Abstract
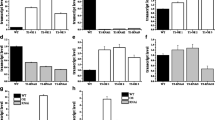
Microtubules are thought to be major determinants of plant morphogenesis, through effects on planes of cell division and on directions of differential cell expansion. In differentiation and redifferentiation processes, tubulin expression may prove a useful early indicator of cell activity. We examined the expression and localization of the pea α-tubulin gene TubA1 in situ and in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa) to explore its use as a probe for plant development, and as a test case for correct developmental expression between two legume species commonly compared for studies of symbiosis with Rhizobium. The TubA1 mRNA was more abundant in root tips and immature leaves than in other tissues of pea. The promoter of TubA1 was fused to β-glucuronidase (GUS) to analyze α-tubulin expression in transgenic alfalfa. Transient assays indicated that the TubA1 gene is transcribed at moderate levels compared to the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter. Histochemical staining for GUS activity confirmed a correlation between TubA1 expression and cell division in nodules, roots and leaves. TubA1 promoter activity was first detected in the inner cortex of the root between 18 h and 24 h after spot inoculation with Rhizobium meliloti. Expression of a c-myc epitope fused to the carboxy-terminus of TubA1 resulted in an incorporation into the microtubular cytoskeleton, demonstrating the effectiveness of at least one epitope tag in creating functional tubulin fusions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brierley, H.L., Webster, P. and Long, S.R. 1995. The Pisum sativum TubA1 gene, a member of a small family of _-tubulin sequences. Plant Mol. Biol. 27: 7115-727.
Carpenter, J.K., Ploense, S.E., Snustad, D.P. and Silflow, C.D. 1992. Preferential expression of an _-tubulin gene of Arabidopsis in pollen. Plant Cell 4: 557-571.
Carpenter, J.L., Kopczak, S.D., Snustad, D.P. and Silflow, C.D. 1993. Semi-constitutive expression of an Arabidopsis thaliana _-tubulin gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 21: 937-942.
Carrino, J.J. and Lafftner, T.G. 1986. Transcription of alpha-tubulin and histone H4 begins at the same point in Physarum cell cycle. J. Cell Biol. 102: 1666-1670.
Cleveland, D.W. 1987. The multi-tubulin hypothesis revisited: what have we learned? J. Cell Biol. 104: 381-383.
Downie, J.A., Knight, C.D., Johnston, A.W.B. and Rossen, L. 1985. Identification of genes and gene products involved in the nodulation of peas by Rhizobium leguminosarum. Mol. Gen. Genet. 198: 255-262.
Doyle, J.J.and Beachy, R.N. 1985. Ribosomal gene variation in soybean (Glycine) and its relatives. Theor. Appi. Genet. 70: 369-376.
Dudley, M.E., Jacobs, T.W. and Long, S.R. 1987. Microscopic studies of cell divisions in alfalfa roots by Rhizobium meliloti. Planta 171: 289-301.
Ehrhardt, D.W., Atkinson, E.M. and Long, S.R. 1992. Depolarization of alfalfa root hair membrane potential by Rhizobium meliloti Nod factors. Science 256: 998-1000.
Emons, A.M. and Wolters-Arts, A.M.C. 1983. Cortical micro-tubule and microfibril deposition in the cell wall of root hairs of Equisetum hyemale. Protorplasma 117: 68-81.
Evan, G.I., Lewis, G.K., Ramsey, G. and Bishop, J.M. 1985. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. J. Cell. Biol. 5: 3610-3616.
Finan, T.M., Kunkel, B., De Vos, G.F. and Signer, E.R. 1986. Second symbiotic megaplasmid in Rhizobium meliloti carrying exopolysaccharide and thiamine synthesis genes. J. Bact. 167: 66-72.
Fisher, R.F., Egelhoff, T.T., Mulligan, J.T. and Long, S.R. 1988. Specific binding of proteins from Rhizobium meliloti cell-free extracts containing NodD to DNA sequences upstream of inducible nodulation genes. Genes Dev. 2: 282-293.
Fosket, D.E. and Morejohn, L.C. 1992. Structural and functional organisation of tubulin. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 43: 210-240.
Gage, D.J., Bobo, T. and Long, S.R. 1996. Use of green fluorescent protein to visualize the early events of symbiosis between Rhizobium meliloti and alfalfa, Medicago sativa. J. Bact. 178: 7159-7166.
Gelvin, S.B. and Liu, C.-N. 1994. Genetic manipulation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains to improve transformation of recalcitrant plant species. In: S.B. Gelvin and R.A. Schilperoort (Eds.), Plant Molecular Biology Manual, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netheriands, pp. B4/1-B4/13.
Gilmour, D.M., Golds, T.L. and Davey, M.R. 1989. Medicago protoplasts: fusion, culture and plant regeneration. In: Y.P.S. Bajai (Ed.), Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 8, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 370-388.
Goddard, R.H., Wick, S.M., Silflow, C.D. and Snustadt, D.P. 1994. Microtubule components of the plant cytoskeleton. Plant Physiol. 104: 1-6.
Green, P.B. 1994. Connecting gene and hormone action to form and pattern organogenesis: biophysical transductions. J. Exp. Bot. 45 (special issue): 1775-1788.
Hauser, M.-T., Morikami, A. and Benfey, P.N. 1995. Conditional root expansion mutants of Arabidopsis. Development 121: 1237-1252.
Hirsch, A.M. 1992. Tansley review no.40: Developmental biology of legume nodulation. New Phytol. 122: 211-237.
Hoyle, H.D. and Raff, E.C. 1990. Two Drosophila _ tubulin isoforms are not functionally equivalent. J. Cell Biol. 111: 1009-1026.
Jefferson, R.A. 1987. Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 5: 387-405.
Kilmartin, J.V., Wright, B. and Milstein, C. 1982. Rat monoclonal antitubulin antibodies derived by using a new non-secreting rat cell line. J. Cell Biol. 93: 576-582.
Koncz, C. and Schell, J. 1986. The promoter of T L-DNA gene 5 controls the tissue-specific expression of chimeric genes carried by a novel type of Agrobacterium binary vector. Mol. Gen. Genet. 204: 383-396.
Krause, M., Harrison, S.W., Xu, S.-Q., Chen, L. and Fire, A. 1994. Elements regulating cell-and stage-specific expression of the C. elegans MyoD family homolog hih-1. Dev. Biol. 166: 133-148.
Lamb, J.W., Hombrecher, G. and Johnston, A.W.B. 1982. Plasmid-determined nodulation and nitrogen-fixation abilities in Rhizobium phaseoli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 86: 449-452.
Lloyd, A.M., Walbot, V. and Davis, R.W. 1992. Arabidopsis and Nicotiana anthocyanin production activated by maize regulators R and Ci. Science 258: 1773-1775.
Luehrsen, K.R., De Wet, J.R. and Walbot, V. 1992. Transient expression analysis in plants using the firefly luciferase reporter gene. Meth. Enzymol. 216: 397-414.
Marshall, L.G., Jeng, R.L., Mulholland, J. and Stearns, T. 1996. Analysis of Tub4p, a yeast-tubulin-like protein: implications for microtubule-organizing center function. J. Cell Biol. 134: 443-454.
Matthews, K.A., Rees, D. and Kaufman, T.C. 1993. A functionally specialized _-tubulin is required for oocyte meiosis and cleavage mitoses in Drosophila. Development 117: 977-991.
Meade, H.M., Long, S.R., Ruvkun, G.B., Brown, S.E. and Ausubel, F.M. 1982. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J. Bact. 149: 114-122.
Meselson, M. and Yuan, R. 1968. DNA restriction enzyme from E. coli. Nature 217: 1110-1114.
Montoliu, L., Puigdomènech, P. and Rigau, J. 1990a. The Tub _3 gene from Zea mays: structure and expression in dividing plant tissues. Gene 94: 201-208.
Montoliu, L., Rigau, J. and Puigdomènech, P. 1990b. A tandem of _-tubulin genes preferentially expressed in radicular tissues from Zea mays. Plant Mol. Biol. 14: 1-16.
Narvaez-Vasquez, J., Orozco-Cardenas, M.L. and Ryan, C.A. 1992. Differential expression of a chimeric CaMV-tomato proteinase inhibitor I gene in leaves of transformed nightshade, tobacco and alfalfa. Plant Mol. Biol. 20: 1149-1157.
Raff, E.C. 1984. Genetics of microtubule systems. J. Cell Biol. 99: 1-10.
Schardl, C.L., Byrd, A.D., Benzion, G., Altschuler, M.A., Hilde-brand, D.F. and Hunt, A.G. 1987. Design and construction of a versatile system for the expression of foreign genes in plants. Gene 61: 1-11.
Schenk, R.U. and Hildebrandt, A.C. 1972. Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledondous plant cell cultures. Can. J. Bot. 50: 199-204.
Seitz Kris, M.H. and Bingham, E. 1988. Interactions of highly regenerative genotypes of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and tissue culture protocols. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 24: 1047-1052.
Stearns, T. 1990. The yeast microtubule cytoskeleton: genetic approaches to structure and function. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 15:1-6.
Stotz, H.U., Powell, A. L.T., Damon, S.E., Greve, L.C., Bennett, A.B. and Labavitch, J.M. 1993. Molecular characterization of a polygalacturonase inhibitor from Pyrus communis L. cv. Bartlett. Plant Physiol. 102: 133-138.
Traas, J., Bellini, C., Nacry, P., Kronenberger, J., Bouchez, D. and Carboche, M. 1995. Normal differentiation patterns in plants lacking microtubular preprophase bands. Nature 375: 676-677.
van Brussel, A.A.N., Bakhuizen, R., van Spronsen, P.C., Spaink, H.P., Tak, T., Lugtenberg, B.J.J. and Kijne, J.W. 1992. Induction of pre-infection thread structures in leguminous host plant by mitogenic lipo-oligosaccharides of Rhizobium. Science 257: 70-72.
Van Larebecke, N., Engler, G., Holsters, M., Van den Elsacker, S., Zaenen, J., Schilperoort, R.A. and Schell, J. 1974. Large plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens essential for crown gall-inducing ability. Nature 252: 169-170.
Villemur, R., Joyce, C.M., Haas, N.A., Goddard, R.H., Kopczak, S.D., Hussey, P.J. and Snustad, D.P. 1992. _-Tubulin gene family of maize (Zea mays L.): evidence for two ancient _-tubulin genes in plants. J. Mol Biol. 227: 81-96.
Wehland, J., Schröder, H.C. and Weber, K. 1984. Amino acid sequence requirements in the epitope recoginzed by the _-tubulin-specific rat monoclonal antibody YL1/2. EMBO J. 3: 1295-1300.
Yang, W.-C., de Blank, C., Meskiene, I., Hirt, H., Bakker, J., van Kammen, A., Franssen, H. and Bisseling, T. 1994. Rhizobium Nod factors reactivate the cell cycle during infection and nodule primordium formation, but the cycle is only completed in primordium formation. Plant Cell 6: 1415-1462.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stotz, H.U., Long, S.R. Expression of the pea (Pisum sativum L.) α-tubulin gene TubA1 is correlated with cell division activity. Plant Mol Biol 41, 601–614 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006338401808
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006338401808