Abstract
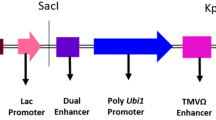
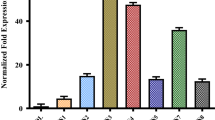
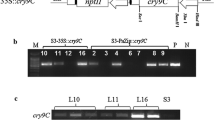
A synthetic cry1Ab gene coding for an insecticidal crystal protein (ICP) of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) was transferred to brinjal (eggplant) by cocultivating cotyledonary explants with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Transformant plants resistant to kanamycin were regenerated. Hybridization experiments demonstrated gene integration and mRNA expression. Double-antibody sandwich ELISA analysis revealed Bt toxin protein expression in the transgenic plants. The expression resulted in a significant insecticidal activity of transgenic brinjal fruits against the larvae of fruit borer (Leucinodes orbonalis). The results also demonstrated that a synthetic gene based on monocot codon usage can be expressed in dicotyledonous plants for insect control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwal AS: Agricultural Pests of India and South-East Asia. Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi (1986).
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of dye-binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254 (1976).
Clark MF, Lister RM, Bar-Joseph M: ELISA techniques. Meth Enzymol 118: 742–766 (1986).
Fischhoff DA, Bowdish KS, Perlak FJ, Marrone PG, McCormick SM, Niedermeyer JG, Dean DA, Kusano-kretzmer K, Mayer EJ, Rochester DE, Rogers SG, Fraley RT: Insect tolerant transgenic tomato plants Bio/technology 5: 807–813 (1987).
Fujimoto H, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K: Insect resistant rice generated by introduction of a modified δ-endotoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis Bio/technology 11: 1151–1155 (1993).
Hofgen R, Willmitzer L: Storage of competent cells for Agrobacterium transformation. Nucl Acids Res 16: 9877 (1988).
Hofgen R, Willmitzer L: Biochemical and genetic analysis of different patatin isoforms expressed in various organs of potato (Solanum tuberosum). Plant Sci 66: 221–230 (1990).
Hood EE, Gelvin SB, Melchers LS, Hoekema A: New Agrobacterium helper plasmids for gene transfer to plants. Transgen Res 2: 208–218 (1993).
Jansens S, Cornellissen M, De clerg R, Reynaerts A, Peferoen M: Phthorimaea operculella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) resistance in potato by expression of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab insecticidal crystal protein. J Econ Entomol 88: 1469–1476 (1995).
Koziel MG, Beland GL, Bowman C, Carozzi NB, Crenshaw R, Crossland L, Dawson J, Desai N, Hill M, Kadwell S, Launis K, Lewis K, Maddox D, McPherson K, Meghji MR, Merlin E, Rhodes R, Warren GW, Wright M, Evola SV: Field performance of elite transgenic maize plants expressing an insecticidal protein derived from Bacillus thuringiensis. Bio/technology 11: 194–200 (1993).
Kumar PA, Sharma RP: Genetic Engineering of crop plants with Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin genes. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 3: 3–9 (1994).
Kumar PA, Mohapatra T, Archak S, Sharma RP: Expression of Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin in transgenic tobacco and cauliflower. In: Chopra VL, Sharma RP, Swaminathan MS (eds) Agricultural Biotechnology, pp. 191–197, Oxford-IBH, New Delhi (1996).
Kumar PA, Sharma RP, Malik V: Insecticidal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Adv Appl Microbiol 42: 1–43 (1996).
Perlak FJ, Fuchs RL, Dean DA, McPherson SL, Fischhoff DA:Modification of the coding sequence enhances plant expression of insect control protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 3324–3328 (1991).
Perlak FJ, Deaton RW, Armstrong TA, Fuchs RL, Sims SR, Grunplate JT, Fischhoff DA: Insect resistant cotton plants. Bio/technology 8: 939–943 (1993).
Rotino GL, Gleddie S: Transformation of eggplant (Solanum melongena) using a binary Agrobacterium tumefaciens vector. Plant Cell Rep 9: 26–29 (1990).
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgenson RA, Allard RW: Ribosomal DNA spacer length polymorphism in barley. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 8014–8018 (1984).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Wunn J, Kloti A, Burkhardt PK, Ghosh Biswas GC, Launis K, Iglesias VA, Potrykus I: Transgenic indica rice breeding line IR58 expressing a synthetic cry1Ab gene from Bacillus thuringiensis provides effective insect pest control. Bio/technology 14: 171–176 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P.A., Mandaokar, A., Sreenivasu, K. et al. Insect-resistant transgenic brinjal plants. Molecular Breeding 4, 33–37 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009694016179
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009694016179