Abstract
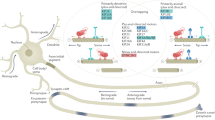
A large number of membrane-bounded organelles, protein complexes, and mRNAs are transported along microtubules to different locations within the neuronal axon. Axonal transport in the anterograde direction is carried out by members of a superfamily of specialized motor proteins, the kinesins. All kinesins contain a conserved motor domain that hydrolyses ATP to generate movement along microtubules. Regions outside the motor domain are responsible for cargo binding and regulation of motor activity. Present in a soluble, inactive form in the cytoplasm, kinesins are activated upon cargo binding. Selective targeting of different types of kinesin motors to specific cargoes is directed by amino acid sequences situated in their variable tails. Cargo proteins with specific function at their destination, bind directly to specific kinesins for transport. Whereas most kinesins move to microtubule plus-ends, a small number of them move to microtubule minus-ends, and may participate in retrograde axonal transport. Axonal transport by kinesins has a logic: Fully assembled, multisubunit, functional complexes (e.g., ion channel complexes, signaling complexes, RNA-protein complexes) are transported to their destination by kinesin motors that interact transiently (i.e., during transport only) with one of the complexes' subunits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AHMARI, S. E., BUCHANAN, J. & SMITH, S. J. (2000) Assembly of presynaptic active zones from cytoplasmic transport packets [see comments]. Nature Neuroscience 3, 445-451.
AIZAWA, H., SEKINE, Y., TAKEMURA, R., ZHANG, Z., NANGAKU, M. & HIROKAWA, N. (1992) Kinesin family in murine central nervous system. Journal of Cell Biology 119, 1287-1296.
ALLEN, R. D., WEISS, D. G., HAYDEN, J. H., BROWN, D. T., FUJIWAKE, H. & SIMPSON, M. (1985) Gliding movement of and bidirectional transport along single native microtubules from squid axoplasm: evidence for an active role of microtubules in cytoplasmic transport. Journal of Cell Biology 100, 1736-1752.
AMARATUNGA, A., LEEMAN, S. E., KOSIK, K. S. & FINE, R. E. (1995) Inhibition of kinesin synthesis in vivo inhibits the rapid transport of representative proteins for three transport vesicle classes into the axon. Journal of Neurochemistry 64, 2374-2376.
AMARATUNGA, A., MORIN, P. J., KOSIK, K. S. & FINE, R. E. (1993) Inhibition of kinesin synthesis and rapid anterograde axonal transport in vivo by an antisense oligonucleotide. Journal of Biological Chemistry 268, 17427-17430.
BAAS, P. W., DEITCH, J. S., BLACK, M. M. & BANKER, G. A. (1988) Polarity orientation of microtubules in hippocampal neurons: uniformity in the axon and nonuniformity in the dendrite. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 85, 8335-8339.
BENNETT, V. & LAMBERT, S. (1999) Physiological roles of axonal ankyrins in survival of premyelinated axons and localization of voltage-gated sodium channels. Journal of Neurocytology 28, 303-318.
BESHARSE, J. C. & HORST, C. J. (1990) The photoreceptor connecting cilium.Amodel for the transition zone. In Cilliary and Flagellar Membranes (edited by BLOODGOOD, R. A.), pp. 389-417. New York, London: Plenum Press.
BEUSHAUSEN, S., KLADAKIS, A. & JAFFE, H. (1993) Kinesin light chains: Identification and characterization of a family of proteins from the optic lobe of the squid Loligo pealii. DNA and Cell Biology 12, 901-909.
BLOOM, G. S., RICHARDS, B. W., LEOPOLD, P. L., RITCHEY, D. M. & BRADY, S. T. (1993) GTP gamma S inhibits organelle transport along axonal microtubules. Journal of Cell Biology 120, 467-476.
BOWMAN, A. B., KAMAL, A., RITCHINGS, B. W., PHILP, A. V., MCGRAIL, M., GINDHART, J. G. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (2000) Kinesin-dependent axonal transport is mediated by the sunday driver (SYD) protein. Cell 103, 583-594.
BRADY, S. T. (1985) A novel brain ATPase with properties expected for the fast axonal transport motor. Nature 317, 73-75.
BRADY, S. T., PFISTER, K. K. & BLOOM, G. S. (1990) A monoclonal antibody against kinesin inhibits both anterograde and retrograde fast axonal transport in squid axoplasm. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 87, 1061-1065.
BRENDZA, R. P., SERBUS, L. R., DUFFY, J. B. & SAXTON, W. M. (2000) A function for kinesin I in the posterior transport of oskar mRNA and Staufen protein. Science 289, 2120-2122.
BREUER, A. C., BOND, M. & ATKINSON, M. B. (1992) Fast axonal transport is modulated by altering transaxolemmal calcium flux. Cell Calcium 13, 249-262.
BURACK, M. A., SILVERMAN, M. A. & BANKER, G. (2000) The role of selective transport in neuronal protein sorting [see comments]. Neuron 26, 465-472.
CLEVELAND, D. W., MONTEIRO, M. J., WONG, P. C., GILL, S. R., GEARHART, J. D. & HOFFMAN, P. N. (1991) Involvement of neurofilaments in the radial growth of axons. Journal of Cell Science. Supplement 15, 85-95.
COLE, D. G. (1999) Kinesin-II, coming and going. Journal of Cell Biology 147, 463-466.
COLE, D. G., CHINN, S. W., WEDAMAN, K. P., HALL, K., VUONG, T. & SCHOLEY, J. M. (1993) Novel heterotrimeric kinesin-related protein purified from sea urchin eggs. Nature 366, 268-270.
COLE, D. G., DIENER, D. R., HIMELBLAU, A. L., BEECH, P. L., FUSTER, J. C. & ROSENBAUM, J. L. (1998) Chlamydomonas kinesin-II-dependent intraflagellar transport (IFT): IFT particles contain proteins required for ciliary assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans sensory neurons. Journal of Cell Biology 141, 993-1008.
CONFORTI, L., BUCKMASTER, E. A., TARLTON, A., BROWN, M. C., LYON, M. F., PERRY, V. H. & COLEMAN, M. P. (1999) The major brain isoform of kif1b lacks the putative mitochondria-binding domain. Mammalian Genome 10, 617-622.
COY, D. L., HANCOCK, W. O., WAGENBACH, M. & HOWARD, J. (1999a) Kinesin's tail domain is an inhibitory regulator of the motor domain [see comments]. Nature Cell Biology 1, 288-292.
COY, D. L. & HOWARD, J. (1994) Organelle transport and sorting in axons. Current Opinion in Neurobiology bf 4, 662-667.
COY, D. L., WAGENBACH, M. & HOWARD, J. (1999b) Kinesin takes one 8-nm step for each ATP that it hydrolyzes. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274, 3667-3671.
CYR, J. L. & BRADY, S. T. (1992) Molecular motors in axonal transport. Cellular and molecular biology of kinesin. Molecular Neurobiology 6, 137-155.
CYR, J. L., PFISTER, K. K., BLOOM, G. S., SLAUGHTER, C. A. & BRADY, S. T. (1991) Molecular genetics of kinesin light chains: generation of isoforms by alternative splicing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88, 10114-10118.
DAHLSTROM, A. B., CZERNIK, A. J. & LI, J. Y. (1992) Organelles in fast axonal transport. What molecules do they carry in anterograde vs retrograde directions, as observed in mammalian systems? Molecular Neurobiology 6, 157-177.
DAHLSTROM, A. B., PFISTER, K. K. & BRADY, S. T. (1991) The axonal transport motor 'kinesin' is bound to anterogradely transported organelles: quantitative cytofluorimetric studies of fast axonal transport in the rat. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 141, 469-476.
DAY, I. S., MILLER, C., GOLOVKIN, M. & REDDY, A. S. (2000) Interaction of a kinesin-like calmodulin-binding protein with a protein kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, 13737-13745.
DE VOS, K., SEVERIN, F., VAN HERREWEGHE, F., VANCOMPERNOLLE, K., GOOSSENS, V., HYMAN, A. & GROOTEN, J. (2000) Tumornecrosis factor induces hyperphosphorylation of kinesin light chain and inhibits kinesin-mediated transport of mitochondria. Journal of Cell Biology 149, 1207-1214.
DESAI, A., VERMA, S., MITCHISON, T. J. & WALCZAK, C. E. (1999) Kin I kinesins are microtubule-destabilizing enzymes. Cell 96, 69-78.
DISTEFANO, P. S., FRIEDMAN, B., RADZIEJEWSKI, C., ALEXANDER, C., BOLAND, P., SCHICK, C. M., LINDSAY, R. M. & WIEGAND, S. J. (1992) The neurotrophins BDNF, NT-3, and NGF display distinct patterns of retrograde axonal transport in peripheral and central neurons. Neuron 8, 983-993.
DORNER, C., CIOSSEK, T., MULLER, S., MOLLER, P. H., ULLRICH, A. & LAMMERS, R. (1998) Characterization of KIF1C, a new kinesin-like protein involved in vesicle transport from the Golgi apparatus to the endoplasmic reticulum. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 20267-20275.
DORNER, C., ULLRICH, A., HARING, H. U. & LAMMERS, R. (1999) The kinesin-like motor protein KIF1C occurs in intact cells as a dimer and associates with proteins of the 14-3-3 family. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274, 33654-33660.
DUROCHER, D., HENCKEL, J., FERSHT, A. R. & JACKSON, S. P. (1999) The FHA domain is a modular phosphopeptide recognition motif. Molecular Cell 4, 387-394.
EBNETH, A., GODEMANN, R., STAMER, K., ILLENBERGER, S., TRINCZEK, B. & MANDELKOW, E. (1998) Overexpression of tau protein inhibits kinesin-dependent trafficking of vesicles, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum: implications for Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Cell Biology 143, 777-794.
ECHARD, A., JOLLIVET, F., MARTINEZ, O., LACAPERE,. J. J., ROUSSELET, A., JANOUEIX-LEROSEY, I. & GOUD, B. (1998) Interaction of a Golgi-associated kinesin-like protein with Rab6. Science 279, 580-585.
ELLURU, R. G., BLOOM, G. S. & BRADY, S. T. (1995) Fast axonal transport of kinesin in the rat visual system: functionality of kinesin heavy chain isoforms [published erratum appears in Mol Biol Cell 1995 Sep; 6(9): 1261]. Molecular Biology of the Cell 6, 21-40.
ENDOW, S. A. (1999) Determinants of molecular motor directionality. Nature Cell Biology 1, E163-167.
FAN, J. & AMOS, L. A. (1994) Kinesin light chain isoforms in Caenorhabditis elegans. Journal of Molecular Biology 240, 507-512.
FERREIRA, A., NICLAS, J., VALE, R. D., BANKER, G. & KOSIK, K. S. (1992) Suppression of kinesin expression in cultured hippocampal neurons using antisense oligonucleotides. Journal of Cell Biology 117, 595-606.
FRIEDMAN, D. S. & VALE, R. D. (1999) Single-molecule analysis of kinesin motility reveals regulation by the cargo-binding tail domain [see comments]. Nature Cell Biology 1, 293-297.
FRIEDMAN, H. V., BRESLER, T., GARNER, C. C. & ZIV, N. E. (2000) Assembly of new individual excitatory synapses: time course and temporal order of synaptic molecule recruitment [see comments]. Neuron 27, 57-69.
GALBRAITH, J. A., REESE, T. S., SCHLIEF, M. L. & GALLANT, P. E. (1999) Slow transport of unpolymerized tubulin and polymerized neurofilament in the squid giant axon. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 96, 11589-11594.
GINDHART, J. G., JR., DESAI, C. J., BEUSHAUSEN, S., ZINN, K. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1998) Kinesin light chains are essential for axonal transport in Drosophila. Journal of Cell Biology 141, 443-454.
GOLDSTEIN, L. S. & GUNAWARDENA, S. (2000) Flying through the drosophila cytoskeletal genome. Journal of Cell Biology 150, F63-68.
GOLDSTEIN, L. S. & PHILP, A. V. (1999) The road less traveled: emerging principles of kinesin motor utilization. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 15, 141-183.
GOLDSTEIN, L. S. & YANG, Z. (2000) Microtubule-based transport systems in neurons: the roles of kinesins and dyneins. Annual Review of Neuroscience 23, 39-71.
GONG, T. W., WINNICKI, R. S., KOHRMAN, D. C. & LOMAX, M. I. (1999)A novel mouse kinesin of theUNC-104/KIF1 subfamily encoded by the Kif1b gene. Gene 239, 117-127.
GYOEVA, F. K., BYBIKOVA, E. M. & MININ, A. A. (2000) An isoform of kinesin light chain specific for the Golgi complex. Journal of Cell Science 113, 2047-2054.
HACKNEY, D. D. (1994) Evidence for alternating head catalysis by kinesin during microtubule-stimulated ATP hydrolysis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 91, 6865-6869.
HACKNEY, D. D., LEVITT, J. D. & SUHAN, J. (1992) Kinesin undergoes a 9 S to 6 S conformational transition. Journal of Biological Chemistry 267, 8696-8701.
HALL, D. H. & HEDGECOCK, E. M. (1991) Kinesin-related gene unc-104 is required for axonal transport of synaptic vesicles in C. elegans. Cell 65, 837-847.
HANADA, T., LIN, L., TIBALDI, E. V., REINHERZ, E. L. & CHISHTI, A. H. (2000) GAKIN, a novel kinesinlike protein associates with the human homologue of the Drosophila discs large tumor suppressor in T lymphocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, 28774-28784.
HANCOCK, W. O. & HOWARD, J. (1998) Processivity of the motor protein kinesin requires two heads. Journal of Cell Biology 140, 1395-1405.
HANLON, D. W., YANG, Z. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1997) Characterization of KIFC2, a neuronal kinesin superfamily member in mouse. Neuron 18, 439-451.
HEIDEMANN, S. R., LANDERS, J. M. & HAMBORG, M. A. (1981) Polarity orientation of axonal microtubules. Journal of Cell Biology 91, 661-665.
HIROKAWA, N. (1994) Microtubule organization and dynamics dependent on microtubule-associated proteins. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 6, 74-81.
HIROKAWA, N. (1996) The molecular mechanism of organelle transport along microtubules: the identification and characterization of KIFs (kinesin superfamily proteins). Cell Structure and Function 21, 357-367.
HIROKAWA, N. (1998) Kinesin and dynein superfamily proteins and the mechanism of organelle transport. Science 279, 519-526.
HIROKAWA, N., FUNAKOSHI, T., SATO-HARADA, R. & KANAI, Y. (1996) Selective stabilization of tau in axons and microtubule-associated protein 2C in cell bodies and dendrites contributes to polarized localization of cytoskeletal proteins in mature neurons. Journal of Cell Biology 132, 667-679.
HIROKAWA, N., PFISTER, K. K., YORIFUJI, H., WAGNER, M. C., BRADY, S. T. & BLOOM, G. S. (1989) Submolecular domains of bovine brain kinesin identified by electron microscopy and monoclonal antibody decoration. Cell 56, 867-878.
HIROKAWA, N., SATO-YOSHITAKE, R., KOBAYASHI, N., PFISTER, K. K., BLOOM, G. S. & BRADY, S. T. (1991) Kinesin associates with anterogradely transported membranous organelles in vivo. Journal of Cell Biology 114, 295-302.
HIROKAWA, N., SATO-YOSHITAKE, R., YOSHIDA, T. & KAWASHIMA, T. (1990) Brain dynein (MAP1C) localizes on both anterogradely and retrogradely transported membranous organelles in vivo. Journal of Cell Biology 111, 1027-1037.
HOANG, E., BOST-USINGER, L. & BURNSIDE, B. (1999) Characterization of a novel C-kinesin (KIFC3) abundantly expressed in vertebrate retina and RPE. Experimental Eye Research 69, 57-68.
HOLLENBECK, P. J. & SWANSON, J. A. (1990) Radial extension of macrophage tubular lysosomes supported by kinesin. Nature 346, 864-866.
HUANG, J. D., BRADY, S. T., RICHARDS, B. W., STENOLEN, D., RESAU, J. H., COPELAND, N. G. & JENKINS, N. A. (1999) Direct interaction of microtubule-and actin-based transport motors [see comments]. Nature 397, 267-270.
HURD, D. D. & SAXTON, W. M. (1996) Kinesin mutations cause motor neuron disease phenotypes by disrupting fast axonal transport in Drosophila. Genetics 144, 1075-1085.
HURD, D. D., STERN, M. & SAXTON, W. M. (1996) Mutation of the axonal transport motor kinesin enhances paralytic and suppresses Shaker in Drosophila. Genetics 142, 195-204.
JONES, D. H., LEY, S. & AITKEN, A. (1995) Isoforms of 14-3-3 protein can form homo-and heterodimers in vivo and in vitro: implications for function as adapter proteins. FEBS Letters 368, 55-58.
KAETHER, C., SKEHEL, P. & DOTTI, C. G. (2000) Axonal membrane proteins are transported in distinct carriers: a two-color video microscopy study in cultured hippocampal neurons. Molecular Biology of the Cell 11, 1213-1224.
KAMAL, A., STOKIN, G. B., YANG, Z., XIA, C. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (2000) Axonal transport of amyloid precursor protein is mediated by direct binding to the kinesin light chain subunit of kinesin-I. Neuron 28, 449-459.
KANAI, Y., OKADA, Y., TANAKA, Y., HARADA, A., TERADA, S. & HIROKAWA, N. (2000) KIF5C, a novel neuronal kinesin enriched in motor neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 20, 6374-6384.
KANJE, M., EDSTROM, A. & HANSON, M. (1981) Inhibition of rapid axonal transport in vitro by the ionophores X-537 A and A 23187. Brain Research 204, 43-50.
KARKI, S. & HOLZBAUR, E. L. (1999) Cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin in cell division and intracellular transport. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 11, 45-53.
KHODJAKOV, A., LIZUNOVA, E. M., MININ, A. A., KOONCE, M. P. & GYOEVA, F. K. (1998) A specific light chain of kinesin associates with mitochondria in cultured cells. Molecular Biology of the Cell 9, 333-343.
KIKKAWA, M., OKADA, Y. & HIROKAWA, N. (2000) 15 A resolution model of the monomeric kinesin motor, KIF1A. Cell 100, 241-252.
KIM, A. J. & ENDOW, S. A. (2000) A kinesin family tree. Journal of Cell Science 113, 3681-3682.
KLOPFENSTEIN, D. R., VALE, R. D. & ROGERS, S. L. (2000) Motor protein receptors. Moonlighting on other jobs. Cell 103, 537-540.
KOHRMANN, M., LUO, M., KAETHER, C., DESGROSEILLERS, L., DOTTI, C. G. & KIEBLER, M. A. (1999) Microtubule-dependent recruitment of Staufen-green fluorescent protein into large RNA containing granules and subsequent dendritic transport in living hippocampal neurons. Molecular Biology of the Cell 10, 2945-2953.
KONDO, S., SATO-YOSHITAKE, R., NODA, Y., AIZAWA, H., NAKATA, T., MATSUURA, Y. & HIROKAWA, N. (1994) KIF3A is a new microtubulebased anterograde motor in the nerve axon. Journal of Cell Biology 125, 1095-1107.
KREITZER, G., LIAO, G. & GUNDERSEN, G. G. (1999) Detyrosination of tubulin regulates the interaction of intermediate filaments with microtubules in vivo via a kinesin-dependent mechanism. Molecular Biology of the Cell 10, 1105-1118.
KUMAR, J., YU, H. & SHEETZ, M. P. (1995) Kinectin, an essential anchor for kinesin-driven vesicle motility. Science 267, 1834-1837.
KUZNETSOV, S. A., LANGFORD, G. M. & WEISS, D. G. (1992) Actin-dependent organelle movement in squid axoplasm. Nature 356, 722-725.
LAFERRIERE, N. B., MACRAE, T. H. & BROWN, D. L. (1997) Tubulin synthesis and assembly in differentiating neurons. Biochemistry and Cell Biology 75, 103-117.
LANGFORD, G. M. (1995) Actin-and microtubuledependent organelle motors: interrelationships between the two motility systems. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 7, 82-88.
LASEK, R. J. & BRADY, S. T. (1982) The axon: A prototype for studying expressional cytoplasm. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 46, 113-124.
LASEK, R. J., GARNER, J. A. & BRADY, S. T. (1984) Axonal transport of the cytoplasmic matrix. Journal of Cell Biology 99, 212s-221s.
LE BOT, N., ANTONY, C., WHITE, J., KARSENTI, E. & VERNOS, I. (1998) Role of xklp3, a subunit of the Xenopus kinesin II heterotrimeric complex, in membrane transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. Journal of Cell Biology 143, 1559-1573.
LEE, K. D. & HOLLENBECK, P. J. (1995) Phosphorylation of kinesin in vivo correlates with organelle association and neurite outgrowth. Journal of Biological Chemistry 270, 5600-5605.
LI, H. P., LIU, Z. M. & NIRENBERG, M. (1997) Kinesin-73 in the nervous system of Drosophila embryos. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 94, 1086-1091.
LIAO, G. & GUNDERSEN, G. G. (1998) Kinesin is a candidate for cross-bridging microtubules and intermediate filaments. Selective binding of kinesin to detyrosinated tubulin and vimentin. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 9797-9803.
LINDESMITH, L., MCILVAIN, J. M., JR., ARGON, Y. & SHEETZ, M. P. (1997) Phosphotransferases associated with the regulation of kinesin motor activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry 272, 22929-22933.
LIPPINCOTT-SCHWARTZ, J., COLE, N. B., MAROTTA, A., CONRAD, P. A. & BLOOM, G. S. (1995) Kinesin is the motor for microtubule-mediated Golgi-to-ER membrane traffic [published errata appear in J Cell Biol 1995 Mar 128(5):following 988 and 1995 May, 129(3):893]. Journal of Cell Biology 128, 293-306.
LOPEZ, L. A. & SHEETZ, M. P. (1993) Steric inhibition of cytoplasmic dynein and kinesin motility by MAP2. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 24, 1-16.
MANNING, B. D. & SNYDER, M. (2000) Drivers and passengers wanted! the role of kinesin-associated proteins. Trends in Cell Biology 10, 281-289.
MARSZALEK, J. R. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (2000) Understanding the functions of kinesin-II. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1496, 142-150.
MARSZALEK, J. R., LIU, X., ROBERTS, E. A., CHUI, D., MARTH, J. D., WILLIAMS, D. S. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (2000) Genetic evidence for selective transport of opsin and arrestin by kinesin-II in mammalian photoreceptors. Cell 102, 175-187.
MARSZALEK, J. R., WEINER, J. A., FARLOW, S. J., CHUN, J. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1999) Novel dendritic kinesin sorting identified by different process targeting of two related kinesins: KIF21A and KIF21B. Journal of Cell Biology 145, 469-479.
MARTIN, M. A. E. & SAXTON, W. M. (1999) Kinesins in the nervous system. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 56, 200-216.
MATTHIES, H. J., MILLER, R. J. & PALFREY, H. C. (1993) Calmodulin binding to and cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of kinesin light chains modulate kinesin ATPase activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry 268, 11176-11187.
MOHR, E. (1999) Subcellular RNA compartmentalization. Progress in Neurobiology 57, 507-525.
MORFINI, G., QUIROGA, S., ROSA, A., KOSIK, K. & CACERES, A. (1997) Suppression of KIF2 in PC12 cells alters the distribution of a growth cone nonsynaptic membrane receptor and inhibits neurite extension. Journal of Cell Biology 138, 657-669.
MORGANS, C. W. (2000) Presynaptic proteins of ribbon synapses in the retina. Microscopy Research and Technique 50, 141-150.
MORRIS, R. L. & HOLLENBECK, P. J. (1993) The regulation of bidirectional mitochondrial transport is coordinated with axonal outgrowth. Journal of Cell Science 104, 917-927.
MORRIS, R. L. & SCHOLEY, J. M. (1997) Heterotrimeric kinesin-II is required for the assembly of motile 9 + 2 ciliary axonemes on sea urchin embryos. Journal of Cell Biology 138, 1009-1022.
MURESAN, V., ABRAMSON, T., LYASS, A., WINTER, D., PORRO, E., HONG, F., CHAMBERLIN, N. L. & SCHNAPP, B. J. (1998) KIF3C and KIF3A form a novel neuronal heteromeric kinesin that associates with membrane vesicles. Molecular Biology of the Cell 9, 637-652.
MURESAN, V., GODEK, C. P., REESE, T. S. & SCHNAPP, B. J. (1996) Plus-end motors override minus-end motors during transport of squid axon vesicles on microtubules. Journal of Cell Biology 135, 383-397.
MURESAN, V., LYASS, A. & SCHNAPP, B. J. (1999) The kinesin motor KIF3A is a component of the presynaptic ribbon in vertebrate photoreceptors. Journal of Neuroscience 1, 1027-1037.
MURESAN, V., STANKEWICH, M. C., STEFFEN, W., MORROW, J. S., HOLZBAUR, E. L. F. & SCHNAPP, B. J. (2001) Dynactin-dependent, dynein-driven vesicle transport in the absence of membrane proteins: A role for spectrin and acidic phospholipids. Molecular Cell 7, 173-183.
NAGATA, K., PULS, A., FUTTER, C., ASPENSTROM, P., SCHAEFER, E., NAKATA, T., HIROKAWA, N. & HALL, A. (1998) The MAP kinase kinase kinase MLK2 co-localizes with activated JNK along microtubules and associates with kinesin superfamily motor KIF3. EMBO Journal 17, 149-158.
NAKAGAWA, T., SETOU, M., SEOG, D., OGASAWARA, K., DOHMAE, N., TAKIO, K. & HIROKAWA, N. (2000) A novel motor, KIF13A, transports mannose-6-phosphate receptor to plasma membrane through direct interaction with AP-1 complex. Cell 103, 569-581.
NAKATA, T. & HIROKAWA, N. (1995) Point mutation of adenosine triphosphate-binding motif generated rigor kinesin that selectively blocks anterograde lysosome membrane transport. Journal of Cell Biology 131, 1039-1053.
NANGAKU, M., SATO-YOSHITAKE, R., OKADA, Y., NODA, Y., TAKEMURA, R., YAMAZAKI, H. & HIROKAWA, N. (1994) KIF1B, a novel microtubule plus end-directed monomeric motor protein for transport of mitochondria. Cell 79, 1209-1220.
NICLAS, J., NAVONE, F., HOM-BOOHER, N. & VALE, R. D. (1994) Cloning and localization of a conventional kinesin motor expressed exclusively in neurons. Neuron 12, 1059-1072.
NIXON, R. A. (1992) Slow axonal transport. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 4, 8-14.
NODA, Y., SATO-YOSHITAKE, R., KONDO, S., NANGAKU, M. & HIROKAWA, N. (1995) KIF2 is a new microtubule-based anterograde motor that transports membranous organelles distinct from those carried by kinesin heavy chain or KIF3A/B. Journal of Cell Biology 129, 157-167.
OKADA, Y. & HIROKAWA, N. (2000) Mechanism of the single-headed processivity: diffusional anchoring between the K-loop of kinesin and the C terminus of tubulin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 97, 640-645.
OKADA, Y., SATO-YOSHITAKE, R. & HIROKAWA, N. (1995a) The activation of protein kinase A pathway selectively inhibits anterograde axonal transport of vesicles but not mitochondria transport or retrograde transport in vivo. Journal of Neuroscience 15, 3053-3064.
OKADA, Y., YAMAZAKI, H., SEKINE-AIZAWA, Y. & HIROKAWA, N. (1995b) The neuron-specific kinesin superfamily protein KIF1A is a unique monomeric motor for anterograde axonal transport of synaptic vesicle precursors. Cell 81, 769-780.
PASCHAL, B. M. & VALLEE, R. B. (1987) Retrograde transport by the microtubule-associated proteinMAP1C. Nature 330, 181-183.
PATEL, N., THIERRY-MIEG, D. & MANCILLAS, J. R. (1993) Cloning by insertional mutagenesis of a cDNA encoding Caenorhabditis elegans kinesin heavy chain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 90, 9181-9185.
PEREIRA, A. J., DALBY, B., STEWART, R. J., DOXSEY, S. J. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1997) Mitochondrial association of a plus end-directed microtubule motor expressed during mitosis in Drosophila. Journal of Cell Biology 136, 1081-1090.
PERETTI, D., PERIS, L., ROSSO, S., QUIROGA, S. & CACERES, A. (2000) Evidence for the involvement of KIF4 in the anterograde transport of L1-containing vesicles. Journal of Cell Biology 149, 141-152.
PIERCE, D. W., HOM-BOOHER, N., OTSUKA, A. J. & VALE, R. D. (1999) Single-molecule behavior of monomeric and heteromeric kinesins. Biochemistry 38, 5412-5421.
POLLARD, T. D. (2001) Genomics, the cytoskeleton and motility. Nature 409, 842-843.
PONTING, C. P. (1995) AF-6/cno: neither a kinesin nor a myosin, but a bit of both. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 20, 265-266.
PREKERIS, R. & TERRIAN, D. M. (1997) Brain myosin V is a synaptic vesicle-associated motor protein: evidence for a Ca2+-dependent interaction with the synaptobrevinsynaptophysin complex. Journal of Cell Biology 137, 1589-1601.
RAHMAN, A., FRIEDMAN, D. S. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1998) Two kinesin light chain genes in mice. Identification and characterization of the encoded proteins [published erratum appears in J Biol Chem 1998 Sep 11,273(37):24280]. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 15395-15403.
RAMEH, L. E., ARVIDSSON, A., CARRAWAY, K. L., 3RD, COUVILLON, A. D., RATHBUN, G., CROMPTON, A., VANRENTERGHEM, B., CZECH, M. P., RAVICHANDRAN, K. S., BURAKOFF, S. J., WANG, D. S., CHEN, C. S. & CANTLEY, L. C. (1997) A comparative analysis of the phosphoinositide binding specificity of pleckstrin homology domains. Journal of Biological Chemistry 272, 22059-22066.
RATNER, N., BLOOM, G. S. & BRADY, S. T. (1998) A role for cyclin-dependent kinase(s) in the modulation of fast anterograde axonal transport: effects defined by olomoucine and the APC tumor suppressor protein. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 7717-7726.
RAY, K., PEREZ, S. E., YANG, Z., XU, J., RITCHINGS, B. W., STELLER, H. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1999) Kinesin-II is required for axonal transport of choline acetyltransferase in Drosophila. Journal of Cell Biology 147, 507-518.
REESE, E. L. & HAIMO, L. T. (2000) Dynein, dynactin, and kinesin II's interaction with microtubules is regulated during bidirectional organelle transport. Journal of Cell Biology 151, 155-166.
ROGERS, G. C., HART, C. L., WEDAMAN, K. P. & SCHOLEY, J. M. (1999) Identification of kinesin-C, a calmodulin-binding carboxy-terminal kinesin in animal (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus) cells. Journal of Molecular Biology 294, 1-8.
ROGERS, K. R., GRIFFIN, M. & BROPHY, P. J. (1997a) The secretory epithelial cells of the choroid plexus employ a novel kinesin-related protein [published erratum appears in Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1998 Apr, 55(2):355]. Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research 51, 161-169.
ROGERS, S. L., TINT, I. S., FANAPOUR, P. C. & GELFAND, V. I. (1997b) Regulated bidirectional motility of melanophore pigment granules along microtubules in vitro. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 94, 3720-3725.
ROTH, D., MORGAN, A., MARTIN, H., JONES, D., MARTENS, G. J., AITKEN, A. & BURGOYNE, R. D. (1994) Characterization of 14-3-3 proteins in adrenal chromaffin cells and demonstration of isoform-specific phospholipid binding. Biochemical Journal 301, 305-310.
RUBIN, G. M., YANDELL, M. D., WORTMAN, J. R., GABOR MIKLOS, G. L., NELSON, et al., (2000) Comparative genomics of the eukaryotes. Science 287, 2204-2215.
SAITO, N., OKADA, Y., NODA, Y., KINOSHITA, Y., KONDO, S. & HIROKAWA, N. (1997) KIFC2 is a novel neuron-specific C-terminal type kinesin superfamily motor for dendritic transport of multivesicular body-like organelles. Neuron 18, 425-438.
SATO-HARADA, R., OKABE, S., UMEYAMA, T., KANAI, Y. & HIROKAWA, N. (1996) Microtubule-associated proteins regulate microtubule function as the track for intracellular membrane organelle transports. Cell Structure and Function 21, 283-295.
SATO-YOSHITAKE, R., YORIFUJI, H., INAGAKI, M. & HIROKAWA, N. (1992) The phosphorylation of kinesin regulates its binding to synaptic vesicles. Journal of Biological Chemistry 267, 23930-23936.
SCHIMMOLLER, F., ITIN, C. & PFEFFER, S. (1997) Vesicle traffic: get your coat! Current Biology 7, R235-237.
SCHNAPP, B. J. (1997) Retroactive motors. Neuron 18, 523-526.
SCHNAPP, B. J. & REESE, T. S. (1989) Dynein is the motor for retrograde axonal transport of organelles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 86, 1548-1552.
SCHNAPP, B. J., REESE, T. S. & BECHTOLD, R. (1992) Kinesin is bound with high affinity to squid axon organelles that move to the plus-end of microtubules. Journal of Cell Biology 119, 389-399.
SCHNAPP, B. J., VALE, R. D., SHEETZ, M. P. & REESE, T. S. (1985) Single microtubules from squid axoplasm support bidirectional movement of organelles. Cell 40, 455-462.
SCHOLEY, J. M. (1996) Kinesin-II, a membrane traffic motor in axons, axonemes, and spindles. Journal of Cell Biology 133, 1-4.
SCHOLEY, J. M., PORTER, M. E., GRISSOM, P. M. & MCINTOSH, J. R. (1985) Identification of kinesin in sea urchin eggs, and evidence for its localization in the mitotic spindle. Nature 318, 483-486.
SCHROER, T. A., STEUER, E. R. & SHEETZ, M. P. (1989) Cytoplasmic dynein is a minus end-directed motor for membranous organelles. Cell 56, 937-946.
SEKINE, Y., OKADA, Y., NODA, Y., KONDO, S., AIZAWA, H., TAKEMURA, R. & HIROKAWA, N. (1994) A novel microtubule-based motor protein (KIF4) for organelle transports, whose expression is regulated developmentally. Journal of Cell Biology 127, 187-201.
SETOU, M., NAKAGAWA, T., SEOG, D. H. & HIROKAWA, N. (2000) Kinesin superfamily motor protein KIF17 and mLin-10 in NMDA receptorcontaining vesicle transport. Science 288, 1796-1802.
SHAH, J. V. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (2000) Does motor protein intelligence contribute to neuronal polarity? [comment]. Neuron 26, 281-282.
SHARP, D. J., YU, W., FERHAT, L., KURIYAMA, R., RUEGER, D. C. & BAAS, P. W. (1997) Identification of a microtubule-associated motor protein essential for dendritic differentiation. Journal of Cell Biology 138, 833-843.
SHIMIZU, K., KAWABE, H., MINAMI, S., HONDA, T., TAKAISHI, K., SHIRATAKI, H. & TAKAI, Y. (1996) SMAP, an Smg GDS-associating protein having arm repeats and phosphorylated by Src tyrosine kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 271, 27013-27017.
SHIMIZU, K., SHIRATAKI, H., HONDA, T., MINAMI, S. & TAKAI, Y. (1998) Complex formation of SMAP/KAP3, a KIF3A/B ATPase motor-associated protein, with a human chromosome-associated polypeptide. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 6591-6594.
SIGNOR, D., WEDAMAN, K. P., ROSE, L. S. & SCHOLEY, J. M. (1999) Two heteromeric kinesin complexes in chemosensory neurons and sensory cilia of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular Biology of the Cell 10, 345-360.
SKOUFIAS, D. A., COLE, D. G., WEDAMAN, K. P. & SCHOLEY, J. M. (1994) The carboxyl-terminal domain of kinesin heavy chain is important for membrane binding. Journal of Biological Chemistry 269, 1477-1485.
SPRINGER, S., SPANG, A. & SCHEKMAN, R. (1999) A primer on vesicle budding. Cell 97, 145-148.
STENOIEN, D. L. & BRADY, S. T. (1997) Immunochemical analysis of kinesin light chain function. Molecular Biology of the Cell 8, 675-689.
STEWART, R. J., PESAVENTO, P. A., WOERPEL, D. N. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1991) Identification and partial characterization of six members of the kinesin superfamily in Drosophila. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88, 8470-8474.
SVOBODA, K., SCHMIDT, C. F., SCHNAPP, B. J. & BLOCK, S. M. (1993) Direct observation of kinesin stepping by optical trapping interferometry [see comments]. Nature 365, 721-727.
TAKEDA, S., YAMAZAKI, H., SEOG, D. H., KANAI, Y., TERADA, S. & HIROKAWA, N. (2000) Kinesin superfamily protein 3 (KIF3) motor transports fodrin-associating vesicles important for neurite building. Journal of Cell Biology 148, 1255-1265.
TAKEMURA, R., NAKATA, T., OKADA, Y., YAMAZAKI, H., ZHANG, Z. & HIROKAWA, N. (1996) mRNA expression of KIF1A, KIF1B, KIF2, KIF3A, KIF3B, KIF4, KIF5, and cytoplasmic dynein during axonal regeneration. Journal of Neuroscience 16, 31-35.
TANAKA, Y., KANAI, Y., OKADA, Y., NONAKA, S., TAKEDA, S., HARADA, A. & HIROKAWA, N. (1998) Targeted disruption of mouse conventional kinesin heavy chain, kif5B, results in abnormal perinuclear clustering of mitochondria. Cell 93, 1147-1158.
TERADA, S., KINJO, M. & HIROKAWA, N. (2000) Oligomeric tubulin in large transporting complex is transported via kinesin in squid giant axons. Cell 103, 141-155.
TRINCZEK, B., EBNETH, A., MANDELKOW, E. M. & MANDELKOW, E. (1999) Tau regulates the attachment/detachment but not the speed of motors in microtubule-dependent transport of single vesicles and organelles. Journal of Cell Science 112, 2355-2367.
TSAI, M. Y., MORFINI, G., SZEBENYI, G. & BRADY, S. T. (2000) Release of kinesin from vesicles by hsc70 and regulation of fast axonal transport. Molecular Biology of the Cell 11, 2161-2173.
TSUKITA, S. & ISHIKAWA, H. (1980) The movement of membranous organelles in axons. Electron microscopic identification of anterogradely and retrogradely transported organelles. Journal of Cell Biology 84, 513-530.
USUKURA, J. & YAMADA, E. (1987) Ultrastructure of the synaptic ribbons in photoreceptor cells of Rana catesbeiana revealed by freeze-etching and freeze-substitution. Cell and Tissue Research 247, 483-488.
VALE, R. D. & FLETTERICK, R. J. (1997) The design plan of kinesin motors. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 13, 745-777.
VALE, R. D., REESE, T. S. & SHEETZ, M. P. (1985) Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell 42, 39-50.
VALLEE, R. B. & SHEETZ, M. P. (1996) Targeting of motor proteins. Science 271, 1539-1544.
VERHEY, K. J., LIZOTTE, D. L., ABRAMSON, T., BARENBOIM, L., SCHNAPP, B. J. & RAPOPORT, T. A. (1998) Light chain-dependent regulation of Kinesin's interaction with microtubules. Journal of Cell Biology 143, 1053-1066.
VERHEY, K. J., MEYER, D., DEEHAN, R., BLENIS, J., SCHNAPP, B. J., RAPOPORT, T. A. & MARGOLIS, B. (2001) Cargo of kinesin identified as JIP scaffolding proteins and associated signaling molecules. Journal of Cell Biology 152, 959-970.
VERNOS, I., RAATS, J., HIRANO, T., HEASMAN, J., KARSENTI, E. & WYLIE, C. (1995) Xklp1, a chromosomal Xenopus kinesin-like protein essential for spindle organization and chromosome positioning. Cell 81, 117-127.
WALCZAK, C. E., MITCHISON, T. J. & DESAI, A. (1996) XKCM1: A Xenopus kinesin-related protein that regulates microtubule dynamics during mitotic spindle assembly. Cell 84, 37-47.
WANG, S. Z. & ADLER, R. (1995) Chromokinesin: A DNAbinding, kinesin-like nuclear protein. Journal of Cell Biology 128, 761-768.
WEDAMAN, K. P., MEYER, D. W., RASHID, D. J., COLE, D. G. & SCHOLEY, J. M. (1996) Sequence and submolecular localization of the 115-kD accessory subunit of the heterotrimeric kinesin-II (KRP85/95) complex. Journal of Cell Biology 132, 371-380.
WESTERHOLM-PARVINEN, A., VERNOS, I. & SERRANO, L. (2000) Kinesin subfamily UNC104 contains a FHA domain: boundaries and physicochemical characterization. FEBS Letters 486, 285-290.
YABE, J. T., PIMENTA, A. & SHEA, T. B. (1999) Kinesin-mediated transport of neurofilament protein oligomers in growing axons. Journal of Cell Science 112, 3799-3814.
YAFFE, M. B., RITTINGER, K., VOLINIA, S., CARON, P. R., AITKEN, A., LEFFERS, H., GAMBLIN, S. J., SMERDON, S. J. & CANTLEY, L. C. (1997) The structural basis for 14-3-3:phosphopeptide binding specificity. Cell 91, 961-971.
YAMAZAKI, H., NAKATA, T., OKADA, Y. & HIROKAWA, N. (1995) KIF3A/B: a heterodimeric kinesin superfamily protein that works as a microtubule plus end-directed motor for membrane organelle transport. Journal of Cell Biology 130, 1387-1399.
YAMAZAKI, H., NAKATA, T., OKADA, Y. & HIROKAWA, N. (1996) Cloning and characterization of KAP3: A novel kinesin superfamily-associated protein of KIF3A/3B. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 93, 8443-8448.
YANG, J. T., LAYMON, R. A. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1989) A three-domain structure of kinesin heavy chain revealed by DNA sequence and microtubule binding analyses. Cell 56, 879-889.
YANG, J. T., SAXTON, W. M., STEWART, R. J., RAFF, E. C. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1990) Evidence that the head of kinesin is sufficient for force generation and motility in vitro. Science 249, 42-47.
YANG, Z. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1998) Characterization of the KIF3C neural kinesin-like motor from mouse. Molecular Biology of the Cell 9, 249-261.
YANG, Z., HANLON, D. W., MARSZALEK, J. R. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (1997) Identification, partial characterization, and genetic mapping of kinesin-like protein genes in mouse. Genomics 45, 123-131.
YANG, Z., XIA, C., ROBERTS, E. A., BUSH, K., NIGAM, S. K. & GOLDSTEIN, L. S. (2001) Molecular cloningand functional analysis of mouse C-terminal kinesin Motor KifC3. Molecular and Cellular Biology 21, 765-770.
YONEKAWA, Y., HARADA, A., OKADA, Y., FUNAKOSHI, T., KANAI, Y., TAKEI, Y., TERADA, S., NODA, T. & HIROKAWA, N. (1998) Defect in synaptic vesicle precursor transport and neuronal cell death in KIF1A motor protein-deficient mice. Journal of Cell Biology 141, 431-441.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muresan, V. One axon, many kinesins: What's the logic?. J Neurocytol 29, 799–818 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010943424272
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010943424272