Abstract
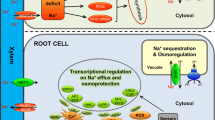
Being sessile in nature, plants have to confront a number of climatic changes such as salinity, drought, heavy metals, and temperature, all of which have damaging effects on plant growth and productivity, resulting in lower overall yields. Salinity is one of the significant abiotic stresses that has a detrimental effect on plant growth and yield. The salinity-affected region accounts for approximately 7% of the world's total land area. Although soil salinity occurs naturally, some other factors also contribute to its elevation, such as climate variation and irrigation practices. Potassium (K+) is the third most important macroelements as per the requirements of plants. It regulates several physiological and metabolic developments like photosynthesis, respiration enzyme instigation, stomata movement, osmoregulation, and provides resistance to abiotic stress. In the present mini-review, attempts have been made to summarize the old findings and recent advances in research regarding salinity toxicity and the role of K in their mitigation in plants. Currently, the climate is changing very fast due to global warming, and its impact on the regulatory role of K is not known. Therefore, future research should focus more on K’s regulatory roles in plants, which are facing tremendous challenges from the worse climate changes.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NaCl:
-
Sodium chloride
- Cl:
-
Chloride
- NHA:
-
Na+/H+ antiporter
- GLRs:
-
Glutamate receptor-like channels
- Ca++ :
-
Calcium ions
- CHX:
-
Cation/H+ exchangers
- CCCs:
-
Cation chloride cotransporters
- CLC:
-
Chloride channel
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- GA3 :
-
Gibberellic acid
- Ψπ :
-
Osmotic potential
- Na:
-
Sodium
- K:
-
Potassium
- NSCCs:
-
Non-selective cation channels
- CNGCs:
-
Cyclic nucleotide-gated channels
- HKTs:
-
High-affinity K+ transporters
- LCT1:
-
Low-affinity cation transporters
- ALMT:
-
Aluminium-activated malate transporter
- NPF:
-
Nitrate transporter 1/peptide transporter
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- OEC:
-
Oxygen-evolving complex
- Ψp:
-
Turgor pressure
References
Acosta-Motos JR, Ortuño MF, Bernal-Vicente A et al (2017) Plant responses to salt stress: adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy 7:18. https://doi.org/10.3390/AGRONOMY7010018
Ahanger MA, Agarwal RM (2017) Potassium up-regulates antioxidant metabolism and alleviates growth inhibition under water and osmotic stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Protoplasma 254:1471–1486. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00709-016-1037-0/METRICS
Ahanger MA, Aziz U, Alsahli AA et al (2019a) Influence of exogenous salicylic acid and nitric oxide on growth, photosynthesis, and ascorbate-glutathione cycle in salt stressed Vigna angularis. Biomolecules 10:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/BIOM10010042
Ahanger MA, Qin C, Begum N et al (2019b) Nitrogen availability prevents oxidative effects of salinity on wheat growth and photosynthesis by up-regulating the antioxidants and osmolytes metabolism, and secondary metabolite accumulation. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12870-019-2085-3/FIGURES/8
Ahmar S, Gill RA, Jung KH et al (2020) Conventional and molecular techniques from simple breeding to speed breeding in crop plants: recent advances and future outlook. Int J Mol Sci 21:2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS21072590
Alkharabsheh HM, Seleiman MF, Hewedy OA et al (2021) Field crop responses and management strategies to mitigate soil salinity in modern agriculture: a review. Agronomy 11:2299. https://doi.org/10.3390/AGRONOMY11112299
Arif Y, Singh P, Siddiqui H et al (2020) Salinity induced physiological and biochemical changes in plants: an omic approach towards salt stress tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 156:64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLAPHY.2020.08.042
Assaha DVM, Ueda A, Saneoka H et al (2017) The role of Na+ and K+ transporters in salt stress adaptation in glycophytes. Front Physiol 8:509. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPHYS.2017.00509/BIBTEX
Betzen BM, Smart CM, Maricle KL, MariCle BR (2019) Effects of increasing salinity on photosynthesis and plant water potential in Kansas salt marsh species. Trans Kansas Acad Sci 122:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1660/062.122.0105
Bustamante M, Muñoz A, Romero I et al (2021) Impact of potassium pre-harvest applications on fruit quality and condition of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivated under plastic covers in southern Chile orchards. Plants 10:2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/PLANTS10122778
Chen T, Shabala S, Niu Y et al (2021) Molecular mechanisms of salinity tolerance in rice. Crop J 9:506–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CJ.2021.03.005
Corwin DL (2021) Climate change impacts on soil salinity in agricultural areas. Eur J Soil Sci 72:842–862. https://doi.org/10.1111/EJSS.13010
de Bang TC, Husted S, Laursen KH et al (2021) The molecular–physiological functions of mineral macronutrients and their consequences for deficiency symptoms in plants. New Phytol 229:2446–2469. https://doi.org/10.1111/NPH.17074
Gaaliche B, Ladhari A, Zarrelli A, ben Mimoun M (2019) Impact of foliar potassium fertilization on biochemical composition and antioxidant activity of fig (Ficus carica L.). Sci Hortic 253:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCIENTA.2019.04.024
Gao Y, Yu C, Zhang K et al (2021) Identification and characterization of the strawberry KT/HAK/KUP transporter gene family in response to K+ deficiency. Acta Physiol Plant 43:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11738-020-03172-3/METRICS
Gong Z, Xiong L, Shi H et al (2020) Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci China Life Sci 63:635–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11427-020-1683-X
Guo Q, Meng L, Han J et al (2020) SOS1 is a key systemic regulator of salt secretion and K+/Na+ homeostasis in the recretohalophyte Karelinia caspia. Environ Exp Bot 177:104098. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVEXPBOT.2020.104098
Gupta S, Schillaci M, Walker R et al (2020) Alleviation of salinity stress in plants by endophytic plant-fungal symbiosis: current knowledge, perspectives and future directions. Plant Soil 461:219–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11104-020-04618-W
Haj-Amor Z, Araya T, Kim DG et al (2022) Soil salinity and its associated effects on soil microorganisms, greenhouse gas emissions, crop yield, biodiversity and desertification: a review. Sci Total Environ 843:156946. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.156946
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan MHMB, Zulfiqar F et al (2020) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants 9:681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIOX9080681
Hassani A, Azapagic A, Shokri N (2021) Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat Commun 12:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26907-3
Hopmans JW, Qureshi AS, Kisekka I et al (2021) Critical knowledge gaps and research priorities in global soil salinity. Adv Agron 169:1–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/BS.AGRON.2021.03.001
Huang H, Ullah F, Zhou DX et al (2019) Mechanisms of ROS regulation of plant development and stress responses. Front Plant Sci 10:800. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPLS.2019.00800/BIBTEX
Hussain S, Hussain S, Ali B et al (2021) Recent progress in understanding salinity tolerance in plants: story of Na+/K+ balance and beyond. Plant Physiol Biochem 160:239–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLAPHY.2021.01.029
Isayenkov SV, Maathuis FJM (2019) Plant salinity stress: many unanswered questions remain. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPLS.2019.00080/FULL
Javaid MH, Khan AR, Salam A et al (2022) Exploring the adaptive responses of plants to abiotic stresses using transcriptome data. Agriculture 12:211. https://doi.org/10.3390/AGRICULTURE12020211
Johnson R, Vishwakarma K, Hossen MS et al (2022) Potassium in plants: growth regulation, signaling, and environmental stress tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 172:56–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLAPHY.2022.01.001
Joshi S, Nath J, Singh AK et al (2022) Ion transporters and their regulatory signal transduction mechanisms for salinity tolerance in plants. Physiol Plant 174:e13702. https://doi.org/10.1111/PPL.13702
Julkowska MM, Koevoets IT, Mol S et al (2018) Genetic components of root architecture remodeling in response to salt stress. Plant Cell 29:3198–3213. https://doi.org/10.1105/TPC.16.00680
Kamran M, Parveen A, Ahmar S et al (2019) An overview of hazardous impacts of soil salinity in crops, tolerance mechanisms, and amelioration through selenium supplementation. Int J Mol Sci 21:148. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS21010148
Kaya C, Higgs D, Ashraf M et al (2020) Integrative roles of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in melatonin-induced tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants to iron deficiency and salt stress alone or in combination. Physiol Plant 168:256–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/PPL.12976
Keisham M, Mukherjee S, Bhatla SC (2018) Mechanisms of sodium transport in plants—progresses and challenges. Int J Mol Sci 19:647. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS19030647
Kumari S, Chhillar H, Chopra P et al (2021) Potassium: a track to develop salinity tolerant plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 167:1011–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLAPHY.2021.09.031
Kuzin A, Solovchenko A (2021) Essential role of potassium in apple and its implications for management of orchard fertilization. Plants 10:2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/PLANTS10122624
Landorfa-Svalbe Z, Andersone-Ozola U, Ievinsh G (2023) Type of anion largely determines salinity tolerance in four Rumex species. Plants 12:92. https://doi.org/10.3390/PLANTS12010092/S1
Liang W, Ma X, Wan P, Liu L (2018) Plant salt-tolerance mechanism: a review. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BBRC.2017.11.043
Liang M, Gao Y, Mao T et al (2020) Characterization and expression of KT/HAK/KUP transporter family genes in willow under potassium deficiency, drought, and salt stresses. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2690760
Llanes A, Palchetti MV, Vilo C, Ibañez C (2021) Molecular control to salt tolerance mechanisms of woody plants: recent achievements and perspectives. Ann for Sci 78:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13595-021-01107-7/FIGURES/2
Methenni K, ben Abdallah M, Nouairi I et al (2018) Salicylic acid and calcium pretreatments alleviate the toxic effect of salinity in the Oueslati olive variety. Sci Hortic 233:349–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCIENTA.2018.01.060
Morton MJL, Awlia M, Al-Tamimi N et al (2019) Salt stress under the scalpel—dissecting the genetics of salt tolerance. Plant J 97:148–163. https://doi.org/10.1111/TPJ.14189
Mostofa MG, Rahman MM, Ghosh TK et al (2022) Potassium in plant physiological adaptation to abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 186:279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLAPHY.2022.07.011
Mukhopadhyay R, Sarkar B, Jat HS et al (2021) Soil salinity under climate change: challenges for sustainable agriculture and food security. J Environ Manag 280:111736. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2020.111736
Munns R, Day DA, Fricke W et al (2020) Energy costs of salt tolerance in crop plants. New Phytol 225:1072–1090. https://doi.org/10.1111/NPH.15864
Neang S, Goto I, Skoulding NS et al (2020) Tissue-specific expression analysis of Na+ and Cl− transporter genes associated with salt removal ability in rice leaf sheath. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12870-020-02718-4/TABLES/3
Numan M, Bashir S, Khan Y et al (2018) Plant growth promoting bacteria as an alternative strategy for salt tolerance in plants: a review. Microbiol Res 209:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICRES.2018.02.003
Panagopoulos A, Haralambous KJ (2020) Environmental impacts of desalination and brine treatment—challenges and mitigation measures. Mar Pollut Bull 161:111773. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2020.111773
Praveen A (2022) Nitric oxide mediated alleviation of abiotic challenges in plants. Nitric Oxide 128:37–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NIOX.2022.08.005
Praveen A, Pandey A, Gupta M (2019) Nitric oxide alters nitrogen metabolism and PIN gene expressions by playing protective role in arsenic challenged Brassica juncea L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 176:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2019.03.054
Praveen A, Singh S, Sharma VK (2022) Action of nanoparticles in the amelioration of heavy metal phytotoxicity. Cereal Res Commun. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42976-022-00340-8/METRICS
Praveen A, Dubey S, Singh S, Sharma VK (2023) Abiotic stress tolerance in plants: a fascinating action of defense mechanisms. 3 Biotech 13:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205-023-03519-W
Rivero RM, Mittler R, Blumwald E, Zandalinas SI (2022) Developing climate-resilient crops: improving plant tolerance to stress combination. Plant J 109:373–389. https://doi.org/10.1111/TPJ.15483
Sardans J, Peñuelas J (2021) Potassium control of plant functions: ecological and agricultural implications. Plants 10:419. https://doi.org/10.3390/PLANTS10020419
Shams M, Khadivi A (2023) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance and their possible application in the breeding of vegetables. BMC Plant Biol 23:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12870-023-04152-8/TABLES/1
Singh A (2022) Soil salinity: a global threat to sustainable development. Soil Use Manag 38:39–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/SUM.12772
Soares JC, Santos CS, Carvalho SMP et al (2019) Preserving the nutritional quality of crop plants under a changing climate: importance and strategies. Plant Soil 443:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11104-019-04229-0
Srivastava AK, Shankar A, Chandran AKN et al (2020) Emerging concepts of potassium homeostasis in plants. J Exp Bot 71:608–619. https://doi.org/10.1093/JXB/ERZ458
Sun Y, Ma C, Kang X et al (2021) Hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide are involved in melatonin-induced salt tolerance in cucumber. Plant Physiol Biochem 167:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLAPHY.2021.07.023
Taha RS, Seleiman MF, Alotaibi M et al (2020) Exogenous potassium treatments elevate salt tolerance and performances of Glycine max L. by boosting antioxidant defense system under actual saline field conditions. Agronomy 10:1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/AGRONOMY10111741
Tränkner M, Tavakol E, Jákli B (2018) Functioning of potassium and magnesium in photosynthesis, photosynthate translocation and photoprotection. Physiol Plant 163:414–431. https://doi.org/10.1111/PPL.12747
Van Zelm E, Zhang Y, Testerink C (2020) Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 71:403–433. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV-ARPLANT-050718-100005
Wang WC, Lin TC, Kieber J, Tsai YC (2019) Response regulators 9 and 10 negatively regulate salinity tolerance in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 60:2549–2563. https://doi.org/10.1093/PCP/PCZ149
Wang X, Niu Y, Zheng Y (2021) Multiple functions of MYB transcription factors in abiotic stress responses. Int J Mol Sciences 22:6125. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS22116125
Wang S, Xiao Y, Zhou ZW et al (2022) Cocos nucifera (coconut). Trends Genet 38:1096–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2022.06.008
Wani SH, Kumar V, Khare T et al (2020) Engineering salinity tolerance in plants: progress and prospects. Planta 251:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00425-020-03366-6/METRICS
Wen W, Timmermans J, Chen Q, van Bodegom PM (2020) A review of remote sensing challenges for food security with respect to salinity and drought threats. Remote Sens 13:6. https://doi.org/10.3390/RS13010006
Wu H, Zhang X, Giraldo JP, Shabala S (2018) It is not all about sodium: revealing tissue specificity and signalling roles of potassium in plant responses to salt stress. Plant Soil 431:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11104-018-3770-Y/TABLES/3
Yang Y, Bocs S, Fan H et al (2021) Coconut genome assembly enables evolutionary analysis of palms and highlights signaling pathways involved in salt tolerance. Commun Biol 4:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01593-x
Zipori I, Erel R, Yermiyahu U et al (2020) Sustainable management of olive orchard nutrition: a review. Agriculture 10:11. https://doi.org/10.3390/AGRICULTURE10010011
Zörb C, Geilfus CM, Dietz KJ (2019) Salinity and crop yield. Plant Biol 21:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/PLB.12884
Acknowledgements
AP thanks the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, for MK Bhan Young researcher fellowship program (HRD-12/4/2020-AFS-DBT-Part (1) (13815).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AP conceived the idea, collected the materials, and drafted the manuscript. Both AP and SS prepared the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest between authors regarding the manuscript.
Additional information
Communicated by Márton Jolánkai.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Praveen, A., Singh, S. The role of potassium under salinity stress in crop plants. CEREAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 52, 315–322 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-023-00393-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-023-00393-3