Abstract
In order to study the three-dimensional structure of radiation fogand to obtain a basic understanding of its generation mechanism,a numerical experiment is performed with a large-eddysimulation model and compared with the observation at Cabauw in the Netherlands. After confirming that the results are insatisfactory agreement with the observations, the structure of thefog and its generation mechanism are examined in more detail.
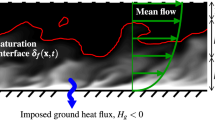
Before the fog forms, the atmosphere is stable and an inversionlayer exists almost adjacent to the ground surface. As the fog grows, however, the stratification is destabilized and a mixed layerdevelops gradually. The longwave radiative cooling near thefog top contributes to the destabilization more than thecondensational heating does.
The evolution of the fog can be classified into three stagesaccording to the behaviour of turbulent kinetic energy (TKE):formation, development, and dissipation stages.The fog layer has different flow structures at each stage.During the formation stage, longitudinal rolls similar tostreaks in channel flows appear near the ground surface.The development stage is characterized by an initiation oftransverse bands due to Kelvin–Helmholtz instability anda sudden increase of TKE. During the dissipation stage, longitudinalrolls and polygonal cells due to convective instability are organized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrén, A.: 1995, 'The Structure of Stably Stratified Atmospheric Boundary Layers: A Large-Eddy Simulation Study', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 121, 961–985.
Asai, T.: 1970, 'Stability of a Plane Parallel Flow with Variable Vertical Shear and Unstable Stratification', J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan 48, 129–139.
Atkinson, B. W. and Zhang, J. Wu: 1996, 'Mesoscale Shallow Convection in the Atmosphere', Rev. Geophys. 34, 403–431.
Beljaars, A. C. M. and Holtslag, A. A. M.: 1991, 'Flux Parameterization over Land Surfaces for Atmospheric Models', J. Appl. Meteorol. 30, 327–341.
Bergot, T. and Guedalia, D.: 1994, 'Numerical Forecasting of Radiation Fog. Part I: Numerical Model and Sensitivity Tests', Mon. Wea. Rev. 122, 1218–1230.
Brown, A. R., Derbyshire, S. H., and Mason, P. J.: 1994, 'Large-Eddy Simulation of Stable Atmospheric Boundary Layers with a Revised Stochastic Subgrid Model', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 120, 1485–1512.
Brown, R. and Roach, W. T.: 1976, 'The Physics of Radiation Fog: II-A Numerical Study', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 102, 335–354.
Brown, R. A.: 1980, 'Longitudinal Instabilities and Secondary Flows in the Planetary Boundary Layer: A Review', Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 18, 683–697.
Businger, J. A., Wyngaard, J. C., Izumi, Y., and Bradley, E. F.: 1971, 'Flux-Profile Relationships in the Atmospheric Surface Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 181–189.
Canuto, V. M. and Minotti, F.: 1993, 'Stratified Turbulence in the Atmosphere and Oceans: A New Subgrid Model', J. Atmos. Sci. 50, 1925–1935.
Chen, C. and Cotton, W. R.: 1983, 'A One-Dimensional Simulation of the Stratocumulus-Capped Mixed Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 25, 289–321.
Davis, P. A. and Peltier, W. R.: 1976, 'Resonant Parallel Shear Instability in the Stably Stratified Planetary Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 33, 1287–1300.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1972, 'Numerical Investigation of Neutral and Unstable Planetary Boundary Layers', J. Atmos. Sci. 29, 91–115.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1978, 'Efficient Prediction of Ground Surface Temperature and Moisture, with Inclusion of a Layer of Vegetation', J. Geophys. Res. 83(C4), 1889–1903.
Duynkerke, P. G.: 1991, 'Radiation Fog: A Comparison of Model Simulation with Detailed Observations', Mon. Wea. Rev. 119, 324–341.
Garratt, J. R.: 1992, The Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 316 pp.
Grossman, R. L.: 1982, 'An Analysis of Vertical Velocity Spectra Obtained in the BOMEX Fair-Weather, Trade-Wind Boundary Layer', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 23, 323–357.
Howard, L. N.: 1961, 'Note on a Paper of John W. Miles', J. Fluid Mech. 10, 509–512.
Hunt, J. C. R., Kaimal, J. C., and Gaynor, J. E.: 1988, 'Eddy Structure in the Convective Boundary Layer-New Measurements and New Concepts', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 114, 827–858.
Katayama, A.: 1972, A Simplified Scheme for Computing Radiative Transfer in the Troposphere, Numerical Simulation ofWeather and Climate, Technical Report No. 6, University of California, Los Angeles, 77 pp.
Khanna, S. and Brasseur, J. G.: 1998, 'Three-Dimensional Buoyancy-and Shear-Induced Local Structure of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 55, 710–743.
Klaassen, G. P. and Peltier, W. R.: 1985, 'Evolution of Finite Amplitude Kelvin-Helmholtz Billows in Two Spatial Dimensions', J. Atmos. Sci. 42, 1321–1339.
Klemp, J. B. and Lilly, D. K.: 1978, 'Numerical Simulation of Hydrostatic Mountain Waves', J. Atmos. Sci. 35, 78–107.
Kunkel, B. A.: 1984, 'Parameterization of Droplet Terminal Velocity and Extinction Coefficient in Fog Models', J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 23, 34–41.
Kurita, S., Okada, K., Naruse, H., Ueno, T., and Mikami, M.: 1990, 'Structure of a Fog in the Dissipation Stage over Land', Atmos. Environ. 24A, 1473–1486.
Lacis, A. A. and Hansen, J. E.: 1974, 'A Parameterization for the Absorption of Solar Radiation in the Earth's Atmosphere', J. Atmos. Sci. 31, 118–133.
Lilly, D.K.: 1966a, 'On the Application of the Eddy-Viscosity Concept in the Inertial Subrange of Turbulence', Manuscript No. 123, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, 19 pp.
Lilly, D.K.: 1966b, 'On the Instability of Ekman Boundary Flow', J. Atmos. Sci. 23, 481–494.
Mason, P. J. and Thomson, D. J.: 1992, 'Stochastic Backscatter in Large-Eddy Simulations of Boundary Layers', J. Fluid Mech. 242, 51–78.
Mellor, G. L.: 1977, 'The Gaussian Cloud Model Relations', J. Atmos. Sci. 34, 356–358.
Mellor, G. L. and Yamada, T.: 1974, 'A Hierarchy of Turbulence Closure Models for Planetary Boundary Layers', J. Atmos. Sci. 31, 1791–1806.
Miles, J. W.: 1961, 'On the Stability of Heterogeneous Shear Flows', J. Fluid Mech. 10, 496–508.
Moeng, C.-H. and Sullivan, P. P.: 1994, 'A Comparison of Shear-and Buoyancy-Driven Planetary Boundary Layer Flows', J. Atmos. Sci. 51, 999–1022.
Moin, P. and Kim, J.: 1982, 'Numerical Investigation of Turbulent Channel Flow', J. Fluid Mech. 118, 341–377.
Musson-Genon, L.: 1987, 'Numerical Simulation of a Fog Event with a One-Dimensional Boundary Layer Model', Mon. Wea. Rev. 115, 592–607.
Pilié, R. J., Mack, E. J., Rogers, C. W., Katz, U., and Kocmond, W. C.: 1979, 'The Formation of Marine Fog and the Development of Fog-Stratus Systems along the California Coast', J. Appl. Meteorol. 18, 1275–1286.
Roach, W. T., Brown, R., Caughey, S. J., Garland, J. A., and Readings, C. J.: 1976, 'The Physics of Radiation Fog: I-A Field Study', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 102, 313–333.
Schumann, U.: 1975, 'Subgrid Scale Model for Finite Difference Simulations of Turbulent Flows in Plane Channels and Annuli', J. Comp. Phys. 18, 376–404.
Smagorinsky, J. S.: 1963, 'General Circulation Experiments with the Primitive Equations: I. The Basic Experiment', Mon. Wea. Rev. 91, 99–164.
Sommeria, G. and Deardorff, J.W.: 1977, 'Subgrid-Scale Condensation in Models of Nonprecipitating Clouds', J. Atmos. Sci. 34, 344–355.
Stephens, G. L.: 1978, 'Radiation Profiles in Extended Water Clouds. II: Parameterization Schemes', J. Atmos. Sci. 35, 2123–2132.
Stephens, G. L., Ackerman, S., and Smith, E. A.: 1984, 'A Shortwave Parameterization Revised to Improve Cloud Absorption', J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 687–690.
Sullivan, P. P., McWilliams, J. C., and Moeng, C.-H.: 1994, 'A Subgrid-Scale Model for Large-Eddy Simulation of Planetary Boundary-Layer Flows', Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 71, 247–276.
Weckwerth, T. M., Wilson, J. W., Wakimoto, R. M., and Crook, N. A.: 1997, 'Horizontal Convective Rolls: Determining the Environmental Conditions Supporting their Existence and Characteristics', Mon. Wea. Rev. 125, 505–526.
Welch, R. M. and Wielicki, B. A.: 1986, 'The Stratocumulus Nature of Fog', J. Clim. Appl.Meteorol. 25, 101–111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakanishi, M. Large-Eddy Simulation Of Radiation Fog. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 94, 461–493 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002490423389
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002490423389