Abstract
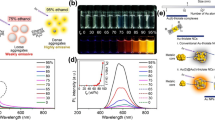
Designing ratiometric sensors for cysteine (Cys) monitoring with high accuracy is of great significance for disease diagnosis and biomedical studies. The current ratiometric methods mainly rely on multiplex probes, which not only complicates the operation but also increases the cost, making it difficult for quantitative Cys detection in resource-limited areas. Herein, one-pot prepared gold nanoclusters (Au NCs) that glow red fluorescent were synthesized by employing glutathione as the stabilizer and reducing agent. When Fe3+ is present with Au NCs, the fluorescence is quenched and the scattering is strong because of the aggregation of Au NCs. With introduction of Cys, Cys can efficiently compete with glutathione-modified Au NCs for Fe3+, which leads to increase of fluorescence and decrease of scattering. The ratiometric determination of Cys can be thereby realized by collecting the fluorescence and SRS spectrum simultaneously. The linear range for Cys was 5–30 µM with a detection limit of 1.5 µM. In addition, the sensing system exhibits good selectivity for Cys and shows potential application in biological samples.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
I. Nandi, S. Chall, S. Chowdhury, T. Mitra, S.S. Roy, K. Chattopadhyay, Protein fibril-templated biomimetic synthesis of highly fluorescent gold nanoclusters and their applications in cysteine sensing. ACS Omega 3, 7703–7714 (2018)
M.H. Stipanuk, J.E. Dominy Jr., J.-I. Lee, R.M. Coloso, Mammalian cysteine metabolism: New insights into regulation of cysteine metabolism. J. Nutr. 136, 1652S-1659S (2006)
M.T. Heafield, S. Fearn, G.B. Steventon, R.H. Waring, A.C. Williams, S.G. Sturman, Plasma cysteine and sulphate levels in patients with motor neurone, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 110, 216–220 (1990)
Y. Ozkan, E. Ozkan, B. Simşek, Plasma total homocysteine and cysteine levels as cardiovascular risk factors in coronary heart disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 82, 269–277 (2002)
T.S.T. Balamurugan, C.-H. Huang, P.-C. Chang, S.-T. Huang, Electrochemical molecular switch for the selective profiling of cysteine in live cells and whole blood and for the quantification of Aminoacylase-1. Anal. Chem. 90, 12631–12638 (2018)
A. Safavi, R. Ahmadi, F.A. Mahyari, Simultaneous electrochemical determination of L-cysteine and L-cysteine disulfide at carbon ionic liquid electrode. Amino Acids 46, 1079–1085 (2014)
A.A. Dutov, D.A. Nikitin, A.A. Fedotov, HPLC determination of plasma/serum homocysteine and cysteine with UV detection and solid-phase extraction on a polymeric sorbent. Biomeditsinskaia Khimiia 56, 609–615 (2010)
A. Kamińska, P. Olejarz, K. Borowczyk, R. Głowacki, G. Chwatko, Simultaneous determination of total homocysteine, cysteine, glutathione, and N-acetylcysteine in brain homogenates by HPLC. J. Sep. Sci. 41, 3241–3249 (2018)
R. Saletti, S. Reina, M.G.G. Pittalà, R. Belfiore, V. Cunsolo, A. Messina, V. De Pinto, S. Foti, High resolution mass spectrometry characterization of the oxidation pattern of methionine and cysteine residues in rat liver mitochondria voltage-dependent anion selective channel 3 (VDAC3). Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1859, 301–311 (2017)
N. Burford, M.D. Eelman, D.E. Mahony, M. Morash, Definitive identification of cysteine and glutathione complexes of bismuth by mass spectrometry: assessing the biochemical fate of bismuth pharmaceutical agents. Chem. Commun. 21, 146–147 (2003)
J. Piechocka, M. Wieczorek, R. Głowacki, Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry based approach for the determination of methionine-related sulfur-containing compounds in human saliva. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 9252 (2020)
A.V. Ivanov, E.D. Virus, B.P. Luzyanin, A.A. Kubatiev, Capillary electrophoresis coupled with 1,1′-thiocarbonyldiimidazole derivatization for the rapid detection of total homocysteine and cysteine in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B. 1004, 30–36 (2015)
D. Zhang, F. Zhang, Y. Liao, F. Wang, H. Liu, Carbon quantum dots from pomelo peel as fluorescence probes for “turn-off–on” high-sensitivity detection of Fe3+ and L-cysteine. Molecules 27, 4099 (2022)
S.-N. Wang, J. Zhu, X. Li, J.-J. Li, J.-W. Zhao, Fluorescence turn-on sensing of trace cadmium ions based on EDTA-etched CdTe@CdS quantum dot. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 201, 119–127 (2018)
A. Pundi, C.-J. Chang, J. Chen, S.-R. Hsieh, M.-C. Lee, A dimedone-phenylalanine-based fluorescent sensor for the detection of iron (III), copper (II), L-cysteine, and L-tryptophan in solution and pharmaceutical samples. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 274, 121108 (2022)
S. Han, H. Zhang, X. Yue, J. Wang, L. Yang, B. Wang, X. Song, A ratiometric, fast-responsive, and single-wavelength excited fluorescent probe for the discrimination of Cys and Hcy. Anal. Chem. 93, 10934–10939 (2021)
J.-J. Li, D. Qiao, J. Zhao, G.-J. Weng, J. Zhu, J.-W. Zhao, Fluorescence turn-on sensing of L-cysteine based on FRET between Au-Ag nanoclusters and Au nanorods. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 217, 247–255 (2019)
R. Joseph, Selective detection of Fe3+, F-, and cysteine by a novel triazole-linked decaamine derivative of pillar[5]arene and its metal ion complex in water. ACS Omega 5, 6215–6220 (2020)
X. Huang, J. Song, B.C. Yung, X. Huang, Y. Xiong, X. Chen, Ratiometric optical nanoprobes enable accurate molecular detection and imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 2873–2920 (2018)
Z. Meng, K.A. Mirica, Covalent organic frameworks as multifunctional materials for chemical detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 13498–13558 (2021)
W. Dong, R. Wang, X. Gong, W. Liang, L. Fan, S. Song, C. Dong, A ratiometric and far-red fluorescence “off-on” sensor for sequential determination of copper(II) and L-histidine based on FRET system between N-acetyl-L-cysteine-capped AuNCs and N, S, P co-doped carbon dots. Microchim. Acta 187, 299 (2020)
X. Yuan, H. Zhao, F. Bai, P. Zhao, L. Zhao, Z. Xiong, Fluorescence and scattering based dual-optical signals ratiometric sensing and logic gate device for acetylcholinesterase activity assay. Microchem. J. 170, 106768 (2021)
Z. Wu, H. Yang, S. Pan, H. Liu, X. Hu, Fluorescence-scattering dual-signal response of carbon dots@ZIF-90 for phosphate ratiometric detection. ACS Sens. 5, 2211–2220 (2020)
S.G. Liu, N. Li, L. Han, L.J. Li, N.B. Li, H.Q. Luo, Size-dependent modulation of fluorescence and light scattering: a new strategy for development of ratiometric sensing. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Mater. Horiz. 5, 454–460 (2018)
L.-Y. Chen, C.-W. Wang, Z. Yuan, H.-T. Chang, Fluorescent gold nanoclusters: recent advances in sensing and imaging. Anal. Chem. 87, 216–229 (2015)
H.-H. Deng, K.-Y. Huang, M.-J. Zhang, Z.-Y. Zou, Y.-Y. Xu, H.-P. Peng, W. Chen, G.-L. Hong, Sensitive and selective nitrite assay based on fluorescent gold nanoclusters and Fe2+/Fe3+ redox reaction. Food Chem. 317, 126456 (2020)
M. Wang, Z. Yu, H. Feng, J. Wang, L. Wang, Y. Zhang, L. Yin, Y. Du, H. Jiang, X. Wang, J. Zhou, In situ biosynthesized gold nanoclusters inhibiting cancer development via the PI3K–AKT signaling pathway. J. Mater. Chem. B. 7, 5336–5344 (2019)
H. Chen, C. Liu, M. Wang, C. Zhang, N. Luo, Y. Wang, H. Abroshan, G. Li, F. Wang, Visible light gold nanocluster photocatalyst: selective aerobic oxidation of amines to imines. ACS Catal. 7, 3632–3638 (2017)
W. Li, X. Wen, H. Zhao, W. Yan, J.F. Trant, Y. Li, Acid-Triggered self-assembled egg white protein-coated gold nanoclusters for selective fluorescent detection of Fe3+, NO2-, and cysteine. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3, 11838–11849 (2020)
F. Ru, P. Du, X. Lu, Efficient ratiometric fluorescence probe utilizing silicon particles/gold nanoclusters nanohybrid for “on-off-on” bifunctional detection and cellular imaging of mercury (II) ions and cysteine. Anal. Chim. Acta 1105, 139–146 (2020)
Y. Zhang, H. Xu, Y. Chen, X. You, Y. Pu, W. Xu, X. Liao, High-sensitivity detection of cysteine and glutathione using au nanoclusters based on aggregation-induced emission. J. Fluoresc. 30, 1491–1498 (2020)
K. Chen, W. Qing, W. Hu, M. Lu, Y. Wang, X. Liu, On-off-on fluorescent carbon dots from waste tea: Their properties, antioxidant and selective detection of CrO42−, Fe3+, ascorbic acid and L-cysteine in real samples. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 213, 228–234 (2019)
X. Yu, C.-X. Zhang, L. Zhang, Y.-R. Xue, H.-W. Li, Y. Wu, The construction of a FRET assembly by using gold nanoclusters and carbon dots and their application as a ratiometric probe for cysteine detection. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 263, 327–335 (2018)
Q. Tang, Y.Z. Fan, L. Han, Y.Z. Yang, N.B. Li, H.Q. Luo, Redox induced dual-signal optical sensor of carbon dots/MnO2 nanosheets based on fluorescence and second-order scattering for the detection of ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 187, 475 (2020)
D. Liu, X. Pan, W. Mu, C. Li, X. Han, Detection of tetracycline in water using glutathione-protected fluorescent gold nanoclusters. Anal. Sci. 35, 367–370 (2019)
W. Dong, J. Yu, X. Gong, W. Liang, L. Fan, C. Dong, A turn-off-on near-infrared photoluminescence sensor for sequential detection of Fe3+ and ascorbic acid based on glutathione-capped gold nanoclusters. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 247, 119085 (2021)
P.M. Brigham, W.H. Stein, S. Moore, The concentrations of cysteine and cystine in human blood plasma. Clin. Invest. 39, 1633 (1960)
F.S. Kariapper, F.Y. Thanzeel, L.S. Zandi, C. Wolf, Selective chiroptical sensing of D/L-cysteine. Org. Biomol. Chem. 20, 3056–3060 (2022)
Y. Su, L. Qi, X. Mu, M. Wang, A fluorescent probe for sensing ferric ions in bean sprouts based on L-histidine-stabilized gold nanoclusters. Anal. Meth. 7, 684–689 (2015)
C. Zhang, Y. Gao, N. Yang, T. You, H. Chen, P. Yin, Direct determination of the tumor marker AFP via silver nanoparticle enhanced SERS and AFP-modified gold nanoparticles as capturing substrate. Microchim Acta 185, 90 (2018)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the funding supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81860610) and Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (20224BAB216116).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L-NH: Conceptualization and writing-original draft; H-TC: Investigation; Y-XF: Formal analysis; L-ZG: Data curation; M-QL: Methodology; KZ: Validation; XM: Writing review & editing; NL: Conceptualization, Writing review & editing, and supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, LN., Cao, HT., Feng, YX. et al. Aggregation-caused dual-signal response of gold nanoclusters for ratiometric optical detection of cysteine. ANAL. SCI. 39, 1719–1726 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00385-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-023-00385-7