Abstract
Background
AO clavicular hook plates have been widely used for treating acromioclavicular (AC) joint dislocation and distal clavicle fractures. Many complications have been reported, and many patients have complained about the discomfort of the plate. However, no study on the impact of clavicular hook plates in AC joint 3D printing models has been reported.
Objective
To evaluate the matching performance of hook plates with different hook depths when they were implanted in 3D printing models of normal Chinese AC joints and to propose a further design to achieve a better match.
Methods
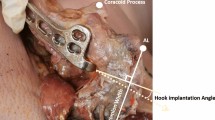
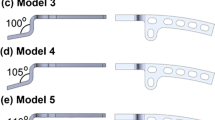
AO clavicular hook plates with two different hook depths of 15 mm and 18 mm were implanted in 3D printing models of forty Chinese normal AC joints. The angle between the distal clavicle and plate (CPA) and the drop between acromion and distal clavicle (ACD) of normal AC joints with and without plates were measured.
Results
Mismatch was found when the hook plates were implanted, with an average CPA of 18.8 ± 5.1° with the 15-mm hook plate and 10.2 ± 4.9° with the 18-mm hook plate. To eliminate the CPA, the ACD decreased by 6.3 ± 1.1 mm with the 15-mm hook plate and 2.9 ± 0.9 mm with the 18-mm hook plate.
Conclusions
The results revealed that AO clavicular hook plates with different hook depths were very likely to result in over-reduction of the AC joint. It is necessary to bend the hook angle to fit the patient’s AC joint to achieve accurate reduction.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Acromioclavicular
- CPA:
-
Angle between clavicle and plate
- ORIF:
-
Open reduction and internal fixation
- ACD:
-
Drop between the distal clavicle and acromion
References
Alexander, D. F., Carmine, Z., Olivo, C., Renzo, P., & Stefano, F. (2012). The use of hook plate in type III and V acromio-clavicular Rockwood dislocations: clinical and radiological midterm results and MRI evaluation in 42 patients. Injury International Journal of the Care of the Injured,43(2), 147–152.
Ejam, S., Lind, T., & Falkenberg, B. (2008). Surgical treatment of acute and chronic acromioclavicular dislocation Tossy type III and V using the Hook plate. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica,74(74), 441–445.
Li, X. N., Richard, M., Asheesh, B., Dines, D. M., Altchek, D. W., & Dines, J. S. (2014). Management of acromioclavicular joint injuries. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American,96(1), 73–84.
Kashii, M., Inui, H., & Yamamoto, K. (2006). Surgical treatment of distal clavicle fractures using the clavicular hook plate. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research,447(447), 158–164.
Meda, P. V. K., Bhuvaneswar, M., Chris, S., Ian, B., Peter, B., & Frostick, S. P. (2006). Clavicular hook plate for lateral end fractures: A prospective study. Injury International Journal of the Care of the Injured,37(3), 277–283.
Meijden, O. A. V. D., Gaskill, T. R., & Millett, P. J. (2012). Treatment of clavicle fractures: current concepts review. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery,21(3), 423–429.
Chen, C. H., Dong, Q. R., Zhou, R. K., Zhen, Q. H., & Jiao, Y. J. (2014). Effects of hook plate on shoulder function after treatment of acromioclavicular joint dislocation. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine,7(9), 2564.
Ding, M., Ni, J., Hu, J., & Song, D. (2011). Rare complication of clavicular hook plate: clavicle fracture at the medial end of the plate. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery,20(7), e18–e20.
Charity, R. M., Haidar, S. G., Ghosh, S., & Tillu, A. B. (2006). Fixation failure of the clavicular hook plate: a report of three cases. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery,14(3), 333–335.
Shahzad Nasir, C., & Mohammad, W. (2006). Clavicular hook plate: complications of retaining the implant. Injury International Journal of the Care of the Injured,37(7), 665.
Athanasios, K., Andreas, M., Apostolou, C. D., Emmanuel, L., Artemisia, P., Christos, T., et al. (2008). Results using the AO hook plate for dislocations of the acromioclavicular joint. Expert Review of Medical Devices,5(5), 567–572.
Lin, H. Y., Wong, P. K., Ho, W. P., Chuang, T. Y., Liao, Y. S., & Wong, C. C. (2014). Clavicular hook plate may induce subacromial shoulder impingement and rotator cuff lesion dynamic sonographic evaluation. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research,9(1), 6–6.
Kim, Y. S., Yoo, Y. S., Jang, S. W., Nair, A. V., Jin, H., & Song, H. S. (2015). Invivo analysis of acromioclavicular joint motion after hook plate fixation using three-dimensional computed tomography. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery,24(7), 1106–1111.
Tapio, F., Jukka, R., Pekka, H. N., & Martti, H. M. L. I. (2002). Surgical treatment of unstable fractures of the distal clavicle: a comparative study of Kirschner wire and clavicular hook plate fixation. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica,73(1), 50–53.
Lee, Y. S., Lau, M. J., Tseng, Y. C., Chen, W. C., Kao, H. Y., & Wei, J. D. (2009). Comparison of the efficacy of hook plate versus tension band wire in the treatment of unstable fractures of the distal clavicle. International Orthopaedics,33(5), 1401–1405.
Yoon, J. P., Lee, Y. S., Song, G. S., & Oh, J. H. (2016). Morphological analysis of acromion and hook plate for the fixation of acromioclavicular joint dislocation. Knee Surgery Sports Traumatology Arthroscopy,25(3), 1–7.
Elmaraghy, A. W., Devereaux, M. W., Kajeandra, R., & Agur, A. M. (2010). Subacromial morphometric assessment of the clavicle hook plate. Injury International Journal of the Care of the Injured,41(6), 613–619.
Colegate-Stone, T., Allom, R., Singh, R., Elias, D. A., Standring, S., & Sinha, J. (2010). Classification of the morphology of the acromioclavicular joint using cadaveric and radiological analysis. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery British,92(5), 743–746.
Lee, C. H., Shih, C. M., Huang, K. C., et al. (2016). Biomechanical analysis of implanted clavicle hook plates with different implant depths and materials in the acromioclavicular joint: A finite element analysis study[J]. Artificial Organs,40(11), 1062–1070.
Wu, X., Wang, G., Rong, K., et al. (2019). 3D printed model used as preoperative tool for treating acromioclavicular joint dislocation with pre-contoured clavicle hook plate[J]. ZeitschriftfürOrthopädie und Unfallchirurgie,14(1), 1–7.
Anetzberger, H., & Putz, R. (1995). Morphometry of the sub-acromial space and its clinical relevance. Unfallchirurg,98(8), 407–414.
Graichen, H., Bonel, H., Stammberger, T., Haubner, M., Rohrer, H., Englmeier, K. H., et al. (1999). Three-dimensional analysis of the width of the subacromial space in healthy subjects and patients with impingement syndrome. American Journal of Roentgenology,172(4), 1081–1086.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Central Laboratory of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University for the technical guidance.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW conceived the study, and XW and GW participated in its design and coordination. QX and KR performed the operations. XW, XY, and GW analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. All authors interpreted the data and participated in drafting the text and tables. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standard statement
The Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University approved this study.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Wang, G., Xia, Q. et al. Digital Technology Combined with 3D Printing to Evaluate the Matching Performance of AO Clavicular Hook Plates. JOIO 54, 141–147 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-019-00034-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-019-00034-0