Abstract
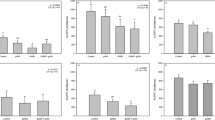
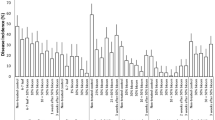
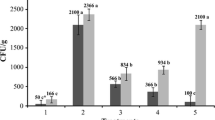
Field or greenhouse grown soybeans were treated with 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acid or benzothiadiazole and subsequently assessed for severity of white mold disease caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Three or four applications of 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acid to field plots in 1993–1995 reduced severity of white mold after natural infection by 20–70% compared with water-treated controls in soybean cultivars Elgin 87 and Williams 82, which are considered to be highly susceptible to the disease. The effect was not as large in the cultivars Corsoy 79 and NKS19-90 which are more resistant to white mold. Two or four applications of benzothiadiazole to field plots in 1995 and 1996 reduced white mold severity by 20–60%, with the greatest reductions again observed in the more susceptible cultivars. Corresponding yields were increased compared with controls, particularly for the susceptible cultivars under conditions of high disease pressure. In greenhouse trials multiple applications of either compound resulted in significantly smaller lesion diameters following subsequent leaf inoculations with the fungus. The compounds did not result in observable phytotoxicity or inhibit growth of Sclerotinia sp. in vitro. We hypothesize that the decrease in disease severity following treatment with INA or BTH is a result of resistance induction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrios GN (1997) Plant Pathology, 4th Edition. Academic Press, San Diego
Bonnet P, Bourdon E, Ponchet M, Blein J-P and Ricci P (1996) Acquired resistance triggered by elicitins in tobacco and other plants. Eur J Plant Path 102: 181-192
Caruso FL and Kuc J (1977) Field protection of cucumber, watermelon and muskmelon against Colletotrichum lagenariumby Collectrichum lagenarium. Phytopathology 67: 1290-1292
Ciba-Geigy Ltd. (1995) CGA 245704 A Plant Activator for Disease Protection. Technical Data Sheet
Dann EK and Deverall BJ (1995) Effectiveness of systemic resistance in bean against foliar and soilborne pathogens as induced by biological and chemical means. Plant Path 44: 458-466
Dann EK and Deverall BJ (1996) 2,6-dichloro-isonicotinic acid (INA) induces resistance in green beans to the rust pathogen, Uromyces appendiculatus, under field conditions. Austr Plant Path 25: 199-204
Deverall BJ (1995) Plant protection using natural defence systems of plants. Adv Plant Path 11: 211-228
Diers BW (1993) Sclerotinia stem rot (white mold) in soybean and the development of resistant varieties. In:: Wilkinson D (ed.) Proceedings of the 23rd Soybean Research Conference (pp. 51- 58)
Fehr WR, Caviness CE, Burmood DT and Pennington JS (1971) Stage of development descriptions for soybeans, Glycine max(L.) Merrill. Crop Sci 11: 929-931
Friedrich L, Lawton K, Ruess W, Masner P, Specker N, Gut Rella M, Meiers B, Dincher S, Staub T, Uknes S, Métraux JP, Kessmann H and Ryals J (1996) Abenzothiadiazole derivative induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco. Plant J 10: 61-70
Görlach J, Volrath S, KnaufBeiter G, Hengy G, Beckhove U, Kogel K-H, Oostendorp M, Staub T, Ward E, Kessmann H and Ryals J (1996) Benzothiadiazole, a novel class of inducers of systemic acquired resistance, activates gene expression and disease resistance in wheat. Plant Cell 8: 629-643
Grau CR, Radke VL and Gillespie FL (1982) Resistance of soybean cultivars to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Plant Dis 66: 506-508
Hammerschmidt R and Kuc J (1995) Induced Resistance to Disease in Plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Amsterdam
Hammerschmidt R and Dann EK (1997) Induced resistance to disease. In: Rechcigl N and Rechcigl J (eds) Environmentally Safe Approaches to Crop Disease Control. CRC Press (in press)
Kessmann H, Ryals J, Staub T, Oostendorp M, Ahl Goy P, Hofmann C, Friedrich L, Delaney T, Lawton K, Weymann K, Ligon H, Vernooij B and Uknes S (1995) CGA 245704: mode of action of a new plant activator. Presentation at the International Plant Protection Congress, The Hague, The Netherlands, 2-7 July
Lawton K, Friedrich L, Hunt M, Weymann K, Delaney T, Kessmann H, Staub T and Ryals J (1996) Benzothiadiazole induces disease resistance in Arabidopsisby activation of the systemic acquired resistance signal transduction pathway. Plant J 10: 71-82
Martyn RD, Biles CL and Dillard EA (1991) Induced resistance to Fusarium wilt of watermelon under simulated field conditions. Plant Dis 75: 874-877
Métraux J-P, Ahl Goy P, Staub T, Speich J, Steinmann A, Ryals J and Ward E (1991) Induced systemic resistance in cucumber in response to 2,6-dichloro-isonicotinic acid and pathogens. In: Hennecke H and Verma DPS (eds) Advances in Molecular Genetics of Plant-Microbe Interactions Vol 1 (pp. 432-439) Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Nielsen KK, Bijsen K, Collinge DB and Mikkelsen JD (1994) Induced resistance in sugar beet against Cercospora beticola: induction by dichloroisonicotinic acid is independent of chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase transcript accumulation. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 45: 89-99
Paxton JD and Chamberlain DW (1967) Acquired local resistance of soybean to Phytophthoraspp. Phytopathology 57: 352-353
Ruess W, Kunz W, Staub T, Müller K, Poppinger N, Speich J and Ahl Goy P (1995) Plant activator CGA 245704, a new technology for disease management. Presentation at the International Plant Protection Congress, The Hague, The Netherlands, 2-7 July
Sutton DC (1982) Field protection of bean against Colletotrichum lindemuthianumby Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Austr Plant Pathol 11: 50-51
Svoboda WE and Paxton JD(1972) Phytoalexin production in locally cross-protected Harosoy and Harosoy-63 soybeans. Phytopathology 62: 1457-1460
Tuzun S, Nesmith W, Ferris RS and Kuc J (1986) Effects of stem injections with Peronospora tabacinaon growth of tobacco and protection against blue mold in the field. Phytopathology 76: 938-941
Uknes S, Mauch-Mani B, Moyer M, Potter S, Williams S, Dincher S, Chandler D, Slusarenko A, Ward E and Ryals J (1992) Acquired resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 4: 645-656
Ward ER, Uknes SJ, Williams SC, Dincher SS, Wiederhold DL, Alexander DC, Ahl Goy P, Métraux J-P and Ryals JA (1991) Coordinate gene activity in ressponse to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 3: 1085-1094
Wrather JA and Elrod JM (1990) Apparent systemic effect of Colletotrichum truncatumand C. lagenariumon the interaction between soybean and C. truncatum. Phytopathology 80: 472- 447
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dann, E., Diers, B., Byrum, J. et al. Effect of treating soybean with 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acid (INA) and benzothiadiazole (BTH) on seed yields and the level of disease caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in field and greenhouse studies. European Journal of Plant Pathology 104, 271–278 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008683316629
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008683316629