C.L., Nyquist, L.E., Bansal, B., Wiesmann, H., and Shih C.-Y.:1995, 'Rapid Accretion and Early Differentiation of Mars Indicated by 142Nd/144Nd in SNC Meteorites', Science 267, 213-217.
Harri, A.M., et al.:2000, 'Network Science Landers for Mars', Adv. Space Res., in press.
Hartmann, W.K., and Berman, D.C.:2000, 'Elysium Planitia Lava Flows: Crater Count Chronology and Geological Implications', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 15,011-15,026.
Hartmann, W.K., Malin M.C., McEwen, A., Carr, M., Soderblom, L., Thomas, P., Danielson, E., James, P., and Veverka, J.:1999, 'Recent Volcanism on Mars from Crater Counts', Nature 397, 586-589.
Hartmann, W.K., and Neukum, G.:2001, 'Cratering Chronoloy and the Evolution of Mars', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Hartmann, W.K., Kallenbach, R., Geiss, J., and Turner, G.:2001, 'Summary:New Views and New Directions in Mars Research', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Head, J.W., Greeley, R., Golombek, M.P., Hartmann, W.K., Hauber, E., Jaumann, R., Masson, P., Neukum, G., Nyquist, L.E., and Carr, M.H.:2001, 'Geological Processes and Evolution', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Jagoutz, E., Sorowka, A., Vogel, J.D., and Wänke, H.:1994, 'ALH84001: Alien or Progenitor of the SNC Family', Meteoritics 28, 548-579.
Jault, D.:1996, 'Sur l'Inhibition de la régénération du Champ Magnétique dans Certains Modèles de Dynamo Planétaire en Présence d'une Graine Solide', C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 323, 451-458.
Lee, D.-C., and Halliday, A.N.:1997, 'Core Formation on Mars and Differentiated Asteroids', Nature 388, 854-857.
Leweling, M., and Spohn, T.:1997, 'Mars: a Magnetic Field due to Thermoremanence?', Planet. Space Sci. 45, 1389-1400.
Lodders K.,:1998, 'A Survey of Shergottite, Nakhlite and Chassigny Meteorites Whole-rock Compositions', Met. Planet. Sci. 33, A183-A190.
Longhi, J., Knittle, E., Holloway, J.R., and Wänke, H.:1992, 'The Bulk Composition, Mineralogy, and Internal Structure of Mars', in H.H. Kieffer et al. (eds.), Mars, University of Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 184-208.
Matyska, C., Yuen, D., Breuer, D., and Spohn, T.:1998, 'Symmetries of Volcanic Distributions on Mars and its Interior Dynamics', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 28,587-28,597.
McEwen, A.S., Malin, M.C., Carr, M.H., and Hartmann, W.K.:1999, 'Voluminous Volcanism on Early Mars Revealed in Valles Marineris', Nature 397, 584-586.
Moresi, L.N., and Solomatov, V.S.:1995, 'Numerical Investigation of 2D Convection With Extremely Large Viscosity Variations', Phys. Fluids 7, 2154-2162.
Mouginis-Mark, P.J., Wilson, L., and Zuber, M. T.:1992, 'The Physical Volcanology of Mars', in H.H. Kieffer et al. (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 424-452.
Ness, N.F., et al.:1999, 'MGS Magnetic Fields and Electron Reflectometer Investigation: Discovery of Paleomagnetic Fields due to Crustal Remanence', Adv. Space Res. 23, 1879-1886.
Neukum, G., and Hiller, H.:1981, 'Martian Ages', J. Geophys. Res. 86, 3097-3121.
Nimmo, F., and Stevenson, D.J., 2000, 'Influence of Early Plate Tectonics on the Thermal Evolution and Magnetic Field of Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 105, 11,969-11,979.
Nyquist, K., Bogard, D., Shih, C.-Y., Greshake, A., Stöffler, D., and Eugster, O.:2001, 'Ages and Geologic Histories of Martian Meteorites', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Phillips, R.J, et al.:2001, 'Ancient Geodynamics and Global Scale Hydrology on Mars', Science, in press.
Pike, R.J.:1978, 'Volcanoes on the Inner Planets: Some Preliminary Comparison of Gross Topography', Proc. 9 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 3239-3273.
Plescia, J.B., and Saunders, R.S.:1979, 'The Chronology of the Martian Volcanoes', Proc. 10 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 2841-2859.
Reasenberg, R.D., Shapiro, I.I., and White, R.D.:1975, 'The Gravity Field of Mars', Geophys. Res. Lett. 2, 89-92.
Richter, F.M., Nataf, H.C., and Daly, S.F.:1983, 'Heat Transfer and Horizontally Averaged Temperature of Convection With Large Viscosity Variations', J. Fluid Mech. 129, 173-192.
Rieder, R., Economou, T., Wänke, H., Turkevich, A., Crisp, J., Brückner, J., Dreibus, G., McSween, H.Y., Jr.:1997, 'The Chemical Composition of Martian Soil and Rocks Returned by the Mobile APXS:Preliminary Results from the X-ray Mode', Science 278, 1771-1774.
Schubert, G., Cassen, P., and Young, R.E.:1979, 'Subsolidus Convective Cooling Histories of Terrestrial Planets, Icarus 38, 192-211.
Schubert, G., and Spohn, T.:1990, 'Thermal History of Mars and the Sulfur-Content of its Core', J. Geophys. Res. 95, 14,095-14,104.
Schubert, G., Solomon, S.C., Turcotte, D.L., Drake, M.J., Sleep, N.H.:1992, 'Origin and Thermal Evolution of Mars', in H.H. Kieffer et al. (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 147-183.
Schubert, G., Russel C.T., Moore, W.B.L.:2000, 'Timing of the Martian Dynamo', Science 408, 666-667.
Schultz, R.A., and Tanaka, K.L.:1994, 'Lithospheric-Scale Buckling and Thrust Structures on Mars: The Coprates Rise and South Tharsis Ridge Belt', J. Geophys. Res. 99, 8371-8385.
Sleep, N.H.:1994, 'Martian Plate Tectonics', J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5639-5655.
Smith, D.E., et al.:1999a, 'The Global Topography of Mars and Implication for Surface Evolution', Science 284, 1495-1503.
Smith, D.E., Sjogren, W.L., Tyler, G.L., Balmino, G., Lemoine, F.G., and Konopliv, A.S.:1999b, 'The Gravity Field of Mars:Results from Mars Global Surveyor', Science 286, 94-97.
Smith, D.E., et al.:2000, 'Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA):Experiment Summary After the First Year of Global Mapping of Mars', J. Geophys. Res., submitted.
Sohl, F., and Spohn, T.:1997, 'The Interior Structure of Mars: Implications from SNC Meteorites', J. Geophys. Res. 102, 1613-1635.
Solomatov, V. S.:1995, 'Scaling of Temperature-and Stress-Dependent Viscosity', Phys. Fluids 7, 266-274.
Spohn, T.:1991, 'Mantle Differentiation and Thermal Evolution of Mars, Mercury, and Venus', Icarus 90, 222-236.
Spohn, T., Sohl, F., and Breuer, D.:1998, 'Mars', Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 8, 181-235.
Spohn, T., Konrad, W., Breuer, D., and Ziethe, R.:2001, 'The Longevity of Lunar Volcanism:Implications of Thermal Evolution Calculations With 2D and 3D Mantle Convection Models', Icarus 149, 54-65.
Stevenson, D.J.:1990, 'Fluid Dynamics of Core Formation', in H.E. Newsom and J.H. Jones (eds.), Origin of the Earth, Oxford Univ. Press, New York, pp. 231-250.
Stevenson, D.J., and Turner, J.S.:1979, 'Fluid Models of Mantle Convection'in M.W. McElhinny (ed.), The Earth, Its Origin, Evolution, and Structure, Wiley, New York, pp. 227-263.
Stevenson, D. J., Spohn, T., and Schubert, G.:1983, 'Magnetism and Thermal Evolution of the Terrestrial Planets', Icarus 54, 466-489.
Stolper, E., Walker, D., Hager, B. H., and Hays, J. F.:1981, 'Melt Segregation From Partially Molten Source Regions:The Importance of Melt Density and Source Region Size', J. Geophys. Res. 91, 6261-6271.
Tanaka, K.L., and Davis, P.A.:1988, 'Tectonic History of the Syria Planum Province of Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 93, 14,893-14,917.
Tanaka, K.L., Isbell, N.K., Scott, D.H., Greeley, R., and Guest, J.E.:1988, 'The Resurfacing History of Mars', Proc. 18 th Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf., 665-678.
Tanaka, K. L., Golombek, M. P., and Banerdt, W. B.:1991, 'Reconciliation of Stress and Structural Histories of the Tharsis Region of Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 96, 15,617-15,633.
Tanaka, K.L., Scott, D.H., and Greeley, R.:1992, 'Global Stratigraphy', in H.H. Kieffer et al. (eds.), Mars, Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 345-382.
Tozer, D.C.:1967, 'Towards a Theory of Thermal Convection in the Mantle', in T.F. Gaskell (ed.), The Earths's Mantle, Academic Press, London, pp. 325-353.
Turcotte, D.L., and Schubert, G.:1982, Geodynamics, Wiley, New York.
Treiman, A.H., Drake, M.J., Janssens, M.-J., Wolf, R., and Ebihara, M.:1986, 'Core Formation in the Earth and Shergottite Parent Body (SPB):Chemical Evidence From Basalts', Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 1071-1091.
Wänke, H., and Dreibus, G.:1988, 'Chemical Composition and Accretion History of Terrestrial Planets', Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A325, 545-557.
Wänke, H., Brückner, J., Dreibus, G., and Ryabchikov, I.:2001, 'Chemical Composition of Rocks and Soils at the Pathfinder Site', Space Sci. Rev., this volume.
Watts, A.W., Greeley, R., and Melosh, H.J.:1991, 'The Formation of Terrains Antipodal to Major Impacts', Icarus 93, 159-168.
Weinstein, S.A.:1995, 'The Effects of a Deep Mantle Endothermic Phase Change on the Structure of Thermal Convection in Silicate Planets', J. Geophys. Res. 100, 11,719-11,728.
Wieczorek, M.A., and Phillips, R.J.:1998, 'Potential Anomalies on a Sphere: Applications to the Thickness of the Lunar Crust', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 1715-1724.
Wilhelms, D.E., and Squyres, S.W.:1984, 'The Martian Hemispheric Dichotomy may be due to a Giant Impact', Nature 309, 138-140.
Wilson, L., and Mouginis-Mark, P.J.:1987, 'Volcanic Input to the Atmosphere from Alba Patera on Mars', Nature 330, 354-357.
Wise, D.U., Golombek, M.P., and McGill, G.E.:1979, 'Tectonic Evolution of Mars', J. Geophys. Res. 84, 7934-7939.
Zhou, H., Breuer, D., Yuen, D.A., and Spohn, T.:1995, 'Phase Transitions in the Martian Mantle and the Generation of Megaplumes', Geophys. Res. Lett. 15, 1945-1948.
Zindler, A., and Hart, S.R.:1986, 'Chemical Geodynamics', Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 14, 493-571.
Zuber, M.T., et al.:2000, 'Internal Structure and Early Thermal Evolution of Mars from Mars Global Surveyor Topography and Gravity', Science 287, 1788-1793.
Zhong, S., and Zuber, M.T.:2001, 'Degree-1 Mantle Convection and Martian Crustal Dichotomy', Nature, submitted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spohn, T., Acuña, M.H., Breuer, D. et al. Geophysical Constraints on the Evolution of Mars. Space Science Reviews 96, 231–262 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011949306989
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011949306989