Abstract
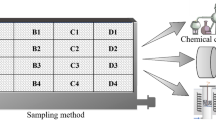
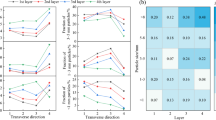
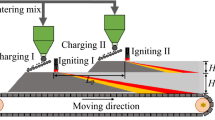
The inhomogeneous sinter properties in super-high bed sintering have been reported in our previous research. To investigate the reasons for the inhomogeneous phenomena, detailed sampling and analysis of mixed material bed and sintered bed in super-high bed sintering plant were executed. The results indicated that the higher porosity and thinner dendrite of silico-ferrite of calcium and aluminum in the upper layer as well as dense structure and higher secondary hematite content in the lower layer led to the heterogeneities of mechanical strength and reduction properties exceeding 20% and 10%, respectively. From the bed top downward, the basicity of mixed material decreased from 2.13 to 1.68 because the average particle size increased from 2.65 to 4.56 mm. Fluxes and fuels gathered in finer particles (− 3 mm) of mixed material, and the − 3 mm particles of mixed material generated more liquid phase than + 3 mm ones. The heat input of super-high sintering bed was inhomogeneous due to the heat accumulation effect and unreasonable fuel distribution. The inhomogeneous sintering heat condition in sintering bed resulted in the different quantities and properties of liquid phase. The inhomogeneous quantities and properties of liquid phase that were influenced by inhomogeneous distribution of chemical composition, particle size, and heat input led to inhomogeneous mineralizing results. Homogeneous mineralizing condition is the key for homogeneous super-high bed sintering.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.Z. Wang, J.L. Zhang, Z.J. Liu, C.B. Du, JOM 69 (2017) 2404–2411.
R.Y. Yin, Z.D. Liu, F.Q. Shangguan, Engineering 7 (2021) 1680–1683.
L.P. Xu, H.B. Liu, Y.C. Zhao, Q. Zhong, Z.L. Dong, G.H. Li, T. Jiang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01074-5.
L.P. Xu, H.B. Liu, Z.L. Dong, Q. Zhong, Y.C. Zhao, G.H. Li, T. Jiang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01073-6.
Y.D. Pei, F.K. Shi, G. An, Z.X. Zhao, Z.M. Cheng, H.J. Wang, J.S. Shi, Sinter. Pelletiz. 38 (2013) No. 1, 9–12+21.
Y.D. Pei, F.K. Shi, G. An, Z.X. Zhao, Z.M. Cheng, H.J. Wang, J.S. Shi, Sinter. Pelletiz. 38 (2013) No. 2, 14–19+47.
H.M. Long, J. Zuo, P. Wang, J.M. Li, S.Q. Shi, A.P. Wang, Sinter. Pelletiz. 38 (2013) No. 4, 1–6.
G.H. Li, C. Liu, Z.W. Yu, M.J. Rao, Q. Zhong, Y.B. Zhang, T. Jiang, Energies 11 (2018) 2382.
Z.W. Yu, Researches on bed structure and mineralization theory of composite agglomeration process (CAP) of iron ore fines and their application, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2016.
C. Liu, Studies on the basis and application of composite agglomeration process for efficiently recovering Fe–C-bearing dusts in steel works, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2019.
B. Xu, Research on fundamental and technology of heat-homogenizing sintering of iron ores, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2011.
K. Higuchi, J. Okazaki, Y. Ito, T. Fuji, S. Nomura, Tetsu-to-Hagane 107 (2021) 185–193.
H.B. Li, D.J. Pinson, P. Zulli, L.M. Lu, R.J. Longbottom, S.J. Chew, B.J. Monaghan, G.Q. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 52 (2021) 267–281.
D.M. Liu, C.E. Loo, ISIJ Int. 56 (2016) 527–536.
L. Andrews, C.E. Loo, G. Evans, ISIJ Int. 56 (2016) 1171–1180.
X.W. Lv, C.G. Bai, Q.Y. Deng, X.B. Huang, G.B. Qiu, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 722–727.
S.L. Wu, H.P. Li, W.L. Zhang, B. Su, Metals 9 (2019) 404.
X.B. Zhai, S.L. Wu, H. Zhou, L.X. Su, X.D. Ma, Ironmak. Steelmak. 47 (2020) 405–416.
R.F. Xin, X.M. Guo, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 53 (2022) 1904–1919.
R.M. German, P. Suri, S.J. Park, J. Mater. Sci. 44 (2009) 1–39.
D.M. Liu, C.E. Loo, G. Evans, Int. J. Miner. Process. 149 (2016) 56–68.
H.M. Long, X.J. Wu, T.J. Chun, Z.X. Di, B. Yu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47 (2016) 2830–2836.
Z.M. Yi, Q. Liu, J.Z. Qin, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 75 (2022) 1545–1553.
S. Machida, K. Nushiro, K. Ichikawa, H. Noda, H. Sakai, ISIJ Int. 45 (2005) 513–521.
J.J. Xin, N. Wang, M. Chen, ISIJ Int. 60 (2020) 2306–2315.
J.J. Xin, L. Gan, N. Wang, M. Chen, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 50 (2019) 2828–2842.
E. Donskoi, S. Hapugoda, J.R. Manuel, A. Poliakov, M.J. Peterson, H. Mali, B. Bückner, T. Honeyands, M.I. Pownceby, Minerals 11 (2021) 562.
X. Zhang, J.L. Zhang, Z.W. Hu, H.B. Zuo, H.W. Guo, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17 (2010) No. 11, 7–12.
J.L. Zhang, Y.P. Zhang, K.J. Li, Y.Z. Wang, Z.J. Liu, G.W. Wang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47 (2016) 3046–3055.
I. Vemdrame Flores, O. Matos, A. Lima da Silva, M. Covcevich Bagatini, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 52 (2021) 1716–1738.
C.Z. Li, T. Honeyands, D. O'Dea, R. Moreno-Atanasio, Powder Technol. 356 (2019) 778–789.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52274290).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Hb., Xu, Lp., Yang, Xd. et al. Super-high bed sintering for iron ores: inhomogeneous phenomena and its mechanism during mineralizing. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01117-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01117-x