Abstract
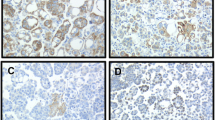
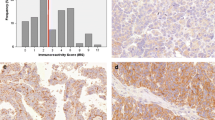
Ets transcription factors play a central role in invasion and metastasis through regulation of synthesis of proteolytic enzymes and angiogenic molecules. The objective of this study was to investigate the role of PEA3 in tumor progression of ovarian and breast carcinoma metastatic to effusions, and to evaluate the expression of Ets-2 and Erg in ovarian carcinoma. Ovarian (83 malignant effusions, 102 corresponding solid lesions) and breast (33 malignant effusions, 40 corresponding solid lesions) carcinomas were evaluated for expression of PEA3 using mRNA in situ Hybridization (ISH). Expression of Ets-2 and Erg mRNA was analyzed in 50 ovarian carcinoma effusions using the same method. PEA3 mRNA expression was comparable at all sites in ovarian carcinoma (44 out of 83; 53% of effusions, 48 out of 102; 47% of solid tumors). PEA3 mRNA expression in effusions correlated with mRNA expression of the previously studied αv (P=0.022), α6 (P<0.001) and β1 (P<0.001) integrin subunits, the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inducer EMMPRIN (P=0.015) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) (P=0.033). Erg and Ets-2 mRNA was expressed in 15 out of 50 (30%) and 18 out of 50 (36%) effusions, respectively, and co-localized with PEA3 (P=0.017 for Erg, P=0.004 for Ets-2). In breast carcinoma, PEA3 expression was seen in 19/40 (48%) of solid lesions, with a significant upregulation in corresponding effusions compared to primary tumors (24 out of 33; 73%, P=0.038). PEA3 mRNA expression in effusions obtained prior to the institution of chemotherapy predicted significantly shorter overall survival in univariate analysis (24 vs 37 months, P=0.03), with a similar trend for Erg (13 vs 30 months, P=0.1). In conclusion, PEA3 is expressed at all anatomic sites in serous ovarian cancer and co-localizes with Erg, Ets-2 and several metastasis-associated molecules. PEA3 mRNA expression is a novel marker for tumor progression to malignant effusion in breast carcinoma, and predicts poor outcome in effusions sampled prior to therapeutic intervention in ovarian carcinoma. These findings support a biological role for Ets transcription factors in these malignancies and suggests that they may be targets for therapeutic intervention.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal H, Murray T, Samuels A et al. Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin 2003; 53: 5–26.
Verger A, Duterque-Coquillaud M. When Ets transcription factors meet their partners. BioEssays 2002; 24: 362–70.
Sharrocks AD. The ETS-domain transcription factor family. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 827–37.
Davidson B, Reich R, Goldberg I et al. Ets-1 mRNA expression is a novel marker of poor survival in ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 551–7.
Borden P, Heller RU. Transcriptional control of matrix metalloproteinases and the tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases. Crit Rev Eukar Gene Exp 1997; 7: 159–78.
Lengyel E, Stepp E, Gum R, Boyd D. Involvement of a mitogenactivated protein kinase signaling pathway in the regulation of urokinase promoter activity by c-Ha-ras. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 23007–12.
Oda N, Abe M, Sato Y. Ets-1 converts endothelial cells to the angiogenic phenotype by inducing the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and integrin β-3. J Cell Physiol 1999; 178: 121–32.
Xin JH, Cowie A, Lachance P, Hassel JA. Molecular cloning and characterization of PEA3, a new member of the Ets oncogene family that is differentially expressed inmouse embryonic cells. Genes Dev 1992; 6: 481–96.
Monte D, Coutte L, Baert JL et al. Molecular characterization of the Ets-related human transcription factor ER81. Oncogene 1995; 11: 771–9.
Monte D, Baert JL, Defossez PA et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of human ERM, a new member of the Ets family closely related to mouse PEA3 and ER81 transcription factors. Oncogene 1994; 9: 1397–406.
Higashino F, Yoshida K, Fujinaga Y et al. Isolation of a new cDNA encoding the adenovirus E1A enhancer binding protein: A new human member of the ets oncogene family. Nucleic Acid Res 1993; 21: 547–53.
Yoshida K, Narita M, Fujinaga Y. Binding sites of HeLa cell nuclear proteins on the upstream region of adenovirus type 5 E1A gene. Nucleic Acids Res 1989; 17: 10015–34.
Higashino F, Yoshida K, Noumi T et al. Ets-related protein E1A-F can activate three different matrix metalloproteinase gene promoters. Oncogene 1995; 10: 1461–3.
Trimble MS, Xin JH, Guy CT et al. PEA3 is overexpressed in mouse metastatic mammary adenocarcinomas. Oncogene 1993; 8: 3037–42.
Shepherd TG, Kockeritz L, Szrajber MR et al. The pea3 subfamily ets genes are required for HER2/Neu-mediated mammary oncogenesis. Curr Biol 2001; 11: 1739–48.
Benz CC, O'Hagan RC, Richter B et al. HER2/Neu and the Ets transcription activator PEA3 are coordinately upregulated in human breast cancer. Oncogene 1997; 15: 1513–25.
Kinoshita J, Kitamura K, Tanaka S et al. Clinical significance of PEA3 in human breast cancer. Surgery 2002; 131: S222–5.
Xing X, Wang SC, Xia W et al. The Ets protein PEA3 suppresses HER-2/neu overexpression and inhibits tumorigenesis. Nat Med 2000; 6: 189–95.
Guerra-Vladusic FK, Vladusic EA, Tsai MS, Lupu R. Signaling molecules implicated in heregulin induction of growth arrest and apoptosis. Oncol Rep 2001; 8: 1203–14.
Baert JL, Monte D, Musgrove EA et al. Expression of the PEA3 group of Ets-related transcription factors in human breast-cancer cells. Int J Cancer 1997; 70: 590–7.
Hiroumi H, Dosaka-Akita H, Yoshida K et al. Expression of E1AF/PEA3, an Ets-related transcription factor in human non-smallcell lung cancers: Its relevance in cell motility and invasion. Int J Cancer 2001; 93: 786–91.
Hida K, Shindoh M, Yasuda M et al. Antisense E1AF transfection restrains oral cancer invasion by reducing matrix metalloproteinase activities. Am J Pathol 1997; 150: 2125–32.
Hida K, Shindoh M, Yoshida K et al. Expression of E1AF, an ets-family transcription factor, is correlated with the invasive phenotype of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 1997; 33: 426–30.
Gavrilov D, Kenzior O, Evans M et al. Expression of urokinase plasminogen activator and receptor in conjunction with the ets family and AP-1 complex transcription factors in high grade prostate cancers. Eur J Cancer 2001; 37: 1033–40.
Simpson S, Woodworth CD, DiPaolo JA. Altered expression of Erg and Ets-2 transcription factors is associated with genetic changes at 21q22.2-22.3 in immortal and cervical carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene 1997; 14: 2149–57.
Nishikawa A, Iwasaki M, Akutagawa N et al. Expression of various matrix proteases and Ets family transcriptional factors in ovarian cancer cell lines: Correlation to invasive potential. Gynecol Oncol 2000; 79: 256–63.
Ito Y, Miyoshi E, Takeda T et al. Linkage of elevated Ets-2 expression to hepatocarcinogenesis. Anticancer Res 2002; 22: 2385–90.
Ito Y, Takeda T, Okada M, Matsuura N. Expression of Ets-1 and Ets-2 in colonic neoplasms. Anticancer Res 2002; 22: 1581–4.
Reddy ESP, Rao VN, Papas TS. The erg gene: A human gene related to the ets oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987; 84: 6131–5.
Sorensen PHB, Lessnick SL, Lopez-Terrada D et al. A second Ewing's sarcoma translocation, t(21;22), fuses the EWS gene to another ETS-family transcription factor, ERG. Nat Genet 1994; 6: 146–51.
Yi HK, Fujimura Y, Ouchida M et al. Inhibition of apoptosis by normal and aberrant Fli-1 and erg proteins involved in human solid tumors and leukemias. Oncogene 1997; 14: 1259–68.
Buttice G, Duterque-Coquillaud M, Basuyaux JP et al. Erg, and Ets-family member, differentially regulates human collagenase1 (MMP1) and stromelysin1 (MMP3) gene expression by physically interacting with the Fos/Jun complex. Oncogene 1996; 13: 2297–306.
Davidson B, Risberg B, Goldberg I et al. Ets-1 mRNA expression in effusions of serous ovarian carcinoma patients is a marker of poor outcome. Am J Surg Pathol 2001; 25: 1493–500.
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Gotlieb WH et al. PEA3 is the second Ets family transcription factor involved in tumor progression in ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 1412–9.
Davidson B, Risberg B, Kristensen G et al. Detection of cancer cells in effusions from patients diagnosed with gynecological malignancies-evaluation of five epithelial markers. Virchows Arch 1999; 435: 43–9.
Davidson B, Berner A, Nesland JM et al. Carbohydrate antigen expression in primary tumors, metastatic lesions, and serous effusions from patients diagnosed with epithelial ovarian carcinoma-evidence of up-regulated Tn and Sialyl Tn antigens expression in effusions. Hum Pathol 2000; 31: 1081–7.
Davidson B, Berner A, Nesland JM et al. E-cadherin and a-, β-and ?-catenin protein expression is up-regulated in ovarian carcinoma cells in serous effusions. J Pathol 2000; 192: 460–9.
Reed JA, Manahan LJ, Parks CS, Brigati DJ. Complete one-hour immunocytochemistry based on capillary action. Biotechniques 1992; 13: 434–43.
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Gotlieb WH et al. High levels of MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1-MMP and TIMP-2 mRNA correlate with poor survival in ovarian carcinoma. Clin Exp Metast 1999; 17: 799–808.
Davidson B, Reich R, Berner A et al. Ovarian carcinoma cells in serous effusions show altered MMP-2 and TIMP-2 mRNA levels. Eur J Cancer 2001; 37: 2040–9.
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Berner A et al. Expression of membrane-type 1,2 and 3 matrix metalloproteinases (MT1-MMP, MT2-MMP, MT3-MMP) mRNA in ovarian carcinoma cells in serous effusions. Am J Clin Pathol 2001; 115: 517–24.
Davidson B, Reich R, Kopolovic J et al. Interleukin-8 and vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA levels are down-regulated in ovarian carcinoma cells in serous effusions. Clin Exp Metast 2002; 19: 135–44.
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Berner A et al. EMMPRIN (extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer) is a novel marker of poor outcome in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Exp Metast 2003; 20: 161–9.
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Reich R et al. The av and β1 integrin subunits are commonly expressed in malignant effusions from ovarian carcinoma patients. Gynecol Oncol 2003; 90: 248–57.
Givant Horwitz V, Davidson B, van de Putte G et al. Dissociated mRNA expression of the 67 kDa laminin receptor and the a6 integrin subunit in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Exp Metast 2003; 20: 599–609.
Davidson B, Risberg R, Reich R, Berner A. Effusion cytology in ovarian cancer-new molecular methods as aids to diagnosis and prognosis. Clin Lab Med 2003; 23: 729–54.
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Kopolovic J et al. Expression of angiogenesis-related genes in ovarian carcinoma-a clinicopathologic study. Clin Exp Metastas 2000; 18: 501–7.
Goldberg I, Davidson B, Reich R et al. aV integrin is a novel marker of poor prognosis in advanced-stage ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 4073–9.
Besser D, Presta M, Nagamine Y. Elucidation of a signaling pathway induced by FGF-2 leading to uPA gene expression in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Cell Growth Differ 1995; 6: 1009–17.
Hapke S, Gawaz M, Dehne K et al. beta(3)A-integrin downregulates the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (u-PAR) through a PEA3/ets transcriptional silencing element in the u-PAR promoter. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 2118–32.
Tremble P, Damsky CH, Werb Z. Components of the nuclear signaling cascade that regulate collagenase gene expression in response to integrin-derived signals. J Biol Cell 1995; 129: 1707–20.
Iguchi A, Kitajima I, Yamakuchi M et al. PEA3 and AP1 are required for constitutive IL-8 gene expression in hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 279: 166–71.
Dieterich M, Goodman SN, Rojas-Corona RR et al. Multivariate analysis of prognostic features in malignant pleural effusions from breast cancer patients. Acta Cytol 1994; 38: 945–52.
Banerjee AK, Willetts I, Robertson JF, Blamey RW. Pleural effusion in breast cancer: A review of the Nottingham experience. Eur J Surg Oncol 1994; 20: 33–6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davidson, B., Goldberg, I., Tell, L. et al. The clinical role of the PEA3 transcription factor in ovarian and breast carcinoma in effusions. Clin Exp Metastasis 21, 191–199 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CLIN.0000037703.37275.35
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CLIN.0000037703.37275.35