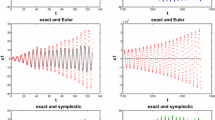
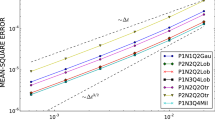
Abstract
Processing techniques are used to approximate the exact flow of near-integrable Hamiltonian systems depending on a small perturbation parameter. We study the reduction of the number of conditions for the kernel for this type of Hamiltonians and we build third, fourth and fifth order methods which are shown to be more efficient than previous algorithms for the same class of problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanes, S.: Estudio de la evolución de sistemas dinámicos clásicos y cuánticos utilizando métodos algebraicos, Ph. D. Thesis. Universitat de València, 1998.
Blanes, S., Casas, F. and Ros, J.: 'Symplectic integrators with processing: a general study', SIAM J. Sci. Comput 21 (1999), 711–727.
Butcher, J.: 'The effective order of Runge-Kutta methods', in: Conference on the numerical solution of differential equations. Lecture Notes in Math., Vol. 109, Springer, Berlin, 1969, 133–139.
Danby, J. M. A.: Fundamentals of Celestial Mechanics, Willmann-Bell, Richmond, 1988.
Gladman, B., Duncan, M. and Candy, J.: 'Symplectic integrators for long-term integrations in Celestial Mechanics', Celest. Mech. & Dyn. Astr. 52 (1991), 221–240.
Kinoshita, H. Yoshida, H. and Nakai, H.: 'Symplectic integrators and their application to Dynamical Astronomy', Celest. Mech. & Dyn. Astr. 50 (1991), 59–71.
Kirchgraber, U.: 'An ODE-solver based on the method of averaging', Numer. Math. 53 (1988), 621–652.
Koseleff, P.-V.: Formal Calculus for Lie Methods in Hamiltonian Mechanics. Ph.D. Thesis, Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory, 1994.
Liao, X.: 'Symplectic integrator for general near-integrable Hamiltonian system', Celest.Mech. & Dyn. Astr. 66 (1997), 243–253.
López-Marcos, M. A., Sanz-Serna, J. M. and Skeel, R. D.: 'Cheap enhancement of symplectic integrators', in: D. F. Griffiths and G. A. Watson (eds), Numerical Analysis 1995, Longman Harlow (Essen), 1996, pp. 107–122.
Magnus, W., Karrass, A. and Solitar, D.: Combinatorial Group Theory, 2nd revised edition, Dover, New York, 1976.
McLachlan, R. I.: 'On the numerical integration of ordinary differential equations by symmetric composition methods', SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 16 (1995), 151–168.
McLachlan, R. I.: Composition methods in the presence of small parameters, BIT 35 (1995), 258–268.
McLachlan, R. I.: 'More on symplectic correctors', In: J. E. Marsden, G. W. Patrick, and W. F. Shadwick (eds) Integration Algorithms and Classical Mechanics, American Mathematical Society, Providence, R.I., 1996, pp. 141–149.
McLachlan, R. I. and Gray, S. K.: 'Optimal stability polynomials for splitting methods, with application to the time-dependent Schrödinger equation', Appl. Numer. Math. 25 (1997), 275–286.
Meirovich, L.: Methods of Analytical Dynamics, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988.
Michel, P. and Valsecchi, G. B.: 'Numerical experiments on the efficiency of second-order mixed-variable symplectic integrators for n-body problems', Celest. Mech. & Dyn. Astr. 65 (1997), 355–371.
Mikkola, S.: 'Practical symplectic methods with time transformation for the few-body problem', Celest. Mech. & Dyn. Astr. 67 (1997), 145–165.
Okunbor, D. I. and Skeel, R. D.: 'Canonical Runge-Kutta-Nyström methods of orders five and six', J. Comp. Appl. Math. 51 (1994), 375–382.
Rowlands, G.: 'A numerical algorithm for Hamiltonian systems', J. Comput. Phys. 97 (1991), 235–239.
Saha, P. and Tremaine, S.: 'Symplectic integrators for solar system dynamics', Astron. J. 104 (1992), 1633–1640.
Sanz-Serna, J. M. and Calvo, M. P.: Numerical Hamiltonian Problems, Chapman & Hall, London, 1994.
Suzuki, M.: 'Improved Trotter-like formula', Phys. Lett. A 180 (1993), 232–234.
Varadarajan, V. S.: Lie Groups, Lie Algebras and Their Representations, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1984.
Wisdom, J. and Holman, M.: 'Symplectic maps for the N-body problem', Astron. J. 102 (1991), 1528–1538.
Wisdom, J., Holman, M. and Touma, J.: 'Symplectic correctors', in: J. E. Marsden,, G. W. Patrick, and W. F. Shadwick, (eds) Integration Algorithms and Classical Mechanics, American Mathematical Society, Providence, R.I., 1996, pp. 217–244.
Yoshida, H.: 'Construction of higher order symplectic integrators', Phys. Lett. A 150 (1990), 262–268.
Yoshida, H.: 'Recent progress in the theory and application of symplectic integrators', Celest. Mech. & Dyn. Astr. 56 (1993), 27–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanes, S., Casas, F. & Ros, J. Processing Symplectic Methods for Near-Integrable Hamiltonian Systems. Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy 77, 17–36 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008311025472
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008311025472