Abstract
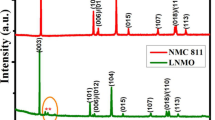
High nickel ternary cathode materials (Ni ≥ 90%) have great potential for application as power batteries in electric vehicles and have become a hot spot for research on cathode materials. However, the residual Li on the surface of the high Ni ternary cathode materials prepared by solid-phase sintering is one of the main reasons affecting their electrochemical performance. It is found that Li1 + x(Ni0.9Co0.05Mn0.05)1-xO2 with x = 0.3, which has a discharge-specific capacity of 205.74 mAh g−1 at 2.7–4.3 V, 0.1C and 184.1 mAh g−1 at 1 C, retained 89% of its initial discharge capacity after 100 cycles at 1 C. The discharge-specific capacity at 10 C was 153.14 mAh g−1. In addition, the Li residue of NCM90-1.03 was 17,189.959 ppm, and the total alkalinity was 4196.896 ppm. The results by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) showed that when the Li excess was 0.3%, it was possible to obtain uniform particle size, a wider Li layer, and reduced cation mixing. Therefore, choosing the right amount of excess Li can stimulate the application prospect of NCM90 in new energy vehicles.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
L. Li, Y. Xu, Development status and trend analysis of lithium-ion power batteries. China’s Man Indus. 38(05), 9–13 (2020)
F.B. Zhang, Development status and research progress of power battery for pure electric vehicles. J Zhangzhou Insti Technol. 22(02), 86–91 (2020)
G.E. Blomgren, The development and future of lithium ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 164(1), A5019–A5025 (2016)
Y. Ding, D. Mu, B. Wu, R. Wang, Z. Zhao, F. Wu, Recent progresses on nickel-rich layered oxide positive electrode materials used in lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. Appl. Energy. 195, 586–599 (2017)
E. Fan, L. Li, Z. Wang, J. Lin, Y. Huang, Y. Yao, R. Chen, F. Wu, Sustainable recycling technology for li-ion batteries and beyond: challenges and future prospects. Chem. Rev. 120(14), 7020–7063 (2020)
Y. Kim, Point defects in layer-structured cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. A. 120(8), 4173–4182 (2016)
A. Masias, J. Marcicki, W.A. Paxton, Opportunities and challenges of lithium ion batteries in automotive applications. ACS Energy Lett. 6(2), 621–630 (2021)
L. Jia, 2017–2016 automotive lithium-ion battery market analysis and research report. Inorg Chem Indus. Inorg Chem Indus. 50(01), 77 (2018)
Z. Qu, S. Liu, P. Zhang, R. Wang, H. Wang, B. He, Y. Gong, J. Jin, S. Li, Enhanced eletrochemical performances of LiCoO2 at high cut-off voltage by introducing LiF additive. Solid State Ion. 365, 115654 (2021)
M. Zou, S. Masaki Yoshio, J.Y. Gopukumar, Synthesis of high-voltage (45 V) cycling doped licoo2 for use in lithium rechargeable cells. Chem. Mater. 15(25), 4699–4720 (2003)
Y. He, Q. Feng, S. Zhang, Q. Zou, X. Wu, X. Yang, Strategy for lowering li source dosage while keeping high reactivity in solvothermal synthesis of LiMnO2 nanocrystals. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 1(6), 570–573 (2013)
N. Leifer, F. Schipper, E.M. Erickson, C. Ghanty, M. Talianker, J. Grinblat, C.M. Julien, B. Markovsky, D. Aurbach, Studies of spinel-to-Layered structural transformations in limn2o4 electrodes charged to high voltages. J. Phys. Chem. A. 121(17), 9120–9130 (2017)
I.D. Seymour, D.J. Wales, C.P. Grey, Preventing structural rearrangements on battery cycling: a first-principles investigation of the effect of dopants on the migration barriers in Layered Li05MnO2. J. Phys. Chem. A. 120(35), 19521–19530 (2016)
T. Zhang, S. Lin, J.G. Yu, Research progress in synthesis and performance enhancement of Li FePO4 cathode materials Inorganic. Chemicals Industry. 53(06), 31–40 (2021)
G. Li, P. Wu, C. Luo, Q. Cui, G. Wang, K. Yan, Mass production of LiFePO4/C energy materials using Fe–P waste slag. J. Energy Chem. 24(4), 375–380 (2015)
T. Teng, L. Xiao, L. Shen, G. Qiu, J. Ran, X. Guo, Y. Zhu, H. Chen, Effect of Nb doping at Fe site on the cycling stability and rate capability of LiFePO4 for lithium-ion batteries. Vacuum 203, 111306 (2022)
Z. Chen, Z. Wang, G.T. Kim, G. Yang, H. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Huang, S. Passerini, Z. Shen, Enhancing the Electrochemical Performance of LiNi0.4Co0.2Mn0.4O2 by V2O5/LiV3O8 Coating. ACS Appl. Mater. 11(30), 26994–27003 (2019)
J. Kasnatscheew, M. Evertz, B. Streipert, R. Wagner, S. Nowak, I. Cekic Laskovic, M. Winter, Changing established belief on capacity fade mechanisms: thorough investigation of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 (NCM111) under high voltage conditions. J. Phys. Chem. A. 121(3), 1521–1529 (2017)
J. Li, Z. Liu, Y. Wang, R. Wang, Investigation of facial B2O3 surface modification effect on the cycling stability and high-rate capacity of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode. J. Alloys Compd. 834, 155150 (2020)
C.H. Shen, Q. Wang, H.J. Chen, C.G. Shi, H.Y. Zhang, L. Huang, J.T. Li, S.G. Sun, In Situ Multitechnical Investigation into Capacity Fading of High-Voltage LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2. ACS Appl. Mater. 8(51), 35323–35335 (2016)
J.-H. Song, J. Bae, K.-W. Lee, I. Lee, K. Hwang, W. Cho, S.J. Hahn, S. Yoon, Enhancement of high temperature cycling stability in high-nickel cathode materials with titanium doping. J Ind Eng Chem. 68, 124–128 (2018)
S. Venkatraman, J. Choi, A. Manthiram, Factors influencing the chemical lithium extraction rate from layered LiNi1−y−zCoyMnzO2 cathodes. Electrochem commun. 6(8), 832–837 (2004)
H.-J. Noh, S. Youn, C.S. Yoon, Y.-K. Sun, Comparison of the structural and electrochemical properties of layered Li[NixCoyMnz]O2 (x = 1/3, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8 and 0.85) cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources. 233, 121–130 (2013)
H.-H. Sun, A. Manthiram, Impact of microcrack generation and surface degradation on a nickel-rich layered Li[Ni0.9Co0.05Mn0.05]O2 cathode for lithium-Ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 29(19), 8486–8493 (2017)
Z. Tai, W. Zhu, M. Shi, Y. Xin, S. Guo, Y. Wu, Y. Chen, Y. Liu, Improving electrochemical performances of Lithium-rich oxide by cooperatively doping Cr and coating Li3PO4 as cathode material for Lithium-ion batteries. J Colloid Interface Sci. 576, 468–475 (2020)
S.F. Amalraj, R. Raman, A. Chakraborty, N. Leifer, R. Nanda, S. Kunnikuruvan, T. Kravchuk, J. Grinblat, V. Ezersky, R. Sun, F.L. Deepak, C. Erk, X. Wu, S. Maiti, H. Sclar, G. Goobes, D.T. Major, M. Talianker, B. Markovsky, D. Aurbach, Boron doped Ni-rich LiNi0.85Co0.10Mn0.05O2 cathode materials studied by structural analysis, solid state NMR, computational modeling, and electrochemical performance. Energy Stor. Mater. 42, 594–607 (2021)
S. Gao, B. Shi, J. Liu, L. Wang, C. Zhou, C. Guo, J. Zhang, W. Li, Boron doping and LiBO2 coating synergistically enhance the high-rate performance of LiNi06Co01Mn03O2 Cathode materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 9(15), 5322–5333 (2021)
W. Mo, Z. Wang, J. Wang, X. Li, H. Guo, W. Peng, G. Yan, Tuning the surface of LiNi08Co01Mn01O2 primary particle with lithium boron oxide toward stable cycling. Chem. Eng. J. 400, 125820 (2020)
K.-J. Park, H.-G. Jung, L.-Y. Kuo, P. Kaghazchi, C.S. Yoon, Y.-K. Sun, Improved cycling stability of Li[Ni0.90Co0.05Mn0.05]O2 through microstructure modification by boron doping for Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 8(25), 18012 (2018)
D.Y. Hwang, C.Y. Kang, J.R. Yoon, S.H. Lee, Reinforcing electrochemical performance of Ni-rich NCM cathode co-modified by mg-doping and Li3PO4-coating. Int. J. Energy Res. 46(11), 15244–15253 (2022)
D.J. Li, H.T. Guo, S.H. Jiang, G.L. Zeng, W. Zhou, Z.A. Li, Microstructures and electrochemical performances of TiO2-coated Mg-Zr co-doped NCM as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries with high power and long circular life. New J. Chem. 45(41), 19446–19455 (2021)
L. Xiao, X.C. Tang, Z. Ban, Z.L. Tang, H.N. Liu, C. Liu, Y.S. Lou, An Mg-Al dual doping strategy to enhance the structural stability and long cycle life of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cathode material. Ionics 28(7), 3101–3112 (2022)
G. Ko, S. Park, W. Kim, K. Kwon, Synergistic effect of Na and Al co-doping on the electrochemical properties of Li Ni0.8Mn0.1Co0.1 O2 cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 925, 16667 (2022)
F.C. Li, G. Zhang, Z.L. Zhang, J. Yang, F.Y. Liu, M. Jia, L.X. Jiang, Regeneration of Al-doped LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 cathode material by simulated hydrometallurgy leachate of spent lithium-ion batteries. T Nonferr Metal Soc. 32(2), 593–603 (2022)
L.S. Li, Z. Zhang, S.H. Fu, Z.Z. Liu, Y.M. Liu, Co-modification by LiAlO2-coating and Al-doping for LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 as a high-performance cathode material for lithium-ion batteries with a high cutoff voltage. J. Alloys Compd. 768, 582–590 (2018)
B. Chu, L. You, G. Li, T. Huang, A. Yu, Revealing the Role of W-Doping in Enhancing the Electrochemical Performance of the LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode at 4.5 V. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 13(6), 7308–7316 (2021)
W. Li, J. Zhang, Y. Zhou, W. Huang, X. Liu, Z. Li, M. Gao, Z. Chang, N. Li, J. Wang, S. Lu, X. Li, W. Wen, D. Zhu, Y. Lu, W. Zhuang, Regulating the grain orientation and surface structure of primary particles through tungsten modification to comprehensively enhance the performance of nickel-rich cathode materials. ACS Appl. Mater. 12(42), 47513–47525 (2020)
G.-T. Park, H.-H. Ryu, N.-Y. Park, C.S. Yoon, Y.-K. Sun, Tungsten doping for stabilization of Li[Ni090Co005Mn005]O2 cathode for Li-ion battery at high voltage. J. Power Source. 442, 2272 (2019)
F. Wu, J. Tian, Y. Su, J. Wang, C. Zhang, L. Bao, T. He, J. Li, S. Chen, Effect of Ni(2+) content on lithium/nickel disorder for Ni-rich cathode materials. ACS Appl. Mater. 7(14), 7702–7708 (2015)
A. Manthiram, J.C. Knight, S.T. Myung, S.M. Oh, Y.K. Sun, Nickel-rich and lithium-rich layered oxide cathodes: progress and perspectives. Adv. Energy Mater. 6(1), 15010 (2016)
W.-G. Ryu, H.-S. Shin, M.-S. Park, H. Kim, K.-N. Jung, J.-W. Lee, Mitigating storage-induced degradation of Ni-rich LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 cathode material by surface tuning with phosphate. Ceram. Int. 45(11), 13942–13950 (2019)
B.W. Xiao, X.L. Sun, Surface and Subsurface Reactions of Lithium Transition Metal Oxide Cathode Materials: An Overview of the Fundamental Origins and Remedying Approaches. Adv. Energy Mater. 8(29), 1123 (2018)
S. Gao, X.W. Zhan, Y.T. Cheng, Structural, electrochemical and Li-ion transport properties of Zr-modified LiNi0.8Co01Mn0.1O2 positive electrode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources. 410, 45–52 (2019)
Y. Kim, H. Park, J.H. Warner, A. Manthiram, Unraveling the intricacies of residual lithium in High-Ni cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 6(3), 941–948 (2021)
K. Park, D.J. Ham, S.Y. Park, J. Jang, D.H. Yeon, S. Moon, S.J. Ahn, High-Ni cathode material improved with Zr for stable cycling of Li-ion rechargeable batteries. RSC Adv. 10(45), 26756–26764 (2020)
Q.P. Mayra, W.S. Kim, Agglomeration of Ni-Rich hydroxide in reaction crystallization: effect of taylor vortex dimension and intensity. Cryst. Growth Des. 15(4), 1726–1734 (2015)
J.H. Duan, R.C. Zhang, Q.H. Zhu, H. Xiao, Q.S. Huang, The effect of controlling strategies of ph and ammonia concentration on preparing full concentration gradient ni08co01mn01(oh)(2) via coprecipitation in a pilot-scale reactor. Energy Technol. 8(5), 19014 (2020)
J.M. Kim, S.M. Chang, J.H. Chang, W.S. Kim, Agglomeration of nickel/cobalt/manganese hydroxide crystals in Couette-Taylor crystallizer. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 384(1–3), 31–39 (2011)
D. Ren, Y. Shen, Y. Yang, L.X. Shen, B.D.A. Levin, Y.C. Yu, D.A. Muller, H.D. Abruna, systematic optimization of battery materials: key parameter optimization for the scalable synthesis of uniform, high-energy, and high stability LiNi0.6Mn0.2Co0.2O2 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9(41), 35811–35819 (2017)
M.S. Whittingham, Lithium batteries and cathode materials. Chem. Rev. 104(10), 4271–4301 (2004)
J.D. Steiner, L.Q. Mu, J. Walsh, M.M. Rahman, B. Zydlewski, F.M. Michel, H.L.L. Xing, D. Nordlund, F. Lin, Accelerated evolution of surface chemistry determined by temperature and cycling history in nickel-rich layered cathode materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10(28), 23842–23850 (2018)
Z.L. Yu, X.Y. Qu, T. Wan, A.C. Dou, Y. Zhou, X.Q. Peng, M.R. Su, Y.J. Liu, D.W. Chu, Synthesis and mechanism of high structural stability of nickel-rich cathode materials by adjusting Li-Excess. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 12(36), 40393–40403 (2020)
F. Schipper, M. Dixit, D. Kovacheva, M. Talianker, O. Haik, J. Grinblat, E.M. Erickson, C. Ghanty, D.T. Major, B. Markovsky, D. Aurbach, Stabilizing nickel-rich layered cathode materials by a high-charge cation doping strategy: zirconium-doped LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2. J. Mater. Chem. A. 4(41), 16073–16084 (2016)
R. Wang, G.Y. Qian, T.C. Liu, M.F. Li, J.J. Liu, B.K. Zhang, W.M. Zhu, S.K. Li, W.G. Zhao, W.Y. Yang, X.B. Ma, Z.D. Fu, Y.T. Liu, J.B. Yang, L. Jin, Y.G. Xiao, F. Pan, Tuning Li-enrichment in high-Ni layered oxide cathodes to optimize electrochemical performance for Li-ion battery. Nano Energy 62, 709–717 (2019)
E.B. Abebe, C.-C. Yang, S.-H. Wu, W.-C. Chien, Y.-J.J. Li, Effect of Li excess on electrochemical performance of Ni-Rich LiNi0.9Co0.05Mn0.05O2 cathode materials for Li-Ion batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 4(12), 14295–14308 (2021)
J. Yang, Y.Y. Xia, Suppressing the Phase Transition of the Layered Ni-Rich Oxide Cathode during High-Voltage Cycling by Introducing Low-Content Li2MnO3. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(2), 1297–1308 (2016)
J.C. Zhang, Z.Z. Yang, R. Gao, L. Gu, Z.B. Hu, X.F. Liu, Suppressing the Structure Deterioration of Ni-Rich LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 through atom-scale interfacial integration of self-forming hierarchical spinel layer with ni gradient concentration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9(35), 29794–29803 (2017)
Y.X. Qian, P. Niehoff, M. Borner, M. Grutzke, X. Monnighoff, P. Behrends, S. Nowak, M. Winter, F.M. Schappacher, Influence of electrolyte additives on the cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI) formation on LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 in half cells with Li metal counter electrode. J. Power Sources. 329, 31–40 (2016)
M. Winter, The solid electrolyte interphase - the most important and the least understood solid electrolyte in rechargeable Li batteries. Z. Phys. Chem. 223(10–11), 1395–1406 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National foreign specialized projects (DL2021023005L), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2021ME219) and Jinan talent project (2020GXRC044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Chu, C., Qin, X. et al. The influence of surface lithium residue to the performance of LiNi0.9Co0.05Mn0.05O2 cathode materials. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 60, 462–473 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-023-00292-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43207-023-00292-7