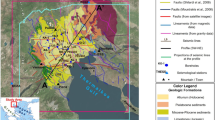
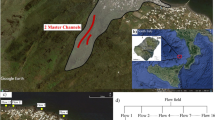
Abstract
The Indus Fan records the erosion of the western Himalayas and Karakoram since India began to collide with Asia during the Eocene, ∼50 Ma. Multi-channel seismic reflection data from the northern Arabian Sea correlated to industrial well Indus Marine A-1 on the Pakistan Shelf show that sedimentation patterns are variable through time, reflecting preferential sedimentation in deep water during periods of lower sea-level (e.g., middle Miocene, Pleistocene), the diversion of sediment toward the east following uplift of the Murray Ridge, and the autocyclic switching of fan lobes. Individual channel-levee systems are estimated to have been constructed over periods of 105–106 yr during the Late Miocene. Sediment velocities derived from sonobuoys and multi-channel stacking velocities allow sections to be time-depth converted and then backstripped to calculate sediment budgets through time. The middle Miocene is the period of most rapid accumulation, probably reflecting surface uplift in the source regions and strengthening of the monsoon at that time. Increasing sedimentation during the Pleistocene, after a late Miocene-Pliocene minimum, is apparently caused by faster erosion during intense glaciation. The sediment-unloaded geometry of the basement under the Pakistan Shelf shows a steep gradient, similar to the continent-ocean transition seen at other rifted volcanic margins, with basement depths on the oceanward side indistinguishable from oceanic crust. Consequently we suggest that the continent-ocean transition is located close to the present shelf break, rather than >350 km to the south, as previously proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, Z., Kutzbach, J. E., Prell, W. L. and Porter, S. C., 2001, Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since late Miocene times, Nature 411, 62–66.
Barker, P. F., 1966, A reconnaissance survey of the Murray Ridge, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., A, 259, 187–197.
Barton, A. J. and White, R. S., 1997, Crustal structure of the Edoras Bank continental margin and mantle thermal anomalies beneath the North Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 3109–3129.
Bellingham, P. and White, N. J., 2000, A general inverse method for modelling extensional sedimentary basins, Basin Res. 12, 219–226.
Berggren, W. A., Kent, D. V., Swisher, C. C. and Aubry, M. P., 1995, A revised Cenozoic geochronology and chronostratigraphy. in Berggren, W. A., Kent, D. V., Aubry, M. P. and Hardenbol, J. (eds.), Geochronology, time scales and global stratigraphic correlation, Soc. Econ. Paleo. Min. Spec. Publ. 54, 129–212.
Blisniuk, P. M., Hacker, B. R., Glodny, J., Ratschbacher, L., Bi, S., Wu, Z., McWilliams, M. O. and Calvert, A., 2001, Normal faulting in central Tibet since at least 13.5 Myr ago, Nature 412, 628–632.
Boillot, G., Beslier, M. O., Krawczyk, C. M., Rappin, D. and Reston, T. J., 1995, The formation of passive margins: Constraints from the crustal structure and segmentation of the deep Galicia margin, Spain. in Scrutton, R. A. et al. (eds.), The Tectonics, Sedimentation and Palaeoceanography of the North Atlantic Region, Geol. Soc. of London Spec. Publ. 90, 71–91.
Burbank, D. W., Derry, L. A. and France-Lanord, C., 1993, Reduced Himalayan sediment production 8 Myr ago despite an intensified monsoon, Nature 364, 48–50.
Burgath, K. P., von Rad, U., van der Linden, W., Block, M., Khan, A. A., Roeser, H. A. and Weiss, W., 2002, Basalt and Peridotite recovered from Murray Ridge: Are they of supra-subduction zone origin? in Clift, P. D., Kroon, D., Craig, J., and Gaedicke, C. (eds.), The Tectonic and Climatic Evolution of the Arabian Sea Region, Geol. Soc. of London Spec. Publ., in press.
Burgess, P. M., and Hovius, N., 1998, Rates of delta progradation during highstands; consequences for timing of deposition in deep-marine systems, J. Geol. Soc. London 155, 217–222.
Clift, P. D. and Gaedicke, C., 2002, Accelerated mass flux to the Arabian Sea during the Middle-late Miocene, Geology 30, 207–210.
Clift, P. D., Lee, J. I., Hildebrand, P., Shimizu, N., Layne, G. D., Blusztajn, J., Blum, J. D., Garzanti, E., and Khan, A. A., 2002a, Nd and Pb isotope variability in the Indus River system: Implications for sediment provenance and crustal heterogeneity in the Western Himalaya, Earth Planet. Sci. Letts. 200, 91–106.
Clift, P. D., Lee, J. I., Blusztajn, J. and Clark, M. K., 2002b, Erosional response of South China to arc rifting and monsoonal strengthening recorded in the South China Sea, Mar. Geol., 184, 207–226.
Clift, P. D. and Lorenzo, J.M., 1999, Flexural unloading and uplift along the Côte d'Ivoire-Ghana Transform Margin, Equatorial Atlantic, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 25,257–25,274.
Clift, P. D., Shimizu, N., Layne, G., Gaedicke, C., Schlüter, H. U., Clark, M. and Amjad, S., 2001, Development of the Indus Fan and its significance for the erosional history of the western Himalaya and Karakoram, Geol. Soc. America Bull. 113, 1039–1051.
Cochran, J. R., 1990, Himalayan uplift, sea level, and the record of Bengal fan sedimentation at the ODP leg 116 sites. in Cochran, J.R., Stow, D. A. V. et al., Proc. Ocean Drill. Prog., Sci. Res. 116, College Station, TX (Ocean Drilling Program), 397–414.
Coleman, M. and Hodges, K., 1995, Evidence for Tibetan plateau uplift before 14 Myr ago from a new minimum age for east-west extension, Nature 374, 49–52.
Copeland, P., Harrison, T. M., Kidd, W. S. F., Xu R. and Zhang Y., 1987, Rapid Miocene acceleration of uplift in the Gangdese belt, Xizang (southern Tibet), and its bearing on accommodation mechanisms of the India-Asia collision, Earth Planet. Sci. Letts. 86, 240–252.
Damuth, J. E., Flood, R. D., Kowsmann, R. O., Belderson, R. H. and Gorini, M. A., 1988, Anatomy and growth pattern of Amazon deep-sea fan as revealed by long-range side-scan sonar (GLORIA) and high-resolution seismic studies, Amer. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull. 72, 885–911.
Derry, L. A. and France-Lanord, C., 1997, Himalayan weathering and erosion fluxes; climate and tectonic controls. in Ruddiman, W. F. (ed.), Tectonic uplift and climate change, Plenum Press, New York, 289–312.
Derry, L. A. and France-Lanord, C., 1996, Neogene Himalayan weathering history and river 87Sr/86Sr; impact on the marine Sr record, Earth Planet. Sci. Letts. 142, 59–74.
Dettman, D. L., Kohn, M. J., Quade, J., Ryerson, F. J., Ojha, T. P. and Hamidullah, S., 2001, Seasonal stable isotope evidence for a strong Asian monsoon throughout the past 10.7 m.y., Geology 29, 31–34.
Droz, L. and Bellaiche, G., 1991, Seismic facies and geologic evolution of the central portion of the Indus Fan. In Weimer, P. and Link, M. H. (eds.), Seismic facies and sedimentary processes of submarine fans and turbidite systems, Springer Verlag, 383–402.
Edwards, R. A. Minshull, T. A. and White, R. S., 2000, Extension across the Indian-Arabian plate boundary: the Murray Ridge, Geophys. J. Int. 142, 461–477.
Eldholm, O. et al., Proc. Ocean Drill. Prog., Init. Repts. 104, College Station, TX (Ocean Drilling Program) 1987.
Falvey, D. and Middleton, M. F., 1981, Passive continental margins: Evidence for a pre-breakup deep crustal metamorphic subsidence mechanism. Ocean. Acta, 4, 103–114.
Gaedicke, C., Schlüter, H. U., Roeser, H. A., Prexl, A., Schreckenberger, B., Meyer, H., Reichert, C., Clift, P. and Amjad, S., 2002, Origin of the northern Indus Fan and Murray Ridge, Northern Arabian Sea: interpretation from seismic and magnetic imaging, Tectonophysics, 355, 127–143.
Galy, A. and France-Lanord, C., 2001, Higher erosion rates in the Himalaya; geochemical constraints on riverine fluxes, Geology 29, 23–26.
George, A., Marshallsea, S. J., Wyrwoll, K. H., Chen, J. and Lu, Y., 2001, Miocene cooling in the northern Qilian Shaan, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, revealed by apatite fission-track and vitrinite-reflectance analysis, Geology 29, 939–942.
Goodbred, S. and Kuehl, S. A., 2000, Enormous Ganges-Brahmaputra sediment discharge during strengthened early Holocene monsoon, Geology 28, 1083–1086.
Guo, Z. T., Ruddiman, W. F., Hao, Q. Z., Wu, H. B., Qiao, Y. S., Zhu, R. X., Peng, S. Z., Wei, J. J.,. Yuan, B. Y. and Liu, T. S., 2002, Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China, Nature 416, 159–163.
Haq, B. U., Hardenbol, J. and Vail, P. R., 1987, Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic, Science 235, 1156–1167.
Harrison, T. M., Copeland, P., Kidd, W. S. F. and Yin, A., 1992, Raising Tibet, Science 255, 1663–1670.
Hildebrand, P. R., Noble, S. R., Searle, M. P., Parrish, R. R. and Shakirullah, 1998, Tectonic significance of 24 Ma crustal melting in the eastern Hindu Kush, Pakistan, Geology 26, 871–874.
Hinz, K., 1981, A hypothesis on terrestrial catastrophes: Wedges of very thick oceanward dipping layers beneath passive continental margins, their origin and paleoenvironmental significance, Geol. Jahr., E22, 3–28.
Horsefield, S. J., Whitmarsh, R. B. White, R. S. and Sibuet, J.-C., 1994, Crustal structure of the Goban Spur rifted continental margin, northeast Atlantic-Results from a detailed seismic refraction study, Geophys. J. Int., 119, 1–19.
Karner, G. D. and Watts, A. B., 1982, On isostasy at Atlantic-type continental margins, J. Geophys. Res. 87, 2923–2948.
Kenyon, N. H., Amir, A. and Cramp, A., 1995, Geometry of the younger sediment bodies of the Indus Fan. in Pickering, K. T., Hiscott, R. N., Kenyon, N. H., Ricci Lucchi, F. and Smith, R. D. A. (eds.), Atlas of deep water environments: architectural style in turbidite systems, Chapman and Hall, London.
Kolla, V. and Coumes, F., 1991, Seismic stratigraphy, canyon and channel characteristics of the Indus continental margin and upper fan. in Weimer, P. and Link, M.H. (eds), Seismic facies and sedimentary processes of submarine fans and turbidite systems, Springer Verlag, 438.
Kolla, V. and Coumes, F., 1987, Morphology, internal structure, seismic stratigraphy, and sedimentation of Indus Fan. Amer. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull., 71, 650–677.
Kolla, V. and Coumes, F., 1984, Morpho-acoustic and sedimentologic characteristics of the Indus Fan, Geo-Mar. Letts. 3, 133–139.
Kroon, D., Steens, T., and Troelstra, S. R., 1991, Onset of Monsoonal related upwelling in the western Arabian Sea as revealed by planktonic foraminifers. in Prell, W.L, Niitsuma, N., et al. (eds.), Proc. Ocean Drill. Prog., Sci. Res. 117, College Station, TX (Ocean Drilling Program), 257–263.
Kusznir, N. J., Roberts, A. M. and Morley, C., 1995, Forward and reverse modeling of rift basin formation. in Lambaise, J. (ed.), The Hydrocarbon Habitat of Rift Basins, Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., 88, 3–56.
Kusznir, N. J. and Egan, S. S., 1989, Simple-shear and pure-shear models of extensional sedimentary basin formation: application to the Jean d'Arc basin, Grand Banks of Newfoundland. in Tankard, A. J. and Balkwill, H. R. (eds.), Extensional tectonics and stratigraphy of the North Atlantic Margins, Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Mem., 46, 305–322.
Larsen, H. C. and Jakobsdóttir, S., 1988, Distribution, crustal properties and significance of seaward-dipping sub-basement reflectors off East Greenland in Morton, A. C. and Parson, L. M. (eds.) Early Tertiary Volcanism and the Opening of the Northeast Atlantic, Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ. 39, 95–114.
Malod, J. A., Droz, L., Kemal, B. M. and Patriat, P., 1997, Early spreading and continental to oceanic basement transition beneath the Indus deep-sea fan: northeastern Arabian Sea, Mar. Geol., 141, 221–235.
Manabe, S. and Terpstra, T.B., 1974, The effects of mountains on the general circulation of the atmosphere as identified by numerical experiments, J. Atmos. Sci., 31, 3–42.
McHargue, T. R., 1991, Seismic facies, processes, and evolution of Miocene inner fan channels, Indus submarine fan. in Weimer, P. and Link, M. H. (eds.), Seismic facies and sedimentary processes of submarine fans and turbidite systems. New York, NY (Springer-Verlag), 403–413.
McHargue, T. R. and Webb, J. E., 1986, Internal geometry, seismic facies, and petroleum potential of canyons and inner fan channels of the Indus submarine fan. Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull., 70, 161–180.
Metcalfe, R. P., 1993, Pressure, temperature and time constraints on metamorphism across the Main Central Thrust zone and high Himalayan slab in the Garhwal Himalaya. in Treloar, P. J. and Searle, M. P. (eds), Himalayan Tectonics, Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., 74, 485–509.
Métivier, F., Gaudemer, Y., Tapponnier, P. and Klein, M., 1999, Mass accumulation rates in Asia during the Cenozoic, Geophys. J. Int., 137, 280–318.
Miles, P. R., Munschy, M. and Ségoufin, J., 1998, Structure and early evolution of the Arabian Sea and east Somali Basin, Geophys. J. Int., 134, 876–888.
Molnar, P., England, P. and Martinod, J., 1993, Mantle dynamics, the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, and the Indian monsoon, Rev. Geophys., 31, 357–396.
Najman, Y. M. R., Clift, P. D., Johnson, M. R. and Robertson, A. H. F. 1993, Early Tertiary foreland basin evolution in the Lesser Himalaya. in Searle, M.P. and Treloar, P. (eds.), Himalayan Tectonics, Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., 74, 541–558.
Naini, B. R. and Kolla, V., 1982, Acoustic character and thickness of sediments of the Indus Fan and the continental margin of western India, Mar. Geol., 47, 181–185.
Parrish, R. R. and Tirrul, R., 1989, U-Pb age of the Baltoro Granite, Northwest Himalaya, and implications for monazite U-Pb systematics, Geology 17, 1076–1079.
Parsons, B. and Sclater, J. G., 1977, An analysis of the variation of ocean floor bathymetry and heat flow with age, J. Geophys. Res. 82, 803–827.
Peterson, L. C., Murray, D. W., Ehrmann, W. U., and Hempel, P., 1992, Cenozoic carbonate accumulation and compensation depth changes in the Indian Ocean. in Duncan, R. A., Rea, D. K., Kidd, R. B., von Rad, U. and Weissel, J.K. (eds), Synthesis of results from scientific drilling in the Indian Ocean, Am. Geophys. Union Monog., 70, 311–333.
Prell, W.L. and Kutzbach, J.E., 1992, Sensitivity of the Indian monsoon to forcing parameters and implications for its evolution. Nature, 360, 647–651.
Prell, W.L, Murray, D.W., Clemens, S.C. and Anderson, D.M., 1992, Evolution and variability of the Indian Ocean Summer Monsoon: evidence from the western Arabian Sea drilling program. in Duncan, R. A., Rea, D. K., Kidd, R. B., von Rad, U. and Weissel, J. K. (eds.), Synthesis of results from scientific drilling in the Indian Ocean, Am. Geophys. Union Monog., 70, 447–469.
Prell, W.L., Niitsuma, N. et al., 1989, Proc. Ocean Drill. Prog., Init. Repts. 117, College Station, TX (Ocean Drilling Program).
Quade, J., Cerling, T. E. and Browman, J. R., 1989, Dramatic ecologic shift in the late Miocene of northern Pakistan, and its significance to the development of the Asian monsoon. Nature, 342, 163–166.
Ramstein, G., Fluteau, F., Besse, J. and Joussaume, S., 1997, Effect of orogeny, plate motion and land-sea distribution on Eurasian climate change over the past 30 million years, Nature 386, 788–795.
Ravenne, C., Coumes, F. and Esteve, J. P., 1988, Relative sea level changes and depositional modes of the shelf and deep sea fan of the Indus. in Bally, A. W. (ed.), Atlas of seismic stratigraphy, AAPG Studies in Geology, 27, 270–276.
Raymo, M. E., and Ruddiman, W. F., 1992, Tectonic forcing of the late Cenozoic climate, Nature 359, 117–122.
Rea, D.K., 1992. Delivery of Himalayan sediment to northern Indian Ocean and its relation to global climate, sea level, uplift and seawater strontium. in Duncan, R. A., Rea, D. K., Kidd, R. B., von Rad, U. and Weissel, J. K. (eds.), Synthesis of Results from Scientific Drilling in the Indian Ocean, Am. Geophys. Union Mono, 70: 387–402.
Roeser, H. A. and Sonne 122 Scientific Party, 1997, MAKRAN I: The Makran accretionary wedge off Pakistan: tectonic evolution and fluid migration-Part I. Cruise Report SONNE cruise SO 122 (7 August-6 September 1997), Report No. 116643, Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe, Germany.
Royden, L. and Keen, C. E., 1980, Rifting processes and thermal evolution of the continental margin of eastern Canada determined from subsidence curves, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 51, 714–717.
Royer, J. Y., Sclater, J. G., Fisher, R. L., Cande, S., Schlich, R., Munschy, M., Dyment, J. and Coffin, M. F., 1992, Indian Ocean Plate tectonic reconstructions since the Late Jurassic. in Duncan, R.A. et al. (eds.) Synthesis of Results from Scientific Drilling in the Indian Ocean, Am. Geophys. Union Mono., 70, 471–475.
Schärer, U., Copeland, P., Harrison, T. M. and Searle, M. P., 1990, Age, cooling history and origin of post-collisional leucogranites in the Karakoram batholith: A multi-system isotope study, J. Geol., 98, 233–251.
Sclater, J. G. and Christie, P. A. F., 1980, Continental stretching; an explanation of the post-Mid-Cretaceous subsidence of the central North Sea basin, J. Geophys. Res., 85, 3711–3739.
Searle, M. P., Weinberg, R. F. and Dunlap, W. J., 1998, Transpression tectonics along the Karakoram fault zone, northern Ladakh; constraints on Tibetan extrusion. in Holdsworth, R. E. et al. (eds.), Continental transpressional and transtensional tectonics, Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ., 135, 307–326.
Searle, M. P., Rex, A. J., Tirrul, R., Rex, D. C., Barnicoat, A. C. and Windley, B. F., 1989, Metamorphic, magmatic, and tectonic evolution of the central Karakoram in the Biafo-Baltoro-Hushe regions of northern Pakistan in Malinconico, L. L. and Lillie, R. J. (eds.), Tectonics of the western Himalayas, Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Paper, 232, 47–73.
Shuaib, S.M., 1982, Geology and hydrocarbon potential of offshore Indus Basin, Pakistan. Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull., 66, 940–946.
Treloar, P. J., Rex, D. C., Guise, P. G., Coward, M. P., Searle, M. P., Windley, B. F., Petterson, M. G., Jan, M. Q. and Luff, I. W., 1989, K-Ar and Ar-Ar geochronology of the Himalayan collision in NW Pakistan: Constraints on the timing of suturing, deformation, metamorphism and uplift, Tectonics 8, 881–909.
Walker, J. D., Martin, M. W., Bowring, S. A., Searle, M. P., Waters, D. J. and Hodges, K. V. 1999, Metamorphism, melting, and extension; age constraints from the High Himalayan slab of Southeast Zanskar and Northwest Lahaul, J. Geol., 107, 473–495.
Weber, M. E., Wiedicke, M. H., Kudrass, H. R., Hübsche, C. and Erlenkeuse, H., 1997, Active growth of the Bengal Fan during sea-level rise and highstand, Geology, 25, 315–318.
Webster, P. J., Magana, V. O., Palmer, T. N., Shukla, J., Tomas, R. A., Yanai, M. and Yasunari, T., 1998, Monsoons: Processes, predictability, and the prospects for prediction, in the TOGA decade, J. Geophys. Res., 103, 14,451–14,510.
White, R. and McKenzie, D. P., 1989, Magmatism at rift zones: The generation of volcanic continental margins and flood basalts, J. Geophys. Res., 94, 7685–7729.
White, R. S., Westbrook, G. K., Bowen, A. N., Fowler, R. S., Spence, G. D., Prescott, C., Barton, P. J., Joppen, M., Morgan, J. and Bott, M. H. P., 1987, Hatton Bank (northwest UK) continental margin structure, Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc., 89, 265–272.
Williams, H., Turner, S., Kelley, S. and Harris, N., 2001, Age and composition of dikes in southern Tibet: New constraints on the timing of east-west extension and its relations to postcollisional volcanism, Geology, 29, 339–342.
Zachos, J. C., Pagani, M., Sloan, L., Thomas, E. and Billups, K., 2001, Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to Present, Science, 292, 686–692.
Zhang, P., Molnar, P. and Downs, W. R., 2001, Increased sedimentation rates and grain sizes 2–4 Myr ago due to the influence of climate change on erosion rates, Nature, 410, 891–897.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clift, P., Gaedicke, C., Edwards, R. et al. The stratigraphic evolution of the Indus Fan and the history of sedimentation in the Arabian Sea. Marine Geophysical Researches 23, 223–245 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023627123093
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023627123093