Abstract
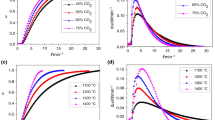
Four chars prepared from pulverized coals were subjected to non-isothermal and isothermal combustion tests in a thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) device. Three different test methods, i. e., non-isothermal single heating rate (A), non-isothermal multiple heating rate (B), and isothermal test (C), were conducted to calculate the kinetic parameters of combustion of coal char. The results show that the combustion characteristics of bituminous coal char is better than that of anthracite char, and both increase of heating rate and increase of combustion temperature can obviously improve combustion characteristics of coal char. Activation energies of coal char combustion calculated by different methods are different, with activation energies calculated by methods A, B and C in the range of 103. 12–153. 77, 93. 87–119. 26, and 46. 48–76. 68 kJ/mol, respectively. By using different methods, activation energy of anthracite char is always higher than that of bituminous coal char. In non-isothermal tests, with increase of combustion temperature, the combustion process changed from kinetic control to diffusion control. For isothermal combustion, the combustion process was kinetically controlled at temperature lower than 580 °C for bituminous coal char and at temperature lower than 630 °C for anthracite char.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Y. Zhang, L. Z. Jin, L. Y. Wang, Y. H. Jin, Coal Sci. Technol. 34 (2006) No. 10, 62–65.
C. L. Qi, J. L. Zhang, X. H. Lin, Q. Y. Liu, X. L. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18 (2011) No. 8, 1–8.
J. L. Zhang, G. W. Wang, X. D. Xing, Q. H. Pang, J. G. Shao, S. Ren, J. Iron Steel Res. 25 (2013) No. 4, 9–14.
N. M. Laurendeau, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 4 (1978) 221–270.
H. Liu, Energ. Fuel 23 (2009) 4278–4285.
G.G. Fouga, G. D. Micco, A. E. Bohe, Fuel 90 (2011) 674–680.
B. Jankovic, Chem. Eng. J. 162 (2010) 331–340.
F. Hua, Z. C. Liu, Shandong Electric Power 24 (1988) No. 6, 6–10.
S. X. Xiao, Q. Y. Fang, P. F. Fu, H. C. Zhou, J. Eng. Thermophys. 25 (2004) 891–893.
A. W. Cpats, J. P. Redfern, Nature 201 (1965) 68–69.
C. Li, Y. Yamamoto, M. Suzuki, D. Hirabayashi, K. Suzuki, J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 95 (2009) 991–997.
M. X. Fang, D. K. Shen, Y. X. Li, C. J. Yu, Z. Y. Luo, K. F. Cen, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 77 (2006) 22–27.
A. G. Dumanli, S. Tas, Y. Yurum, J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 103 (2011) 925–933.
S. P. Zou, Y. L. Wu, M. D. Yang, C. Li, J. M. Tong, Biore-sour. Technol. 101 (2010) 359–365.
C. D. Doyle, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 6 (1962) 639–642.
N. Zouaoui, J. F. Brilhac, F. Mechati, M. Jeguirim, B. Djel-louli, P. Gilot, J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 102 (2010) 837–849.
M. Kalogirou, P. Pistikopoulos, L. Ntziachristos, Z. Samaras, J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 95 (2009) 141–147.
Y. Q. Hu, H. Nikzat, M. Nawata, N. Kobayashi, M. Hasa-tani, Fuel 80 (2001) 2111–2116.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Natuml Science Foundation of China and Baosteel (51134008); National Key Technology Research and Development Program in the 12th Five-year Plan of China (2011BAC01B02)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Gw., Zhang, Jl., Shao, Jg. et al. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Coal Char Combustion Kinetics. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21, 897–904 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60159-X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60159-X