Abstract
Background
Posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) entrapment syndrome is a rare condition and is predisposed by anatomical factors such as narrow passages through fibrous arcades; whereas, the Arcade of Frohse (AF) is the most common entrapment point. The aim of this study was to evaluate the entrance and exit points of the PIN into the supinator in detail.
Materials and Methods
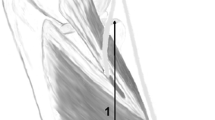
One hundred unpaired upper extremities underwent dissection. The PIN’s entrance and exit points from the supinator were depicted. The distances between the tip of the radial head (RH) and the AF and the exit point of the PIN from the supinator were measured. Further, it was checked if the borders of the AF and the exit point were muscular, tendinous or a combination of these.
Results
The interval between the PIN’s entry into the supinator and the tip of the RH was at a mean of 28.9 mm. Concerning the border of the AF, in 54 cases a muscular and in 46 specimens a tendinous version could be observed. The interval between the exit point of the PIN and the tip of the RH proved to be at a mean of 64.2 mm. Further, the exit’s border was muscular in 65 specimens and tendinous in 35 cases.
Conclusion
During surgical treatment of the PIN syndrome, it needs to be kept in mind that approximately one-third of all patients might also suffer from entrapment at the exit point of the PIN.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, Y., Ha, D. H., & Lee, S. M. (2017). Ultrasonographic findings of posterior interosseous nerve syndrome. Ultrasonography, 36, 363–369.
Werner, C. O. (1979). Lateral elbow pain and posterior interosseous nerve entrapment. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica, 174, 1–62.
Anania, P., Fiaschi, P., Ceraudo, M., Balestrino, A., Zaottini, F., Martinoli, C., et al. (2018). Posterior interosseous nerve entrapments: Review of the literature: Is the entrapment distal to the arcade of Frohse a really rare condition? Acta Neurochir (Wien), 160, 1857–1864.
Bäumer, P., Kele, H., Xia, A., Weiler, M., Schwarz, D., Bendszus, M., et al. (2016). Posterior interosseous neuropathy: Supinator syndrome vs fascicular radial neuropathy. Neurology, 87, 1884–1891.
Latinovic, R., Gulliford, M. C., & Hughes, R. A. (2006). Incidence of common compressive neuropathies in primary care. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 77, 263–265.
Niu, X., Hu, Y., Zha, G., Hu, J., Yi, J., & Xiao, L. (2019). Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome secondary to compression by an intramuscular hemangioma. Muscle and Nerve, 60, E5–E6.
Hazani, R., Engineer, N. J., Mowlavi, A., Neumeister, M., Lee, W. P., & Wilhelmi, B. J. (2008). Anatomic landmarks for the radial tunnel. Eplasty, 8, e37.
Portilla Molina, A. E., Bour, C., Oberlin, C., Nzeusseu, A., & Vanwijck, R. (1998). The posterior interosseous nerve and the radial tunnel syndrome: An anatomical study. International Orthopaedics, 22, 102–106.
Carfi, J., & Ma, D. M. (1985). Posterior interosseous syndrome revisited. Muscle and Nerve, 8, 499–502.
Tan, J. S., & Yam, A. K. (2011). Spontaneous partial posterior interosseous nerve palsy not caused by an adjacent ganglion. Hand Surgery, 16, 171–172.
Thomas, S. J., Yakin, D. E., Parry, B. R., & Lubahn, J. D. (2000). The anatomical relationship between the posterior interosseous nerve and the supinator muscle. The Journal of Hand Surgery: American Volume, 25, 936–941.
Thiel, W. (2002). Supplement to the conservation of an entire cadaver according to W. Thiel. Annals of Anatomy, 184, 267–269.
R Core Team. (2015). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/.
Anderhuber, F., Pera, F., & Waldeyer, S. J. (2012). Anatomie des Menschen. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Braus, H., & Elze, C. (1940). Anatomie des Menschen: Ein Lehrbuch für Studierende und Ärzte: 4. Band: Periphere Leitungsbahnen II, Haut und Sinnesorgane, Vegetatives Nervensystem. Berlin: Verlag Julius von Springer.
Hafferl, A. (1953). Lehrbuch der topographischen Anatomie. Berlin: Springer.
Sieglbauer, F. (1940). Lehrbuch der normalen Anatomie des Menschen. Berlin: Urban und Schwarzenberg.
Loh, Y. C., Stanley, J. K., Jari, S., & Trail, I. A. (1998). Neuroma of the distal posterior interosseous nerve. A cause of iatrogenic wrist pain. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery: British Volume, 80, 629–630.
Wada, T., Ogino, T., Usui, M., & Ishii, S. (1997). Distal posterior interosseous nerve syndrome. Handchirurgie, Mikrochirurgie, Plastische Chirurgie, 29, 129–132.
Tubbs, R. S., Mortazavi, M. M., Farrington, W. J., Chern, J. J., Shoja, M. M., Loukas, M., et al. (2013). Relationships between the posterior interosseous nerve and the supinator muscle: Application to peripheral nerve compression syndromes and nerve transfer procedures. Journal of Neurological Surgery A, 74, 290–293.
Keogh, A., Graham, D. J., & Tan, B. (2018). Posterior interosseous artery pedicle flap: An anatomical study of the relationship between the posterior interosseous nerve and artery. Journal of Hand and Surgery: European Volume, 43, 1050–1053.
Reyes, L. M., Kho, P. A. B., & Wang, E. H. (2017). The relationship of the posterior interosseous nerve to the supinator muscle in the dorsal approach to the proximal radius: A descriptive and quantitative anatomic study of Filipino cadavers. Acta Medica Philippina, 51, 74–78.
Spinner, M. (1968). The arcade of Frohse and its relationship to posterior interosseous nerve paralysis. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery: British Volume, 50, 809–812.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AMS: Protocol development; Data collection; Manuscript writing. GMH: Protocol development; Data collection; Manuscript writing. PG: Data collection; Manuscript editing. MJM: Statistical analysis; Manuscript editing. US: Data collection; Manuscript editing. SK: Data analysis; Manuscript editing. AG: Data analysis; Manuscript editing. AW: Protocol development; Manuscript writing & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Andreas Heinrich Weiglein: Deceased.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hohenberger, G.M., Schwarz, A.M., Grechenig, P. et al. Morphology of the Posterior Interosseous Nerve with Regard to Entrapment Syndrome. JOIO 54 (Suppl 1), 188–192 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-020-00084-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-020-00084-9