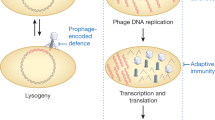
Abstract
The study of the interactions between lactic acid bacteria and their bacteriophages has been a vibrant and rewarding research activity for a considerable number of years. In the more recent past, the application of molecular genetics for the analysis of phage-host relationships has contributed enormously to the unravelling of specific events which dictate insensitivity to bacteriophage infection and has revealed that while they are complex and intricate in nature, they are also extremely effective. In addition, the strategy has laid solid foundations for the construction of phage resistant strains for use in commercial applications and has provided a sound basis for continued investigations into existing, naturally-derived and novel, genetically-engineered defence systems. Of course, it has also become clear that phage particles are highly dynamic in their response to those defence systems which they do encounter and that they can readily adapt to them as a consequence of their genetic flexibility and plasticity. This paper reviews the exciting developments that have been described in the literature regarding the study of phage-host interactions in lactic acid bacteria and the innovative approaches that can be taken to exploit this basic information for curtailing phage infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann H-W & DuBow MS (1987) Bacteriophage taxonomy. In: Viruses of prokaryotes, Vol. 1, (pp. 1-11). CRC Press, Boca Raton
Akcelik M & Tunail N (1992) A 30 kDa cell wall protein produced by plasmid DNA which encodes inhibition of phage adsorption in Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis P25. Milchwissenschaft 47: 215-217
Allison GE & Klaenhammer TR (1998) Phage resistance mechanisms in lactic acid bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 8: 207-226
Anba J, Bidnenko E, Hillier A, Ehrlich SD & Chopin M-C (1995) Characterisation of the lactococcal abiD1 gene coding for phage abortive infection. J. Bacteriol. 177: 3818-3823
Arendt EK, Daly C, Fitzgerald GF & van de Guchte M (1994) Molecular characterisation of lactococcal bacteriophage Tuc2009 and identification and analysis of genes encoding lysin, a putative holin and two structural proteins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 1875-1883
Auad L, Peril MAA, Holgado AAPR & Raya RR (1998) Evidence of a restriction-modification system in Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. lactis CNRZ 326. Curr. Microbiol. 36: 271-273
Auvray F, Coddeville M, Ritzenthaler P & Dupont L (1997) Plasmid integration in a wide range of bacteria mediated by the integrase of Lactobacillus delbrueckii bacteriophage mv4. J. Bacteriol. 179: 1837-1845
Batt CA, Erlandson K & Bsat N (1995) Design and implementation of a strategy to reduce bacteriophage infection of dairy starter cultures. Int. Dairy J. 5: 949-962
Benbadis L, Faelen M, Slos P, Fazel A & Mercenier A (1990) Characterisation and comparison of virulent bacteriophages of Streptococcus thermophilus isolated form yoghurt. Biochimie: 72: 855-862
Benbadis L, Garel JR & Hartley DL (1991) Purification, properties and sequence specificity of SslI, a new type II restriction endonuclease from Streptococcus salivarius ssp. thermophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 3677-3678
Beresford TPJ, Ward LJH & Jarvis AW (1993) Temporally regulated transcriptional expression of the genomes of lactococcal bacteriophages c2 and sk1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 3708-3712
Bickle TA & Kruger DH (1993) Biology of DNA restriction. Microbiol. Rev. 57: 434-450
Bickle TA (1993) The ATP-dependent restriction enzymes. In: Linn SM, Lloyd RS & Roberts RJ (Eds) Nucleases, 2nd edn (pp 89-109). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Bidnenko E, Ehrlich SD & Chopin M-C (1995) Phage operon involved in sensitivity to the Lactococcus lactis abortive infection mechanism AbiD1. J. Bacteriol. 177: 3824-3829
Bidnenko E, Ehrlich SD & Chopin MC (1998) Lactococcus lactis phage operon coding for an endonuclease homologous to RuvC. Mol. Microbiol. 28: 823-834
Birkeland N-D (1994) Cloning, molecular characterisation and expression of the genes encoding the lytic functions of lactococcal bacteriophage øLC3: a dual lysis system of modular design. Can. J. Microbiol. 40: 658-665
Botstein (1980) A theory of modular evolution for bacteriophages. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 354: 484-491
Boyce JD, Davidson BE & Hillier AJ (1995) Sequence analysis of the Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage BK5-T and demonstration that the phage DNA has cohesive ends. Appl. Environ Microbiol. 61: 4089-4098
Bradley DE (1967) Ultrastructure of bacteriophages and bacteriocins. Bacteriol. Rev. 31: 230-314
Brondsted L & Hammer K (1999) Use of the integration elements encoded by the temperate lactococcal bacteriophage TP901-1 to obtain chromosomal single-copy transcriptional fusions in Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 752-758
Brooker BE (1976) Cytochemical observations on the extracellular carbohydrate produced by Streptococcus cremoris. J. Dairy Res. 43: 283-290
Bruttin A, Desiere F, Lucchini S, Foley S & Brussow H (1997) Characterisation of the lysogeny DNA module from the temperate Streptococcus thermophilus bacteriophage øSfi21. Virology 233: 136-148
Budde-Niekiel A & Teuber M (1987) Electron microscopy of the adsorption of bacteriophages to lactic acid streptococci. Milchwissenschaft 42: 551-553
Callegari ML, Cocconcelli PS, Kok J, Venema G & Morelli L (1996) Heterologous expression of Lactobacillus helveticus CNRZ 892 S-layer gene in Lactococcus lactis mg1363. In: Proceedings of 5th Symposium on Lactic Acid Bacteria, Genetics, Metabolism and Applications, Veldhoven, the Netherlands. Abs D12
Callegari ML, Riboli B, Sanders JW, Cocconcelli PS, Kok J, Venema G, Morelli L (1998) The S-layer gene of Lactobacillus helveticus CNRZ 892: cloning sequence and heterologous expression. Microbiology 144: 719-726
Casey CN, Morgan E, Daly C & Fitzgerald GF (1993) Characterisation and classification of virulent lactococcal bacteriophages isolated from a Cheddar cheese plant. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 74: 268-275
Casey J, Daly C & Fitzgerald GF (1992) Controlled integration into the Lactococcus chromosome of the pCI829-encoded abortive infection gene from Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis UC811. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 3283-3291
Chandry PS, Davidson BE & Hillier AJ (1994) Temporal transcription map of the Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage sk1. Gene 138: 123-126
Chandry PS, Moore SC, Boyce JD, Davidson BE & Hillier AJ (1997) Analysis of the DNA sequence, gene expression origin of replication and modular structure of the Lactococcus lactis lytic bacteriophage sk1. Mol. Microbiol. 26: 49-64
Chopin A, Chopin M-C, Mollio-Batt A & Langella P (1984) Two plasmid determined restriction and modification systems in Streptococcus lactis. Plasmid 11: 260-263
Christiansen B, Brondsted L, Vogensen FK & Hammer K (1996) A resolvase-like protein is required for the site-specific integration of the temperate lactococcal bacteriophage TP901-1. J. Bacteriol. 178: 5164-5173
Chung DK, Chung SK & Batt CA (1992) Antisense RNA directed against the major capsid protein from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris bacteriophage F4-1 confers partial resistance to the host. Appl. Microbiol. Technol. 37: 79-83
Chung DK, Kim JH & Batt CA (1991) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the major capsid protein from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris bacteriophage F4-1. Gene 101: 121-125
Cluzel P-J, Chopin A, Ehrlich SD and Chopin M-C (1991) Phage abortive infection mechanism from Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis, expression of which is mediated by an iso-ISS1 element. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 3547-3551
Coakley M, Fitzgerald GF & Ross RP (1997) Application and evaluation of phage resistance-and bacteriocin-encoding plasmid pMRC01 for the improvement of dairy starter cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 1434-1440
Coffey AG, Fitzgerald GF & Daly C (1989) Identification and characterisation of a plasmid encoding abortive infection from Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis UC811. Neth. Milk. Dairy J. 43: 229-244
Coffey AG, Fitzgerald GF & Daly C (1991) Cloning and characterisation of the determinant for abortive infection from the lactococcal plasmid pCI829. J. Gen. Microbiol. 143: 1355-1362
Costello V (1988) Characterisation of bacteriophage-host interaction in Streptococcus cremoris UC503 and related streptococci. Ph.D. thesis, National University of Ireland
Crow VL & Gopal PK (1995) Cell surface differences in lactococcal strains. Int. Dairy J. 5: 45-68
Daly C, Fitzgerald GF & Davis R (1996) Biotechnology of lactic acid bacteria with special reference to bacteriophage resistance. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 70: 99-110
Daly C, Fitzgerald GF, O'Connor L & Davis R (1998) Technological and health benefits of dairy starter cultures. Int. Dairy J. 8: 195-205
Davis R, van der Leile D, Mercenier A, Daly C & Fitzgerald GF (1993) ScrFI restriction-modification system of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris UC503: cloning and characterisation of two ScrFI methylase genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 777-785
de Ruyter PGGA, Kuipers OP, Meijer WC & de Vos WM (1997) Food-grade controlled lysis of Lactococcus lactis for accelerated cheese ripening. Nat. Biotechnol. 15: 976-979
de Vos WM (1989) On the carrier state of bacteriophages in starter lactococci: an elementary explanation involving a bacteriophage resistance plasmid. Neth. Milk Dairy J. 43: 221-227
de Vos WM, Underwood HM & Davies FL (1984). Plasmid-encoded bacteriophage resistance in Streptococcus cremoris SK11. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 23: 175-178
Deng Y-M, Harvey ML, Liu CQ & Dunn NW (1997) A novel plasmid-encoded phage abortive infection system for Lactococcus lactis biovar diacetylactis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 146: 149-154
Deng YM, Liu CQ & Dunn NW (1999) Genetic organisation and functional analysis of a novel abortive infection system, AbiL, from Lactococcus lactis. J. Biotechnol. 67: 135-149
Diersken KP, Ebel W, Marks J, Sandine WE & Trempy JE (1995) Polysaccharide expression in lactococci. In: Ferretti JJ, Gilmore MS, Klaenhammer TR & Brown F (Eds) Genetics of streptococi, enterococci and lactococci (pp 469-480). Dev. Biol. Stand. Basel, Karger
Dinsmore PK & Klaenhammer TR (1994) Phenotypic consequences of altering the copy number of abiA, a gene responsible for aborting bacteriophage infections in Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 1129-1136
Dinsmore PK & Klaenhammer TR (1995) Bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus. Mol. Biotechnol. 4: 297-314
Dinsmore PK & Klaenhammer TR (1997) Molecular characterisation of a genomic region in a Lactococcus bacteriophage that is involved in its sensitivity to the phage defence mechanism AbiA. J. Bacteriol. 179: 2949-2957
Dinsmore PK, O'Sullivan DJ & Klaenhammer TR (1998) A leucine repeat motif in AbiA is required for resistance of Lactococcus lactis to phages representing three species. Gene 212: 5-11
Djordjevic GM & Klaenhammer TR (1996) Positive selection, cloning vectors for Gram positive bacteria based on a restriction endonuclease cassette. Plasmid 35: 37-45
Djordjevic GM & Klaenhammer TR (1997) Genes and gene expression in Lactococcus bacteriophages. Int. Dairy J. 7: 489-508
Djordjevic GM, O' Sullivan DJ, Walker SA, Conkling MA & Klaenhammer TR (1997) Bacteriophage-triggered defence systems: phage adaptation and design improvements. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 4370-4376
Dupont L, Boizet-Bonhoure B, Coddeville M, Auvray F & Ritzenthaler P (1995) Characterisation of genetic elements required for site-specific integration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus bacteriophage mv4 and construction of an integration-proficient vector for Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Bacteriol. 177: 586-595
Durmaz E & Klaenhammer TR (1995) A starter culture rotation strategy incorporating paired restriction-modification and abortive infection bacteriophage defences in a single Lactococcus lactis strain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 1266-1273
Durmaz E, Higgins DL & Klaenhammer TR (1992) Molecular characterisation of a second abortive phage resistance gene present in Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis ME2. J. Bacteriol. 174: 7463-7469
Dybvig K & Yu H (1994) Regulation of a restriction and modification system via DNA inversion in Mycoplasma pulmonis. Mol. Microbiol. 12: 387-395
Emond E, Dion E, Walker SA, Vedamuthu ER, Kondo JK & Moineau S (1998) AbiQ, an abortive infection mechanism from Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 4748-4756
Emond E, Holler BJ, Boucher PA, Vandenbergh P, Vedamuthu ER, Kondo JK & Moineau S (1997) Phenotypic and genetic characterisation of the bacteriophage abortive infection mechanism AbiK from Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 1274-1283
Engel G, Altermann E, Jurgen RK & Henrich B (1998) Structure of a genome region of the Lactobacillus gasseri temperate phage øadh covering a repressor gene and cognate promoters. Gene 210: 61-70
Fitzgerald GF, Daly C, Brown LR & Gingeras TR (1982) ScrFI: a new sequence-specific endonuclease from Streptococcus cremoris. Nuc. Acid Res. 10: 8171-8179
Foley S, Lucchini S, Zwahlen MC & Brussow H (1998) A short non-coding viral DNA element showing characteristics of a replication origin confers bacteriophage resistance to Streptococcus thermophilus. Virology 250: 377-387
Forde A, Daly C & Fitzgerald GF (1999) Identification of four phage resistance plasmids from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris HO2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 1540-1547
Forde A & Fitzgerald GF (1999) Analysis of exopolysaccharide (EPS) production mediated by the bacteriophage adsorption blocking plasmid, pCI658, isolated from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris HO2. Int. Dairy J (In press)
Fremaux C, De Antoni GL, Raya RR & Klaenhammer TR (1993) Genetic organisation and sequence of the region encoding integrative functions from Lactobacillus gasseri temperate bacteriophage øadh. Gene 126: 61-66
Froseth BR, Harlander SK & McKay LL (1988) Plasmid-mediated reduced phage sensitivity in Streptococcus lactis KR5. J. Dairy Sci. 71: 275-284
Garbutt KC, Kraus J & Geller BL (1997) Bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis engineered by replacement of a gene for a bacteriophage receptor. J. Dairy Sci. 80: 1512-1519
Garvey P, van Sinderen D, Twomey DP, Hill C & Fitzgerald GF (1995a) Molecular genetics of bacteriophage and natural phage defence systems in the genus Lactococcus. In. Dairy J. 5: 905-947
Garvey P, Fitzgerald GF & Hill C (1995b) Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of two abortive infection phage resistance determinants from the lactococcal plasmid pNP40. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 4321-4328
Garvey P, Rince A, Hill C & Fitzgerald GF (1997) Identification of a RecA homolog (RecA L P ) on the conjugative lactococcal phage resistance plasmid pNP40: evidence of a role for chromosomally encoded RecA L in abortive infection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 1244-1251
Garvey PA, Hill C & Fitzgerald GF (1996) The lactococcal plasmid pNP40 encodes a third bacteriophage resistance mechanism, one which affects phage DNA penetration. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 676-679
Geis A, Janzen T, Teuber M & Wirsching F (1992) Mechanism of plasmid-mediated bacteriophage resistance in lactococci. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 94: 7-14
Geis A, Neve H & Teuber M (1987) Plasmid-dependent bacteriophage resistance in lactic acid streptococci: isolation, characterisation and cloning of plasmids. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 46: Abs 16
Geller BL, Ivey RG, Trempy JE & Hettinger-Smith B (1993) Cloning of a chromosomal gene required for phage infection of Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis C2. J. Bacteriol. 175: 5510-5519
Gopal PK & Crow VL (1993) Characterisation of loosely associated material from the cell surface of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris E8 and its phage-resistant variant strain 398. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 3177-3182
Gopal PK & Reilly KI (1995) Molecular architecture of lactococcal cell surface as it relates to important industrial properties. Int. Dairy J. 5: 1095-1111
Guimont C, Henry P & Linden G (1993) Restriction-modification in Streptococcus thermophilus: isolation and characterisation of a type II restriction endonuclease Sth455I. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39: 216-220
Harrington A & Hill C (1991) Construction of a bacteriophage resistance derivative of Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis 425A by using the conjugal plasmid pNP40. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 3405-3409
Harrington A & Hill C (1992) Plasmid involvement in the formation of a spontaneous bacteriophage insensitive mutant Lactococcus lactis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 96: 132-142
Hill C (1993) Bacteriophage and bacteriophage resistance in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 12: 87-108
Hill C, Miller LA & Klaenhammer TR (1990a) Cloning, expression, and sequence determination of a bacteriophage fragment encoding bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis. J. Bacteriol. 172: 6419-6426
Hill C, Miller LA & Klaenhammer TR (1990b) Nucleotide sequence and distribution of the pTR2030 resistance determinant (hsp) which aborts bacteriophage infection in lactococci. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 2255-2258
Hill C, Miller LA & Klaenhammer TR (1991) In vivo genetic exchange of a functional domain from a type II A methylase between lactococcal plasmid pTR2030 and a virulent bacteriophage. J. Bacteriol. 173: 4363-4370
Hill C, Pierce K & Klaenhammer TR (1989) The conjugative plasmid pTR2030 encodes two bacteriophage defence mechanisms in lactococci, restriction-modification (R+/M+) and abortive infection (Hsp+). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 2416-2419
Jarvis AW & Klaenhammer TR (1986) Bacteriophage resistance conferred on lactic streptococci by the conjugative plasmid pTR2030: effects on small isometric-, large isometric-and prolate headed phages. Appl. Environ Microbiol. 51: 1272-1277
Jarvis AW (1988) Conjugal transfer in lactic streptococci of plasmid-encoded insensitivity to prolate-and small isometric-headed bacteriophages. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 777-784
Jarvis AW (1989) Bacteriophages of lactic acid bacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 72: 3406-3428
Jarvis AW (1992) Analysis of phage resistance mechanisms encoded by lactococcal plasmid pAJ2074. Can. J. Microbiol. 39: 252-258
Jarvis AW (1995) Relationships by DNA homology between lactococcal phages 7-9, P335 and New Zealand industrial lactococcal phages. Int. Dairy J. 5: 355-366
Jarvis AW, Fitzgerald GF, Mata M, Mercenier A, Neve H, Powell IB, Ronda C, Saxelin M & Teuber M (1991) Species and types of phages of lactococcal bacteriophages. Intervirol. 32: 2-9
Johnsen MG, Appel KF, Madsen PL, Vogensen FK, Hammer K & Arnau J (1996) A genomic region of lactocccal temperate bacteriophage TP901-1 encoding major virion proteins. Virology 218: 306-315
Johnsen MG, Neve H, Vogensen FK & Hammer K (1995) Virion positions and relationships of lactocccal temperate bacteriophage TP901-1 proteins. Virology 212: 595-606
Josephsen J & Klaenhammer TR (1990) Stacking of three different restriction and modification systems in Lactococcus lactis by co-transformation. Plasmid 23: 71-75
Josephsen J & Neve H (1998) Bacteriophages and Lactic Acid Bacteria. In: Salminen S & van Wright A (Eds) Lactic Acid Bacteria: Microbiology and Functional Aspects, 2nd edn (pp 385-436). Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Josephsen J & Vogensen FK (1989) Identification of three different plasmid-encoded restriction-modification systems in Streptococcus lactis ssp. cremoris W56. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 59: 161-166
Kannan P, Cowan GM, Daniel AS, Gann AAF & Murray NE (1989) Conservation and organisation in the specificity polypeptideds of two families of type I restriction enzymes. J. Mol. Biol. 209: 335-344
Kelly W, Dobson J, Jorck-Ramberg D, Fitzgerald GF & Daly C (1990) Introduction of bacteriophage resistance plasmids into commercial Lactococcus starter cultures. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 87: Abst. C20
Keogh BP & Pettinghill g (1983) Adsorption of bacteriophage eb7 on Streptococcus cremoris EB7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45: 1946-1948
Kim SG & Batt CA (1991a) Nucleotide sequence and deletion analysis of a gene coding for a structural protein of Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage F4-1. Food Microbiol. 8: 27-36
Kim SG & Batt CA (1991b) Identification of a nucleotide sequence conserved in Lactococcus lactis bacteriophages. Gene 98: 95-100
Kim SG & Batt CA (1991c) Antisense mRNA-mediated bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 1109-1113
Kim SG, Bor Y-C & Batt CA (1992) Bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis using antisense ribonucleic acid. J. Dairy Sci. 75: 1761-1767
King WR, Collins EB & Barrett EL (1983) Frequencies of bacteriophage-resistant and slow-acid producing variants of Streptococcus cremoris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45: 1481-1485
Klaenhammer TR & Fitzgerald GF (1994) Bacteriophage and bacteriophage resistance. In: Gasson MJ & de Vos WM (Eds) Genetics and Biotechnology of Lactic Acid Bacteria (pp 106-168). Blackie Academic and Professional, Glasgow
Klaenhammer TR (1991) Development of bacteriophage resistant strains of lactic acid bacteria. Biochemical Soc. Transactions 19: 675-681
Kneale GG (1994) A symmetrical model for the domain structure of type I DNA methylatransferases. J. Mol. Biol. 243: 1-5
Kodaira K-I, Oki M, Kakikawa M, Watanabe N, Hirakawa M, Yamada K & Taketo A (1997) Genome structure of the Lactobacillus temperate phage øgle: the whole genome sequence and the putative promoter/repressor system. Gene 187: 45-53
Kulakauskas S, Lubys A & Ehrlich SD (1995) DNA restriction-modification systems mediate plasmid-maintenance. J. Bacteriol. 177: 3451-3454
Langella P & Chopin A (1989) Effect of restriction-modification systems on transfer of foreign DNA into Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 59: 301-306
Larbi D, Decaris B & Simonet J-M (1992) Different bacteriophage resistance mechanisms in Streptococcus salivarius ssp. thermophilus. J. Dairy Res 59: 349-357
Lawrence RC (1978) Action of bacteriophage on lactic acid bacteria: consequences and protection. N.Z. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 11: 251-256
Lillehaug D & Birkeland N-K (1993) Characterisation of genetic elements required for site-specific integration of the temperate lactococcal bacteriophage øLC3 and construction of integration-negative øLC3 mutants. J. Bacteriol. 175: 1745-1755
Lillehaug D, Lindquist BH & Birkeland N-K (1991) Characterisation of øLC3, a Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris temperate bacteriophage with cohesive single-stranded DNA ends. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 3206-3211
Lillehaug D, Nes IF & Birkland N-K (1997) A highly efficient and stable system for site-specific integration of genes and plasmids into the phage øLC3 attachment (attB) of the Lactococcus lactis chromosome. Gene 188: 129-136
Limsowtin GKY & Terzaghi BE (1976) Phage resistant mutants: their selection and use in cheese factories. N.Z. J. Dairy Sci. 11: 251-256
Limsowtin, GKY, Powell IB & Parente, E (1996) Types of starters. In: Cogan TM and Accolas J-P (Eds) Dairy Starter Cultures (pp 101-129). VCH Publishers Inc., New York
Lubbers MW, Waterfield NR, Beresford TPJ, LePage RWF & Jarvis AW (1995) Sequencing and analysis of the prolate-headed lactococcal bacteriophage c2 genome and identification of the structural genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 4348-4356
Lucey M, Daly C & Fitzgerald GF (1992) Cell surface characteristics of Lactococcus lactis harbouring pCI528, a 46 kb plasmid encoding inhibition of bacteriophage adsorption. J. Gen. Microbiol. 138: 2137-2143
Madsen A & Josephsen J (1998a) Characterisation of LlaCI, a new restriction-modification system from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris W15. Biol. Chem. 379: 443-449 Madsen A & Josephsen J (1998b) Cloning and characterisation of the lactococcal plasmid-encoded type II restriction-modification system, LlaDII. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 2424-2431
Madsen PL & Hammer K (1998) Temporal transcription of the lactococcal temperate phage TP901-1 and DNA sequence of the early promoter region. Microbiology 144: 2203-2215
Malone T, Blumenthal RM & Cheng X (1995) Structure-guided analysis reveals nine sequence motifs conserved among DNA-methyltransferases and suggests a catalytic mechanism for these enzymes. J. Mol. Biol. 253: 618-632
Marshall RJ & Berridge NJ (1976) Selection and some properties of phage resistant starters for cheese-making. J. Dairy Res. 43: 449-458
Mayo B, Hardisson C & Brana AF (1991) Nucleolytic activities in Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis NCDO497. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 79: 195-198
McGrath S, Seegers JF, Fitzgerald GF & van Sinderen D (1999) Molecular characterisation of a phage-encoded resistance system in Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 1891-1899
McLandsborough LA, Kolaetis KM, Requena T & McKay LL (1995) Cloning and characterisation of the abortive infection genetic determinant abiD isolated from pBF61 of Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis KR5. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 2023-2026
Mikkonen M, Raisanen L & Alatossava T (1996) The early gene region completes the nucleotide sequence of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. lactis phage LL-H. Gene 175: 49-57
Moineau S, Fortier J, Ackermann HW & Pandian S (1992) Characterisation of lactococcal bacteriophages from Quebec cheese plants. Can. J. Microbiol. 38: 875-882
Moineau S, Pandian S & Klaenhammer TR (1993a) Restriction-modification systems and restriction endonucleases are more effective on lactococcal bacteriophages that have emerged recently in the dairy industry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 197-202
Moineau S, Durmaz E, Pandian S & Klaenhammer TR (1993b) Differenciation of two abortive mechanisms by using monoclonal antibodies directed towards lactococcal bacteriophage capsid proteins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 208-212
Moineau S, Bernier D, Jobin M, Herbert J, Klaenhammer TR & Pandian S (1993c) Production of monoclonal antibodies against the major capsid protein of the Lactococcus bacteriophage u136 and development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for direct phage detection in whey and milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 2034-2040
Moineau S, Borkaev M, Walker SA, Vedamuthu ER & Vandenbergh PA (1994a) Novel starter rotation system based on phage species sensitivity. J. Dairy Sci. 77: 18
Moineau S, Pandian S & Klaenhammer TR (1994b) Evolution of a lytic bacteriophage via DNA acquisition from the Lactococcus lactis chromosome. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 1832-1841
Moineau S, Walker SA, Vedamuthu ER & Vandenbergh PA (1995a) Cloning and sequencing of LlaII restriction-modification genes from Lactococcus lactis and relatedness of this system to the Streptococcus pneumoniae DpnII system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 2193-2202
Moineau S, Walker SA, Holler BJ, Vedamuthu ER & Vandenbergh PA (1995b) Expression of aLactococcus lactis phage resistance mechanism by Streptococcus thermophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 2461-2466
Monteville MR, Ardestani B & Geller BR (1994) Lactococcal phages require a host cell wall carbohydrate and a plasma membrane protein for adsorption and ejection of DNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 3204-3211
Murray NE, Daniel AS, Cowan GM & Sharp PM (1993) Conservation of motifs within the unusually variable polypeptide sequences of type I restriction and modification enzymes. Mol. Microbiol. 9: 133-143
Naito Y, Naito T & Kobayashi I (1998) Selfish restriction-modification genes: resistance of a resident R/M plasmid to displacement by an incompatible plasmid mediated by host killing. Biol. Chem. 379: 429-436
Nauta A, van Sinderen D, Karsens H, Smit E, Venema G & Kok J (1996) Inducible gene expression mediated by a repressor-operator system isolated from Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage rlt. Mol. Microbiol. 19: 1331-1341
Neve H (1996) Bacteriophage. In: Cogan TM and Accolas J-P (Eds) Dairy Starter Cultures (pp 157-189). VCH Publishers Inc., New York
Neve H, Zenz KI, Desiere F, Kock A, Heller K & Brussow H (1998) Comparison of the lysogeny modules from the temperate Streptococcus thermophilus bacteriophages TP-J34 and Sfi21: implications for the modular theory of evolution. Virology 241: 61-72
Nyengaard N, Vogensen FK & Josephsen J (1993) LlaAI and LlaBI, two type II restriction endonucleases from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris W9 and W56 recognising, respectively, 5′-/GATC-3′ and 5′-C/TRYAG-3′. Gene 136: 371-372
Nyengaard N, Vogensen FK & Josephsen J (1995) Restriction-modification systems in Lactococcus lactis. Gene: 157: 13-18
Nyengaard NR, Falkenberg-Klok J & Josephsen J (1996) Cloning and analysis of the restriction-modification system LlaBI, a bacteriophage resistance system from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris W56. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 3494-3498
O'Connor L, Coffey A, Daly C & Fitzgerald GF (1996) AbiG, a genotypically novel abortive infection mechanism encoded by plasmid pCI750 of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris UC653. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 3075-3082
O'Connor L, Tangney M & Fitzgerald GF (1999) Expression, regulation and mode of action of the AbiG abortive infection system of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris UC653. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 330-335
O'Sullivan D, Coffey A, Fitzgerald GF, Hill C & Ross RP (1998) Design of a phage-insensitive lactococcal dairy starter via sequential transfer of naturally occurring conjugative plasmids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 4618-4622
O'Sullivan DJ & Klaenhammer TR (1998) Control of expression of LlaI restriction in Lactococcus lactis. Mol. Microbiol. 27: 1009-1020
O'Sullivan DJ, Hill C & Klaenhammer TR (1993) Effect of increasing the copy number of bacteriophage origins of replication, in trans, on incoming-phage proliferation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 2449-2456
O'Sullivan DJ, Walker SA, West SG & Klaenhammer TR (1996) Development of an expression system using a lytic phage to trigger explosive plasmid amplification and gene expression. Biotechnology 14: 82-87
O'Sullivan DJ, Zagula K & Klaenhammer TR (1995) In vivo restriction by LlaI is encoded by three genes, arranged in an operon with llaIM, on the conjugative Lactococcus plasmid pTR2030. J. Bacteriol. 177: 134-143
O'Sullivan T, van Sinderen D & Fitzgerald GF (1999) Structural and functional analysis of pCI65st, a 6.5 kb plasmid from Streptococcus thermophilus NDI-6. Microbiology 145: 127-134
Oram, J D & Reiter B (1968) The adsorption of phage to group N streptococci. The specificity of adsorption and the location of phage receptor substances in cell wall and plasma membrane fractions. J. Gen. Virol. 3: 103-11
Parreira R, Valyasevi R, Lerayer LS, Ehrlich SD & Chopin M-C (1996a) Gene organisation and transcription of a late-expressed region of a Lactococcus lactis phage. J. Bacteriol. 178: 6158-6165
Parreira R, Ehrlich SD & Chopin M-C (1996b) Dramatic decay of phage transcripts in lactococcal cells carrying the abortive infection determinant AbiB. Mol. Microbiol. 19: 221-230
Platteeuw C & de Vos WM (1992) Location, characterisation and expression of lytic enzyme-encoding gene lytA, of Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage øUS3. Gene 118: 115-120
Poch MT, Somkuti GA & Solaiman DKY (1997) Sth132I, a novel class IIS restriction endonuclease of Streptococcus thermophilus ST132. Gene 195: 201-206
Polzin KM, Collins LJ, Lubbers MW & Jarvis AW (1996) Effect of various mRNAs on bacteriophage c2 replication. In: Proceedings of 5th Symposium on Lactic Acid Bacteria, Genetics, Metabolism and Applications, Veldhoven the Netherlands. Abs F2
Prevots F & Ritzenthaler P (1998) Complete sequence of the new lactococcal abortive phage resistance gene abiO. J. Dairy Sci. 81: 1483-1485
Prevots F, Daloyau M, Bonin O, Dumont X & Tolou S (1996) Cloning and sequencing of the novel abortive infection gene abiH of Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis biovar. diacetylactis S94. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 142: 295-299
Prevots F, Mata M & Ritzenthaler P (1990) Taxonomic differenciation of 101 lactococcal bacteriophages and characterisation of bacteriophages with unusually large genomes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 1313-1318
Prevots F, Tolou S, Delpech B, Kaghad M & Daloyau M (1998) Nucleotide sequence and analysis of the new chromosomal abortive infection gene abiN of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris S114. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 159: 331-336
Raya RR, Fremaux C, De Antoni GL & Klaenhammer TR (1992) Site-specific integration of the temperate bacteriophage øadh into the Lactobacillus gasseri chromosome and molecular characterisation of the phage (attP) and bacterial (attB) attachment sites. J. Bacteriol. 174: 5584-5592
Reyes-Gavilan CG, Limsowtin GKY, Sechaud L, Veaux M & Acolas JP (1990) Evidence for a plasmid-linked restriction-modification system in Lactobacillus helveticus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 3412-3419
Sanders ME & Klaenhammer TR (1983) Characterisation of phage-sensitive mutants from a phage-insensitive strain of Streptococcus lactis: evidence for a plasmid determinant that prevents phage adsorption. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 46: 1125-1133
Sanders ME, Leonard PJ, Sing WD & Klaenhammer TR (1986) Conjugal strategy for the construction of fast-acid producing, bacteriophage-resistant lactic streptococci for use in dairy fermentations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 52: 1101-1107
Sanford JC & Johnston SA (1985) The concept of parasite-derived resistance-deriving resistance genes from the parasites own genome. J. Theor. Biol. 113: 395-405
Schafer A, Geis A, Neve H & Teuber M (1991) Bacteriophage receptors of Lactococcus lactis ssp. diacetylactis F7/2 and Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris Wg2-1. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 78: 69-74
Schouler C, Bouet C, Ritzenthaler P, Drouet X & Mata M (1992) Characterisation of Lactococcus lactis phage antigens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 2479-2484
Schouler C, Clier F, Lerayer AD Ehrlich SD & Chopin M-C (1998a) A type IC restriction-modification system in Lactococcus lactis. J. Bacteriol. 180: 407-411
Schouler C, Gautier S, Ehrlich SD & Chopin M-C (1998b) Combinational variation of restriction-modification specificities in Lactococcus lactis. Mol. Microbiol. 28: 169-178
Schouler C, Ehrlich SD and Chopin M-C (1994) Sequence and organisation of the lactococcal prolate-headed bIL67 phage genome. Microbiology 140: 3061-3069
Shearman CA, Jury K & Gasson MJ (1992) Autolytic Lactococcus lactis expressing a lactococcal bacteriophage lysin gene. Bio/Technology 10: 196-199
Shearman CA, Underwood H, Jury K & Gasson M (1989) Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of a Lactococcus bacteriophage lysin gene. Mol Gen. Genet. 218: 214-221
Sheehan MM, Garcia JL, Lopez R & Garcia P (1996) Analysis of the catalytic domain of the lysin of the lactococcal bacteriophage Tuc2009 by chimeric gene assembling. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 140: 23-28
Sijtsma L, Hellingwerf KJ & Wouters JTM (1991) Composition and phage binding capacity of cell walls isolated from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris SK110 and SK112. Neth. Milk Dairy J. 45: 81-95
Sijtsma L, Jansen N, Hazeleger WC, Wouters JTM & Hellingwerf KJ (1990) Cell surface characteristics of bacteriophage resistant Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris SK110 and its bacteriophage sensitive variant SK112. Appl. Environ.Microbiol. 56: 3230-3233
Sijtsma L, Sterkenburg A & Wouters JTM (1988) Properties of the cell walls of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris SK110 and their relation to bacteriophage resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 2808-2811
Sing WD & Klaenhammer TR (1986) Conjugal transfer of bacteriophage resistance determinants on pTR2030 into Streptococcus cremoris strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 51: 1264-1271
Sing WD & Klaenhammer TR (1991) Characterization of restriction-modification plasmids from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris and their effects when combined with pTR2030. J. Dairy Sci. 74: 1133-1144
Sing WD & Klaenhammer TR (1993) A strategy for rotation of different bacteriophage defences in a lactococcal single-strain starter culture system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 365-372
Solaiman DKY & Somkuti GA (1990) Isolation and characterisation of a type II restriction endonuclease from Streptococcus thermophilus ST117. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 80: 261-266
Solaiman DKY & Somkuti GA (1991) A type II restriction endonuclease from Streptococcus thermophilus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 67: 261-266
Stanley E, Fitzgerald GF, Le Marrec C, Fayard B & van Sinderen D (1997) Sequence analysis and characterisation of ø01205, a temperate bacteriophage infecting Streptococcus thermophilus CNRZ1205. Microbiology 143: 3417-3429
Steenson LR & Klaenhammer TR (1986) Plasmid heterogeneity in Streptococcus cremoris M12R: effects on proteolytic activity and host-dependent phage replication. J. Dairy Sci. 69: 2227-2236
Stingele F, Neeser JR & Mollet B (1996) Identification and characterisation of the eps (exopolysaccharide) gene cluster from Streptococcus thermophilus Sfi6. J. Bacteriol. 178: 1680-1690
Su P, Harvey M, Im HJ & Dunn NW (1997) Isolation, cloning and characterisation of the abiI gene from Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis M138 encoding abortive phage infection. J. Biotechnol. 54: 95-104
Su P, Im H, Hsieh H, Kang' AS & Dunn NW (1999) LlaFI, a type III restriction and modification system in Lactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 686-693
Takano T, Ochi A & Yamamoto N (1990) Restriction enzyme from Lactobacillus fermentum. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 87: Abs C64
Timinkas A, Butkus V & Janulaitas A (1995) Sequence motifs characteristic for DNA [cytosine-N4] and DNA [adenine-N6] methyltransferases. Classification of all DNA methyltransferases. Gene 157: 3-11
Tortorello ML, Chang PK, Ledford RA & Dunny GM (1990) Plasmid associated antigens associated with resistance to phage adsorption in Lactococcus lactis. In Abstracts of the 3rd International ASM Conference on Streptococcal Genetics, Abs 50
Tremblay DM & Moineau S (1999) Complete genomic sequence of the lytic bacteriophage DT1 of Streptococcus thermophilus. Virology 255: 63-76
Twomey DP, Davis R, Daly C & Fitzgerald GF (1993) Sequence of the gene encoding a second ScrFI m5C methyltransferase of Lactococcus lactis. Gene 136: 205-209
Twomey DP, Gabillet N, Daly C & Fitzgerald GF (1997) Molecular characterisation of the restriction endonuclease gene (scrFIR) associated with the ScrFI restriction-modification system from Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris UC503. Microbiology 143: 2277-2286
Twomey DP, McKay LL & O'Sullivan DJ (1998) Molecular characterisation of the Lactococcus lactis LlaKR2I restriction-modification system and effect of an IS982 element positioned between the restriction and modification genes. J. Bacteriol. 180: 5844-5854
Valeyasevi R, Sandine WE & Geller BL (1990) Bacteriophage kh receptor of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris KH is rhamnose of extracellular wall polysaccharide. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 1882-1889.
Valyasevi R, Sandine WE & Geller BL (1991) A membrane protein is required for bacteriophage c2 infection of Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis C2. J. Bacteriol. 173: 6095-6100
Valeyasevi R, Sandine WE & Geller BL (1994) Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis C2 bacteriophage sk1 receptor involves rhamnose and glucose moieties in the cell wall. J. Dairy Sci. 77: 1-6
van de Guchte M, Daly C, Fitzgerald GF & Arendt EK (1994a) Identification of the putative repressor-encoding gene cl of the temperate lactococcal bacteriophage Tuc2009. Gene 144: 93-95
van de Guchte M, Daly C, Fitzgerald GF & Arendt EK (1994b) Identification of int and attP on the genome of lactococcal bacteriophage Tuc2009 and their use for site-specific plasmid integration in the chromosome of Tuc2009-resistant Lactococcus lactis MG1363. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 2324-2329
van Kranenburg R, Marugg JD, van Swam II, Willem NJ & de Vos WM (1997) Molecular characterisation of the plasmid-encoded eps gene cluster essential for exopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Lactococcus lactis. Mol. Microbiol. 24: 387-397
van Sinderen D, Karsens H, Kok J, Terpstra P, Ruiters MHJ, Venema g & Nauta A (1996) Sequence analysis and molecular characterisation of the temperate lactococcal bacteriophage rlt. Mol. Micorbiol. 19: 1343-1355
Verrips CT & van den Berg DJC (1996) Barriers to application of genetically modified lactic acid bacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 70: 299-316
Vlegels PAP, Hazeleger WC, Helmerborst TH & Wouters JTM (1988) Phage resistance of Streptococcus cremoris due to low adsorption efficiency. Neth. Milk Dairy J. 42: 195-206
Walker SA, O'Sullivan DJ, West SG & Klaenhammer TR (1996) Molecular characterisation of a phage inducible middle promoter from the lactococcal bacteriophage ø31. In: Proceedings of 5th Symposium on Lactic Acid Bacteria, Genetics, Metabolism and Applications, Veldhoven, the Netherlands. Abs F25
Watanabe K, Ishibashi K, Nadashima Y & Sakurai T (1984) A phage-resistant mutant of Lactobacillus casei which permits phage adsorption but not genome injection. J. Gen. Virol. 65: 981-986
Whitehead HR & Cox GA (1935) The occurrence of bacteriophage in lactic streptococci. N.Z. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 16: 319-320
Wilson GG & Murray NM (1991) Restriction and modification systems. Annu. Rev. Genet. 25: 585-627
Xu G, Willert J, Kapfer W & Trautner TA (1995) BsuCI, a type I restriction-modification system in Bacillus subtilis. Gene 157: 59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forde, A., Fitzgerald, G.F. Bacteriophage defence systems in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 76, 89–113 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002027321171
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002027321171